Abstract
Background
Microneedling refers to a minimally invasive technique that uses multiple fine needles targeted skin epidermis for mechanical stimulation to obtain therapeutic or cosmetic effects. It is suitable for the treatment of a variety of dermatological conditions, including androgenetic alopecia (AGA).
Objective
This article aims to make a comprehensive review of the relevant studies on microneedling for the management of AGA.
Methods
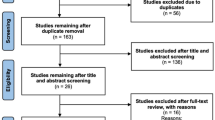
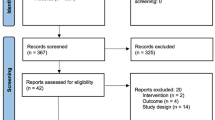
Extensive literature search was performed using PubMed, Web of Science, and EBSCO databases. 4 in vivo studies and 25 clinical trials were included according to the inclusion and exclusion criteria.
Results
The effects of microneedling on AGA was investigated in animal experiments. Several clinical trials, including randomized controlled trials, strengthen the validity of the findings. Microneedling therapy showed some encouraging results with minor complications when used alone or in combination with topical products.
Conclusions
Microneedling appears to be a safe and effective therapeutic option for AGA. Larger and more randomized controlled trials regarding the role of microneedling in AGA are strongly recommended to provide more definitive evidence.
Level of Evidence IV
This journal requires that authors assign a level of evidence to each article. For a full description of these Evidence-Based Medicine ratings, please refer to the Table of Contents or the online Instructions to Authors www.springer.com/00266


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gupta M, Mysore V (2016) Classifications of patterned hair loss: a review. J Cutan Aesthet Surg 9(1):3–12
Wang TL, Zhou C, Shen YW, Wang XY, Ding XL, Tian S et al (2010) Prevalence of androgenetic alopecia in China: a community-based study in six cities. Br J Dermatol 162(4):843–847
Lee WS, Lee HJ (2012) Characteristics of androgenetic alopecia in Asian. Ann Dermatol 24(3):243–252
Saed S, Ibrahim O, Bergfeld WF (2017) Hair camouflage: a comprehensive review. Int J Womens Dermatol 3(1 Suppl):S75–S80
Nazarian RS, Farberg AS, Hashim PW, Goldenberg G (2019) Nonsurgical hair restoration treatment. Cutis 104(1):17–24
Orentreich DS, Orentreich N (1995) Subcutaneous incisionless (subcision) surgery for the correction of depressed scars and wrinkles. Dermatol Surg 21(6):543–549
Henry S, McAllister DV, Allen MG, Prausnitz MR (1998) Microfabricated microneedles: a novel approach to transdermal drug delivery. J Pharm Sci 87(8):922–925
Iriarte C, Awosika O, Rengifo-Pardo M, Ehrlich A (2017) Review of applications of microneedling in dermatology. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol 10:289–298
Kim S, Eum J, Yang H, Jung H (2019) Transdermal finasteride delivery via powder-carrying microneedles with a diffusion enhancer to treat androgenetic alopecia. J Control Release 316:1–11
Fang JH, Liu CH, Hsu RS, Chen YY, Chiang WH, Wang HD et al (2020) Transdermal composite microneedle composed of mesoporous iron oxide nanoraspberry and PVA for androgenetic alopecia treatment. Polymers (Basel) 12(6):1392
Yuan A, Xia F, Bian Q, Wu H, Gu Y, Wang T et al (2021) Ceria nanozyme-integrated microneedles reshape the perifollicular microenvironment for androgenetic alopecia treatment. ACS Nano 15(8):13759–13769
Cao S, Wang Y, Wang M, Yang X, Tang Y, Pang M et al (2021) Microneedles mediated bioinspired lipid nanocarriers for targeted treatment of alopecia. J Control Release 329:1–15
Lee YB, Eun YS, Lee JH, Cheon MS, Park YG, Cho BK et al (2013) Effects of topical application of growth factors followed by microneedle therapy in women with female pattern hair loss: a pilot study. J Dermatol 40(1):81–83
Dhurat R, Sukesh M, Avhad G, Dandale A, Pal A, Pund P (2013) A randomized evaluator blinded study of effect of microneedling in androgenetic alopecia: a pilot study. Int J Trichol 5(1):6–11
Dhurat R, Mathapati S (2015) Response to microneedling treatment in men with androgenetic alopecia who failed to respond to conventional therapy. Indian J Dermatol 60(3):260–263
Sasaki GH (2017) Micro-needling depth penetration, presence of pigment particles, and fluorescein-stained platelets: clinical usage for aesthetic concerns. Aesthet Surg J 37(1):71–83
Shah KB, Shah AN, Solanki RB, Raval RC (2017) A comparative study of microneedling with platelet-rich plasma Plus Topical Minoxidil (5%) and Topical Minoxidil (5%) Alone in Androgenetic Alopecia. Int J Trichol 9(1):14–18
Herakal KC, Vallabhbhai PP, Siddalingappa K, Shale M, Deepika MG, Kusuma MR (2017) Microneedling with platelet-rich plasma versus microneedling with topical 5% Minoxidil in patients with androgenetic alopecia-a comparative study. J Evol Med Dent Sci-JEMDS 6(26):2182–2186
Yu AJ, Luo YJ, Xu XG, Bao LL, Tian T, Li ZX et al (2018) A pilot split-scalp study of combined fractional radiofrequency microneedling and 5% topical minoxidil in treating male pattern hair loss. Clin Exp Dermatol 43(7):775–781
Kumar MK, Inamadar AC, Palit A (2018) A randomized controlled, single-observer blinded study to determine the efficacy of topical minoxidil plus microneedling versus topical Minoxidil alone in the treatment of Androgenetic Alopecia. J Cutan Aesthet Surg 11(4):211–216
Jha AK, Vinay K, Zeeshan M, Roy PK, Chaudhary RKP, Priya A (2019) Platelet-rich plasma and microneedling improves hair growth in patients ofandrogenetic alopecia when used as an adjuvant to minoxidil. J Cosmet Dermatol. https://doi.org/10.1111/jocd.12864
Aggarwal K, Gupta S, Jangra RS, Mahendra A, Yadav A, Sharma A (2020) Dermoscopic assessment of microneedling alone versus microneedling with platelet-rich plasma in cases of male pattern Alopecia: a split-head comparative study. Int J Trichology 12(4):156–163
Burns LJ, Hagigeorges D, Flanagan KE, Pathoulas J, Senna MM (2021) A pilot evaluation of scalp skin wounding to promote hair growth in female pattern hair loss. Int J Womens Dermatol 7(3):344–345
Starace M, Alessandrini A, Brandi N, Piraccini BM (2020) Preliminary results of the use of scalp microneedling in different types of alopecia. J Cosmet Dermatol 19(3):646–650
Bao L, Gong L, Guo M, Liu T, Shi A, Zong H et al (2020) Randomized trial of electrodynamic microneedle combined with 5% minoxidil topical solution for the treatment of Chinese male Androgenetic alopecia. J Cosmet Laser Ther 22(1):1–7
Parajuli S, Paudel U (2020) Microneedling for androgenetic alopecia not responding to conventional treatment. Our Dermatol Online 11(2):140–142
Steward EN, Patel H, Pandya H, Dewan H, Bhavsar B, Shah U et al (2020) Efficacy of platelet-rich plasma and concentrated growth factor in treating Androgenetic Alopecia - a retrospective study. Ann Maxillofac Surg 10(2):409–416
Yu CQ, Zhang H, Guo ME, Li XK, Chen HD, Li YH et al (2020) Combination therapy with topical minoxidil and nano-microneedle-assisted fibroblast growth factor for male androgenetic alopecia: a randomized controlled trial in Chinese patients. Chin Med J (Engl) 134(7):851–853
Gentile P, Dionisi L, Pizzicannella J, de Angelis B, de Fazio D, Garcovich S (2020) A randomized blinded retrospective study: the combined use of micro-needling technique, low-level laser therapy and autologous non-activated platelet-rich plasma improves hair re-growth in patients with androgenic alopecia. Expert Opin Biol Ther 20(9):1099–1109
Faghihi G, Nabavinejad S, Mokhtari F, Fatemi Naeini F, Iraji F (2021) Microneedling in androgenetic alopecia; comparing two different depths of microneedles. J Cosmet Dermatol 20(4):1241–1247
Sohng C, Lee EH, Woo SK, Kim JY, Park KD, Lee SJ et al (2021) Usefulness of home-use microneedle devices in the treatment of pattern hair loss. J Cosmet Dermatol 20(2):591–596
Fujita J (2021) Favorable effects of microneedling on long-standing androgenetic alopecia in an elderly man: a case report. J Cosmet Dermatol 20(2):588–590
Ramadan WM, Hassan AM, Ismail MA, El Attar YA (2021) Evaluation of adding platelet-rich plasma to combined medical therapy in androgenetic alopecia. J Cosmet Dermatol 20(5):1427–1434
Yepuri V, Venkataram M (2021) Platelet-rich plasma with microneedling in Androgenetic Alopecia: study of efficacy of the treatment and the number of sessions required. J Cutan Aesthet Surg 14(2):184–190
Bao L, Zong H, Fang S, Zheng L, Li Y (2022) Randomized trial of electrodynamic microneedling combined with 5% minoxidil topical solution for treating androgenetic alopecia in Chinese males and molecular mechanistic study of the involvement of the Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway. J Dermatolog Treat 33(1):483–493
Ozcan KN, Sener S, Altunisik N, Turkmen D (2022) Platelet rich plasma application by dermapen microneedling and intradermal point-by-point injection methods, and their comparison with clinical findings and trichoscan in patients with androgenetic alopecia. Dermatol Ther 35(1):e15182
Gentile P, Garcovich S, Lee S-I, Han S (2022) Regenerative biotechnologies in plastic surgery: a multicentric, retrospective, case-series study on the use of micro-needling with low-level light/laser therapy as a hair growth boost in patients affected by androgenetic Alopecia. Appl Sci (Basel) 12(1):217
Ma G, Wu C (2017) Microneedle, bio-microneedle and bio-inspired microneedle: a review. J Control Release 251:11–23
Singh A, Yadav S (2016) Microneedling: advances and widening horizons. Indian Dermatol Online J 7(4):244–254
Doddaballapur S (2009) Microneedling with dermaroller. J Cutan Aesthet Surg 2(2):110–111
McCrudden MT, McAlister E, Courtenay AJ, González-Vázquez P, Singh TR, Donnelly RF (2015) Microneedle applications in improving skin appearance. Exp Dermatol 24(8):561–566
Cohen BE, Elbuluk N (2016) Microneedling in skin of color: a review of uses and efficacy. J Am Acad Dermatol 74(2):348–355
Tan MG, Jo CE, Chapas A, Khetarpal S, Dover JS (2021) Radiofrequency microneedling: a comprehensive and critical review. Dermatol Surg 47(6):755–761
Aldawood FK, Andar A, Desai S (2021) A comprehensive review of microneedles: types, materials, processes, characterizations and applications. Polymers (Basel) 13(16):2815
Badran KW, Sand JP (2018) Platelet-rich plasma for hair loss: review of methods and results. Facial Plast Surg Clin North Am 26(4):469–485
Gassmueller J, Rowold E, Frase T, Hughes-Formella B (2009) Validation of TrichoScan technology as a fully-automated tool for evaluation of hair growth parameters. Eur J Dermatol 19(3):224–231
Dhurat R, Saraogi P (2009) Hair evaluation methods: merits and demerits. Int J Trichol 1(2):108–119
Mehta V (2010) Platelet-rich plasma: a review of the science and possible clinical applications. Orthopedics 33(2):111
Alves R, Grimalt R (2018) A review of platelet-rich plasma: history, biology, mechanism of action, and classification. Skin Appendage Disord 4(1):18–24
Uebel CO, da Silva JB, Cantarelli D, Martins P (2006) The role of platelet plasma growth factors in male pattern baldness surgery. Plast Reconstr Surg 118(6):1458–1466
Sanchez-Gonzalez DJ, Mendez-Bolaina E, Trejo-Bahena NI (2012) Platelet-rich plasma peptides: key for regeneration. Int J Pept 2012:532519
Li ZJ, Choi HI, Choi DK, Sohn KC, Im M, Seo YJ et al (2012) Autologous platelet-rich plasma: a potential therapeutic tool for promoting hair growth. Dermatol Surg 38(7 Pt 1):1040–1046
Gentile P, Garcovich S (2020) Systematic review-the potential implications of different platelet-rich plasma (PRP) concentrations in regenerative medicine for tissue repair. Int J Mol Sci 21(16):5702
de Boer HC, van Oeveren-Rietdijk AM, Rotmans JI, Dekkers OM, Rabelink TJ, van Zonneveld AJ (2013) Activated platelets correlate with mobilization of naive CD34(+) cells and generation of CD34(+) /KDR(+) cells in the circulation. A meta-regression analysis. J Thromb Haemost 11(8):1583–1592
Wikramanayake TC, Rodriguez R, Choudhary S, Mauro LM, Nouri K, Schachner LA et al (2012) Effects of the Lexington LaserComb on hair regrowth in the C3H/HeJ mouse model of alopecia areata. Lasers Med Sci 27(2):431–436
Gentile P, Garcovich S (2019) Advances in regenerative stem cell therapy in androgenic alopecia and hair loss: wnt pathway, growth-factor, and mesenchymal stem cell signaling impact analysis on cell growth and hair follicle development. Cells 8(5):466
Asif M, Kanodia S, Singh K (2016) Combined autologous platelet-rich plasma with microneedling verses microneedling with distilled water in the treatment of atrophic acne scars: a concurrent split-face study. J Cosmet Dermatol 15(4):434–443
Ornelas J, Foolad N, Shi V, Burney W, Sivamani RK (2016) Effect of microneedle pretreatment on topical anesthesia: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA Dermatol 152(4):476–477
Waghule T, Singhvi G, Dubey SK, Pandey MM, Gupta G, Singh M et al (2019) Microneedles: a smart approach and increasing potential for transdermal drug delivery system. Biomed Pharmacother 109:1249–1258
Ingrole RSJ, Azizoglu E, Dul M, Birchall JC, Gill HS, Prausnitz MR (2021) Trends of microneedle technology in the scientific literature, patents, clinical trials and internet activity. Biomaterials 267:120491
Fakhraei Lahiji S, Seo SH, Kim S, Dangol M, Shim J, Li CG et al (2018) Transcutaneous implantation of valproic acid-encapsulated dissolving microneedles induces hair regrowth. Biomaterials 167:69–79
Yang G, Chen Q, Wen D, Chen Z, Wang J, Chen G et al (2019) A therapeutic microneedle patch made from hair-derived keratin for promoting hair regrowth. ACS Nano 13(4):4354–4360
Kim YS, Jeong KH, Kim JE, Woo YJ, Kim BJ, Kang H (2016) Repeated microneedle stimulation induces enhanced hair growth in a murine model. Ann Dermatol 28(5):586–592
Fertig RM, Gamret AC, Cervantes J, Tosti A (2018) Microneedling for the treatment of hair loss? J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol 32(4):564–569
Liebl H, Kloth LC (2012) Skin cell proliferation stimulated by microneedles. J Am Coll Clin Wound Spec 4(1):2–6
Kloth LC (2005) Electrical stimulation for wound healing: a review of evidence from in vitro studies, animal experiments, and clinical trials. Int J Low Extrem Wounds 4(1):23–44
Yang G, Chen G, Gu Z (2021) Transdermal drug delivery for hair regrowth. Mol Pharm 18(2):483–490
Sharma A, Surve R, Dhurat R, Sinclair R, Tan T, Zou Y et al (2020) Microneedling improves minoxidil response in androgenetic alopecia patients by upregulating follicular sulfotransferase enzymes. J Biol Regul Homeost Agents 34(2):659–661
Gupta AK, Quinlan EM, Venkataraman M, Bamimore MA (2022) Microneedling for hair loss. J Cosmet Dermatol 21(1):108–117
Lima EVdA, Lima MdA, Takano D (2013) Microneedling:experimental study and classification of the resulting injury. Surg Cosmet Dermatol 5(2):110–114
Fernandes D, Signorini M (2008) Combating photoaging with percutaneous collagen induction. Clin Dermatol 26(2):192–199
Funding
This work was supported by the Featured Clinical Discipline Project of Shanghai Pudong fund (grant number PWYts2021-07) and the East Hospital affiliated to Tongji University introduced talent research startup fund (grant number DFRC2019008).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Human and Animal Rights
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Informed Consent
For this type of study, informed consent is not required.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Jia, L., Xiong, J., Guo, R. et al. A Comprehensive Review of Microneedling as a Potential Treatment Option for Androgenetic Alopecia. Aesth Plast Surg 46, 2979–2994 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-022-03042-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-022-03042-y