Abstract
Background
The main aim of this study was to present an automatic method based on image processing algorithms for facial anatomical landmark localization and angular photogrammetric analysis applicable for rhinoplasty surgery. We studied and measured color profile photographs of 100 patients before and after rhinoplasty surgery.
Methods
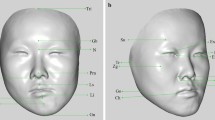
In facial anthropometry analysis, anatomical landmarks are often defined by specialists, manually. This process is time-consuming and requires training and skill. The Cascade Regression Method (CRM) was utilized for facial landmark detection to overcome the mentioned problem. In this study, 11 anatomical landmarks were used to measure 9 facial angular metrics. Finally, a t-test (with the significance level set at a p-value of 0.05) was applied to analyze before surgery versus after surgery comparisons.
Results
Experimental results dedicated that there is a significance difference (p < 0.001) in nasofrontal, nasolabial, mentolabial, nasomental, facial convexity including nose, facial convexity excluding nose, projection of the upper lip to chin, and H angles before and after surgery. Also, results showed that there is not a significance difference in nose tip angle.
Conclusion
We believe that the presented system can aim to reduce the personal errors made by manual measurement and to facilitate facial anthropometry analysis before and after surgery with high accuracy. Also, the normative data for Iranian women can be used as a guide for the diagnosis and planning of oral and maxillofacial, ENT, and plastic surgeries.
Level of Evidence II
This journal requires that authors assign a level of evidence to each article. For a full description of these Evidence-Based Medicine ratings, please refer to the Table of Contents or the online Instructions to Authors www.springer.com/00266.





Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
20 September 2023
A Correction to this paper has been published: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-023-03665-9
Reference
Fagundes MSC, Moreira AT, Tambara EM, Tenório SB, Fraga RD, Hamerschmidt R (2016) Objective assessment of surgical technique in rotation and nasal projection variation. Braz J Otorhinolaryngol 82:47–55
Pham AM, Tollefson TT (2010) Objective facial photograph analysis using imaging software. Fac Plast Surg Clin 18(2):341–349
Chuang J, Barnes C, Wong BJ (2016) Overview of facial plastic surgery and current developments. Surg J 2(01):e17–e28
Kaipainen AE, Sieber KR, Nada RM, Maal TJ, Katsaros C, Fudalej PS (2016) Regional facial asymmetries and attractiveness of the face. Eur J Orthod 38(6):602–608
Kaya KS, Türk B, Cankaya M, Seyhun N, Coşkun BU (2019) Assessment of facial analysis measurements by golden proportion. Braz J Otorhinolaryngol 85:494–501
Wei W, Ho ES, McCay KD, Damaševičius D, Maskeliūnas R, Esposito A (2022) Assessing facial symmetry and attractiveness using augmented reality. Pattern Anal Appl 25:635–651
Liu Y, Huang ML, Huang W, Liang J (2017) A physiognomy based method for facial feature extraction and recognition. J Vis Lang Comput 43:103–109
Chen F, Zhang D (2016) Combining a causal effect criterion for evaluation of facial attractiveness models. Neurocomputing 177:98–109
Zhang B, Xiao X, Lu G (2018) Facial beauty analysis based on features prediction and beautification models. Pattern Anal Appl 21:529–542
Chen F, Xiao X, Zhang D (2016) Data-driven facial beauty analysis: prediction, retrieval and manipulation. IEEE Trans Affect Comput 9(2):205–216
Bakhshali MA, Shamsi M (2015) Estimating facial angles using Radon transform. Turk J Electr Eng Comput Sci 23(3):804–812
Porto LF et al (2019) Automatic cephalometric landmarks detection on frontal faces: an approach based on supervised learning techniques. Digit Investig 30:108–116
Gerós A, Horta R, Aguiar P (2016) Facegram–objective quantitative analysis in facial reconstructive surgery. J Biomed Inform 61:1–9
Gode S, Tiris FS, Akyildiz S, Apaydin F (2011) Photogrammetric analysis of soft tissue facial profile in Turkish rhinoplasty population. Aesthetic Plast Surg 35(6):1016–1021
Beugre J-B, Diomande M, Assi AR, Koueita MK, Vaysse F (2017) Angular photogrammetric analysis and evaluation of facial esthetics of young Ivorians with normal dental occlusion. Int Orthod 15(1):25–39
Malá PZ, Krajíček V, Velemínská J (2018) How tight is the relationship between the skeletal and soft-tissue facial profile: a geometric morphometric analysis of the facial outline. Forensic Sci Int 292:212–223
Ajami S, Najafi HZ, Mahdavi S (2015) Angular photogrammetric analysis of the soft tissue facial profile of Iranian young adults. Iran J Orthod 10(2):1–8
Jafargholkhanloo AF, Shamsi M (2023) Cephalometry analysis of facial soft tissue based on two orthogonal views applicable for facial plastic surgeries. Multimed Tools Appl 82(20):30643–30668
Liu S, Fan Y-Y, Samal A, Guo Z (2016) Advances in computational facial attractiveness methods. Multimed Tools Appl 75(23):16633–16663
Xue Z, Li SZ, Teoh EK (2003) Bayesian shape model for facial feature extraction and recognition. Pattern Recogn 36(12):2819–2833
Xiong X, De la Torre F (2013) Supervised descent method and its applications to face alignment. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. pp. 532–539
Feng Z-H, Hu G, Kittler J, Christmas W, Wu X-J (2015) Cascaded collaborative regression for robust facial landmark detection trained using a mixture of synthetic and real images with dynamic weighting. IEEE Trans Image Process 24(11):3425–3440
Cootes TF, Edwards GJ, Taylor CJ (2001) Active appearance models. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 23(6):681–685
Lu H, Yang F (2014) Active shape model and its application to face alignment. In: Chen YW, Jain LC (eds) Subspace methods for pattern recognition in intelligent environment. Studies in Computational Intelligence, vol 552. Springer, Berlin, pp. 1–31
Ojansivu V, Heikkilä J (2008) Blur insensitive texture classification using local phase quantization. In: Elmoataz A, Lezoray O, Nouboud F, Mammass D (eds) Image and signal processing. ICISP 2008. Lecture notes in computer science, vol 5099. Springer, Berlin, pp. 236–243
Bakhshali M, Shamsi M, Sadeghi M (2015) Evaluation of facial soft tissue parameters for Northwestern students in Iran. J Craniomaxillofac Res 2(1–2):78–82
Vieira TF, Bottino A, Laurentini A, De Simone M (2014) Detecting siblings in image pairs. Vis Comput 30(12):1333–1345
Shamsi M, Zoroofi RA, Lucas C, Hasanabadi MS, Alsharif MR (2008) Automatic facial skin segmentation based on em algorithm under varying illumination. IEICE Trans Inf Syst 91(5):1543–1551
Amorim E et al (2015) Facing the high-dimensions: inverse projection with radial basis functions. Comput Graph 48:35–47
Malkoç S, Demir A, Uysal T, Canbuldu N (2009) Angular photogrammetric analysis of the soft tissue facial profile of Turkish adults. Eur J Orthod 31(2):174–179
Fortes HNDR, Guimarães TC, Belo IML, Matta ENRD (2014) Photometric analysis of esthetically pleasant and unpleasant facial profile. Dental Press J Orthod 19:66–75
Ukoha U, Ekezie J, Madueke O, Osmond A (2017) Angular craniofacial pho-tometric analysis of the facial profile of Igalas in Nigeria. Anthropol Open J. https://doi.org/10.17140/ANTPOJ-SE-2-101
Akter L, Hossain M (2017) Angular photogrammetric soft tissue facial profile analysis of Bangladeshi young adults. APOS Trends Orthod 7(6):279–279
Filipović GL et al (2019) Differences in angular photogrammetric soft-tissue facial characteristics among parents and their offspring. Medicina 55(5):197
Karki A (2020) Photographic analysis of aesthetically pleasant facial profile in Aryan group of Nepalese population. Eur J Med Sci 2(2):51–57
Funding
The authors received no financial support for the research, authorship, and publication of this article.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Ethical Approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed Consent
Study participants were informed about the aims and the methodology of this study and provided written informed consent for the use of their personal and their face images for research purposes.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Jafargholkhanloo, A.F., Shamsi, M., Rahavi-Ezabadi, S. et al. Angular Photogrammetric Analysis of Facial Soft Tissue by Image Processing Algorithms. Aesth Plast Surg 48, 1426–1435 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-023-03643-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-023-03643-1