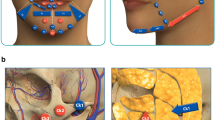
Abstract
Background
Botulinum toxin alone is unable to sufficiently reduce the muscle in cases of severe static glabellar lines due to the folded skin and dermal breakdown that frequently accompany these conditions. Augmentation of the soft tissue and removal of folded skin at the same time is the final solution. To simultaneously resolve interbrow skin laxity and replenish tissue volume, we present for the first time the method of glabellar lines excision combined with FDFG.
Methods
This retrospective study involved 23 patients with moderate-to-severe static glabellar lines underwent resection and/or free dermal fat grafting (FDFG) from June 2022 to June 2023. Fifteen of them underwent glabellar lines excision combined with FDFG, and seven were filled only. These patients were followed up at least 6 months to evaluate the effect. We utilized FACE-Q and WSRS for assessment in order to investigate the clinical results.
Results
There is no complication such as discoloration, hematoma, infection and palpability in all cases. After 6–15 months of follow-up, all the patients’ dynamic and static lines were improved to a certain degree, and the patients were satisfied with the results with the WSRS score decreased from 3.5 ± 0.47 to 1.8 ± 0.62, and FACE-Q assessments in “Line between the eyebrows” decreased from 87 ± 7.39 to 43 ± 10.3.
Conclusions
Resection in conjunction with FDFG is a brief, innovative and effective technique to correct static and dynamic severe glabellar wrinkles and maintain an acceptable outcome over an extended period of time which worthy clinical promotion.
Level of Evidence IV
This journal requires that authors assign a level of evidence to each article. For a full description of these Evidence-Based Medicine ratings, please refer to the Table of Contents or the online Instructions to Authors www.springer.com/00266.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Solish N, Kane MAC, Biesman BS, Brown J, Gallagher CJ (2023) Impact of daxibotulinumtoxina for injection on brow position and frontalis muscle activity following treatment of glabellar lines. Aesthet Surg J 43(Suppl 1):S1–S9
Solish N, Bertucci V, Green JB, Kane MAC (2023) Optimizing outcomes when treating glabellar lines. Aesthet Surg J 43:786–788
Hu X, Xue Z, Qi H, Chen B (2017) Percutaneous myotomy with a small needle-knife and lipoinjection for treatment of glabellar frown lines. Aesthet Surg J 37:1168–1174
Sparavigna A, Tenconi B, Giori AM, Bellia G, La Penna L (2019) Evaluation of the efficacy of a new hyaluronic acid gel on dynamic and static wrinkles in volunteers with moderate aging/photoaging. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol 12:81–90
Lee JH, Choi MS, Kim YH (2014) Correction of deep static glabellar lines with acellular dermal matrix insertion. Ann Plast Surg 73:627–630
Day DJ, Littler CM, Swift RW, Gottlieb S (2004) The wrinkle severity rating scale: a validation study. Am J Clin Dermatol 5:49–52
Tanna N, Joshi AS, Vira D, Lindsey WH (2010) Direct excision of glabellar furrows: an alternative treatment for severe glabellar rhytides. Plast Reconstr Surg 125:247e–248e
Kim HS, Kim C, Cho H, Hwang JY, Kim YS (2014) A study on glabellar wrinkle patterns in Koreans. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol 28:1332–1339
Lee W, Moon HJ, Kim JS, Yang EJ (2021) Safe glabellar wrinkle correction with soft tissue filler using doppler ultrasound. Aesthet Surg J 41:1081–1089
Peer LA (1956) The neglected free fat graft, its behavior and clinical use. Am J Surg 92:40–47
Hintschich CR, Beyer-Machule CK (1996) Dermis-Fett-transplantat als autologes orbitaimplantat dermal fat transplant as autologous orbital implant. Klin Monbl Augenheilkd 208:135–141
Dufresne CR, Poling MI (2020) Free dermal fat autografting for complex craniofacial wounds. J Craniofac Surg 31:1563–1567
Suh MK (2018) Dorsal augmentation using autogenous tissues. Facial Plast Surg Clin North Am 26:295–310
Kijima Y, Yoshinaka H, Hirata M (2012) Clinical and pathologic evaluation of implanted free dermal fat grafts after breast cancer surgery: a retrospective analysis. Surgery 151:444–455
Choi MH, He WJ, Son KM, Choi WY, Cheon JS (2020) The efficacy of dermofat grafts from the groin for correction of acquired facial deformities. Arch Craniofac Surg 21:92–98
Little JW (2002) Applications of the classic dermal fat graft in primary and secondary facial rejuvenation. Plast Reconstr Surg 109:788–804
Zhi J, Yao C, Zhao Y (2023) Free dermal fat grafting a novel technique for the correction of nasolabial folds during facelift surgery. Aesthet Surg J. https://doi.org/10.1093/asj/sjad369,December19,2023
Kim JH, Song JW, Park SW (2017) Contracted nose correction with dermofat and conchal cartilage. Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open 5:1272–1273
Ottenhof MJ, Veldhuizen IJ, Hensbergen LJV (2022) The use of the FACE-Q aesthetic: a narrative review. Aesthetic Plast Surg 46:2769–2780
Gibstein AR, Chen K, Nakfoor B (2021) Facelift surgery turns back the clock: artificial intelligence and patient satisfaction quantitate value of procedure type and specific techniques. Aesthet Surg J 41:987–999
Funding
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no financial interests to disclose in relation to the content of this article.
Ethical Approval
Ethical approval of the study was granted by the Institutional Review Board (IRB). This study was conducted in accordance with the Helsinki Declaration.
Informed Consent
For this type of study, informed consent is not required.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Dong, G., Chen, F., Zhang, S. et al. Surgical Procedures of the Correction of Severe Static Glabellar Lines by Utilizing Resection with Free Dermal Fat Grafting (FDFG). Aesth Plast Surg (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-024-03984-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-024-03984-5