Abstract
Introduction
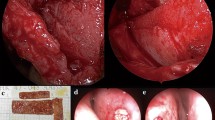
Rhinoplasty for caudal septal cartilage defects is a challenge due to the difficulty of fixation of the grafts.
Objectives
This study presents an approach for correcting defects in caudal septal cartilage with the costal cartilaginous framework using a mortise–tenon technique.
Methods
From May 2019 through May 2022, a retrospective analysis of patients with caudal septal cartilage defects underwent rhinoplasty using a mortise–tenon cartilaginous framework by a senior surgeon was performed. The surgical outcomes were evaluated both preoperatively and postoperatively.
Results
This study involved 17 patients, ranging in age from 27 to 58 years. There were 22.4 months of follow-up on average. There was no long-term or short-term complication observed. The aesthetic outcome of all cases was satisfactory. The mean score for the patients of the perceptions of improvement in their noses was 8.11.
Conclusion
Correction of caudal septal cartilage defects with this costal cartilaginous framework using the mortise–tenon technique is feasible and effective.
Level of Evidence IV
This journal requires that authors assign a level of evidence to each article. For a full description of these Evidence-Based Medicine ratings, please refer to the Table of Contents or the online Instructions to Authors www.springer.com/00266.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
RK Daniel 2007 Rhinoplasty: septal saddle nose deformity and composite reconstruction Plast Reconstr Surg 119 3 1029 1043 https://doi.org/10.1097/01.prs.0000252503.30804.5e
SE Metzinger RG Boyce PL Rigby 1994 Ethmoid bone sandwich grafting for caudal septal defects Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 120 10 1121 1125 https://doi.org/10.1001/archotol.1994.01880340061010
P Min Z Wang Z Zhang 2021 Septal reconstruction with folded porous polythylene implants: an alternative technique for the correction of severe saddle nose deformities in Asian populations J Craniofac Surg 32 4 1325 1330 https://doi.org/10.1097/SCS.0000000000007260
YY Chen YJ Jang 2018 Refinements in saddle nose reconstruction Facial Plast Surg 34 4 363 372 https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0038-1660824
TZ Shipchandler BJ Chung DS Alam 2008 Saddle nose deformity reconstruction with a split calvarial bone L-shaped strut Arch Facial Plast Surg 10 5 305 311 https://doi.org/10.1001/archfaci.10.5.305
Z Song Y Xu X Zhang 2023 Application of a modified costal cartilaginous framework in correction of severe saddle nose deformity Aesthet Surg J 43 8 830 839 https://doi.org/10.1093/asj/sjad047
Z Tan W Sun W Yang 2020 Y-shaped en-bloc mortise-tenon rhinoplasty technique Aesthet Surg J 40 1 NP8 NP20 https://doi.org/10.1093/asj/sjz120
L Wu H Wang L Tian 2022 The plug-in graft, the essential supplement for a stable cartilaginous framework in rhinoplasty Aesthet Surg J 42 8 862 870 https://doi.org/10.1093/asj/sjac009
RY Ha HS Byrd 2003 Septal extension grafts revisited: 6-year experience in controlling nasal tip projection and shape Plast Reconstr Surg 112 7 1929 1935 https://doi.org/10.1097/01.PRS.0000091424.69765.0C
Y Xu X Zhang J You 2023 Analysis of the cause of cartilage warping in the rhinoplasty of costal cartilage and application of embed-in graft in revisional surgery Aesthet Surg J 43 6 646 654 https://doi.org/10.1093/asj/sjad011
L Tian J You Y Xu 2022 Modification of nasal dorsal onlay graft based on anatomic findings of rhinion area Aesthet Plast Surg 46 2 843 849 https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-021-02672-y
R Zheng X Wang H Wang 2023 Improvement of nasal dorsal onlay graft appearance after augmentation rhinoplasty with costal cartilage for thin-skinned patients Aesthet Plast Surg 47 1 330 335 https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-022-03082-4
FG Fedok 2016 Costal cartilage grafts in rhinoplasty Clin Plast Surg 43 1 201 212 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cps.2015.08.002
HJ Lee S Bukhari YJ Jang 2021 Dorsal augmentation using crushed autologous costal cartilage in rhinoplasty Laryngoscope 131 7 E2181 E2187 https://doi.org/10.1002/lary.29398
Z Zhang Z Yu B Song 2022 Septal extension graft for correcting short nose in East Asians: review of autologous cartilage grafts and postoperative stability Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg 60 9 1159 1165 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bjoms.2022.06.004
Funding
This study was funded by Chinese Academy of Medical Science Innovation Fund for Medical Sciences (2021-I2M-1-052)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
XZ and ZS are responsible for the design of the study, acquisition of data, analysis, and interpretation of data and drafting the manuscript. YX, JY, HW, RZ, TL, and JG participated in the discussion and revision of the manuscript. FF is responsible for designing the study, revising the manuscript, and final approval of the version to be published.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval
All procedures performed in studies involving the human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed Consent
Informed consents were obtained from the patients in this study.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, X., Song, Z., Xu, Y. et al. Rhinoplasty with Mortise–Tenon Cartilaginous Framework for Caudal Septal Cartilage Defects. Aesth Plast Surg 48, 1737–1744 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-023-03733-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-023-03733-0