Abstract
Background
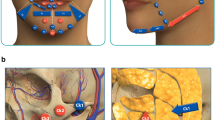
Arterial embolism is a rare complication caused by hyaluronic acid (HA) injection. However, it is one of the most serious complications. Once it happens, the complication would have a great and long-term impact on patients. Intra-arterial recanalization has been reported for recovering the visual acuity in patients with visual loss caused by hyaluronic acid. There is little report about the benefits of superselective intra-arterial recanalization therapy for skin wounds caused by hyaluronic acid vascular embolization.
Methods
Eight patients who had received the superselective intra-arterial recanalization therapy were retrospectively reviewed. Hyaluronidase was injected into the facial artery by superselective intra-arterial recanalization therapy, followed by symptomatic treatment. The facial artery recanalization was successfully performed and no interventional procedure-related adverse events happened.
Results
Arterial embolization accompanies by the interruption or reduction of blood supply, followed by ochrodermia, pain, numbness, swelling, yellowish white secreta and even necrosis on skin wound area. Early detection of skin blood supply disorders and early recovery of blood supply are very critical to treat facial artery embolization caused by HA. After superselective intra-arterial recanalization therapy, the blood supply to facial skin was restored and skin wounds recovered in all patients. Only 1 patient was left with small and superficial scars.
Conclusion
Superselective intra-arterial recanalization therapy is an effective and safe method that can alleviate skin wounds caused by HA vascular embolization.
Level of Evidence IV
This journal requires that authors assign a level of evidence to each article. For a full description of these Evidence-Based Medicine ratings, please refer to the Table of Contents or the online Instructions to Authors www.springer.com/00266.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Carruthers J, Carruthers A, Humphrey S (2015) Introduction to fillers. Plast Reconstr Surg 136(5 Suppl):120s–131s. https://doi.org/10.1097/prs.0000000000001770
Lowe NJ (2003) Arterial embolization caused by injection of hyaluronic acid (Restylane). Br J Dermatol 148(2):379. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-2133.2003.05097_13.x
Signorini M, Liew S, Sundaram H et al (2016) Global aesthetics consensus: avoidance and management of complications from hyaluronic acid fillers-evidence- and opinion-based review and consensus recommendations. Plast Reconstr Surg 137(6):961e–971e. https://doi.org/10.1097/prs.0000000000002184
Sclafani AP, Fagien S (2009) Treatment of injectable soft tissue filler complications. Dermatol Surg 35(Suppl 2):1672–1680. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1524-4725.2009.01346.x
Kassir R, Kolluru A, Kassir M (2011) Extensive necrosis after injection of hyaluronic acid filler: case report and review of the literature. J Cosmet Dermatol 10(3):224–231. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1473-2165.2011.00562.x
Chen Q, Liu Y, Fan D (2016) Serious vascular complications after nonsurgical rhinoplasty: a case report. Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open 4(4):e683. https://doi.org/10.1097/gox.0000000000000668
Heim N, Faron A, Wiedemeyer V, Teschke M, Reich RH, Martini M (2015) Delayed infection after upper lip augmentation with absorbable hyaluronic acid filler. Handchir Mikrochir Plast Chir 47(4):268–270. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0035-1549917
Zhang LX, Lai LY, Zhou GW et al (2020) Evaluation of intraarterial thrombolysis in treatment of cosmetic facial filler-related ophthalmic artery occlusion. Plast Reconstr Surg 145(1):42e–50e. https://doi.org/10.1097/prs.0000000000006313
Xu X, Zhou G, Fu Q et al (2021) Efficacy of intra-arterial thrombolytic therapy for vision loss resulting from hyaluronic acid filler embolization. J Cosmet Dermatol 20(10):3205–3212. https://doi.org/10.1111/jocd.14111
Zheng C, Fu Q, Zhou GW et al (2022) Efficacy of percutaneous intraarterial facial/supratrochlear arterial hyaluronidase injection for treatment of vascular embolism resulting from hyaluronic acid filler cosmetic injection. Aesthet Surg J 42(6):649–655. https://doi.org/10.1093/asj/sjab425
Zheng C, Fu Q, Zhou GW et al (2022) Efficacy of percutaneous superficial temporal arterial hyaluronidase injection for hyaluronic acid filler-induced necrosis of frontotemporal skin and/or the ipsilateral scalp with subsequent alopecia. Aesthet Surg J. https://doi.org/10.1093/asj/sjac270
Lee SK, Kim SM, Cho SH, Lee JD, Kim HS (2015) Adverse reactions to injectable soft tissue fillers: memorable cases and their clinico-pathological overview. J Cosmet Laser Ther 17(2):102–108. https://doi.org/10.3109/14764172.2014.968584
Serra-Mestre JM, Fernandez Peñuela R, Foti V, D’Andrea F, Serra-Renom JM (2017) Breast cleavage remodeling with fat grafting: a safe way to optimize symmetry and to reduce intermammary distance. Plast Reconstr Surg 140(5):665e–672e. https://doi.org/10.1097/prs.0000000000003788
Money SM, Wall WB, Davis LS, Edmondson AC (2021) An anatomical guide to the terminal facial artery: lumen diameter and associated anatomy relevant to dermatologic procedures. Dermatol Surg 47(6):797–801. https://doi.org/10.1097/dss.0000000000002992
Carruthers JDA, Fagien S, Rohrich RJ, Weinkle S, Carruthers A (2014) Blindness caused by cosmetic filler injection: a review of cause and therapy. Plast Reconstr Surg 134(6):1197–1201. https://doi.org/10.1097/prs.0000000000000754
DeLorenzi C (2017) New high dose pulsed hyaluronidase protocol for hyaluronic acid filler vascular adverse events. Aesthet Surg J 37(7):814–825. https://doi.org/10.1093/asj/sjw251
Myung Y, Kwon H, Pak C, Lee H, Jeong JH, Heo CY (2016) Radiographic evaluation of vessel count and density with quantitative magnetic resonance imaging during external breast expansion in Asian women: a prospective clinical trial. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg 69(12):1588–1597. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bjps.2016.09.019
Doerfler L, Hanke CW (2019) Arterial occlusion and necrosis following hyaluronic acid injection and a review of the literature. J Drugs Dermatol 18(6):587–591
Murray G, Convery C, Walker L, Davies E (2021) Guideline for the management of hyaluronic acid filler-induced vascular occlusion. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 14(5):E61-e69
Cavallini M, Gazzola R, Metalla M, Vaienti L (2013) The role of hyaluronidase in the treatment of complications from hyaluronic acid dermal fillers. Aesthet Surg J 33(8):1167–1174. https://doi.org/10.1177/1090820x13511970
Wang J, Shen H, Liu T, Li Q, Lyu Z, Yu Y (2021) An efficacy and safety study of intra-arterial recanalization of occluded ophthalmic arteries in patients with monocular blindness caused by injection of hyaluronic acid in facial tissues. Aesthetic Plast Surg 45(4):1573–1578. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-021-02224-4
Hayreh SS, Kolder HE, Weingeist TA (1980) Central retinal artery occlusion and retinal tolerance time. Ophthalmology 87(1):75–78. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0161-6420(80)35283-4
Hayreh SS, Podhajsky PA, Zimmerman B (1997) Nonarteritic anterior ischemic optic neuropathy: time of onset of visual loss. Am J Ophthalmol 124(5):641–647. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0002-9394(14)70902-x
Acknowledgments
None.
Funding
This research did not receive any funding of research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors declare that they did not have any conflict of interests with others.
Ethical Approval
The study was approved by the Fourth Medical Center of Chinese People’s Liberation Army General Hospital ethical committee (2021KY018-KS001). The procedures were conducted in accordance with institutional and national ethical standards and Declaration of Helsinki.
Informed Consent
Written informed consents of analysis and publication of personal information were obtained from all patients.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Fu, H., Fu, Q., Yu, Y. et al. Efficacy of Superselective Intra-arterial Recanalization of Embolized Arteries Resulting from Facial Hyaluronic Acid Injection. Aesth Plast Surg (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-024-04004-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-024-04004-2