Abstract
Background
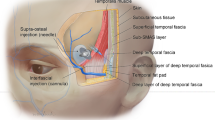
Temporal hollowing is an early sign of aging, and many techniques comprising the injection of fillers into the temporal fossa to correct this hollowing have been described.
Objective
To assess the safety of a new technique in which stromal vascular fraction gel is used for temporal hollowing.
Methods
Thirty-three patients with temporal hollowing were corrected with the aforementioned gel using deep injection and shallow pave filling at the Department of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery, Guangdong Women and Children Hospital, China, between January 2017 and April 2021. This gel was injected into the double plane via a needle and cannula by the same cutaneous access points to prevent severe vascular injury. Improvement was evaluated by self-assessment, the Hollowness Severity Rating Scale (grade range, 0–3; lower grades represent minimal hollowness), and a satisfaction survey.
Results
Self-assessment questionnaire (6 questions) results were satisfactory; 44 temples (67%) demonstrated more than 2 grades of magnitude of clinical improvement. Thirty-one patients (94%) were satisfied with their outcomes; the complaint ratio was low.
Conclusion
The high satisfaction rate of patients treated using the stromal vascular fraction gel by deep injection and shallow pave filling suggests that this technique is simple, effective, and safe.
Level of Evidence IV
This journal requires that authors assign a level of evidence to each submission to which Evidence-Based Medicine rankings are applicable. This excludes Review Articles, Book Reviews, and manuscripts that concern Basic Science, Animal Studies, Cadaver Studies, and Experimental Studies. For a full description of these Evidence-Based Medicine ratings, please refer to the Table of Contents or the online Instructions to Authors www.springer.com/00266.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rose AE, Day D (2013) Esthetic rejuvenation of the temple. Clin Plast Surg 40:77–89
Pessa JE, Kenkel JM, Heldermon CD (2017) Periorbital and temporal anatomy, “targeted fat grafting”, and how a novel circulatory system in human peripheral nerves and brain may help avoid nerve injury and blindness during routine facial augmentation. Aesthet Surg J 37:969–973
Rohrich RJ, Pessa JE (2007) The fat compartments of the face: anatomy and clinical implications for cosmetic surgery. Plast Reconstr Surg 119:2219–2227
Huang RL, Xie Y, Wang W, Herrler T, Zhou J, Zhao P, Pu LLQ, Li Q (2017) Anatomical study of temporal fat compartments and its clinical application for temporal fat grafting. Aesthet Surg J 37:855–862
Cotofana S, Gaete A, Hernandez CA, Casabona G, Bay S, Pavicic T, Coimbra D, Suwanchinda A, Swift A, Green JB, Nikolis A, Frank K (2020) The six different injection techniques for the temple relevant for soft tissue filler augmentation procedures-clinical anatomy and danger zones. J Cosmet Dermatol 19:1570–1579
Hu J, Chen W, Wu Y, Chen K, Luo C, Liang Y, Shi S (2011) Middle cerebral artery occlusion following autologous bitemporal fat injection. Neurol India 59:474–475
Lu L, Xu X, Wang Z, Ye F, Fan X (2013) Retinal and choroidal vascular occlusion after fat injection into the temple area. Circulation 128:1797–1798
Strong AL, Cederna PS, Rubin JP, Coleman SR, Levi B (2015) The current state of fat grafting: a review of harvesting, processing, and injection techniques. Plast Reconstr Surg 136:897–912
Yao Y, Dong Z, Liao Y, Zhang P, Ma J, Gao J, Lu F (2017) Adipose extracellular matrix/stromal vascular fraction gel: a novel adipose tissue-derived injectable for stem cell therapy. Plast Reconstr Surg 139:867–879
Gerth DJ, King B, Rabach L, Glasgold RA, Glasgold MJ (2014) Long-term volumetric retention of autologous fat grafting processed with closed-membrane filtration. Aesthet Surg J 34:985–994
Luo S, Zhang X, Dong H, Wen C, Hao L (2020) Correction of the tear trough deformity and concomitant infraorbital hollows with extracellular matrix/stromal vascular fraction gel. Dermatol Surg 46:e118–e125
Pu LL, Yoshimura K, Coleman SR (2015) Fat grafting: current concept clinical application, and regenerative potential, part 2. Preface. Clin Plast Surg 42:xiii–xiv
Juhász ML, Marmur ES (2015) Temporal fossa defects: techniques for injecting hyaluronic acid filler and complications after hyaluronic acid filler injection. J Cosmet Dermatol 14:254–259
Huang RL, Xie Y, Wang W, Tan P, Li Q (2018) Long-term outcomes of temporal hollowing augmentation by targeted volume restoration of fat compartments in Chinese adults. JAMA Facial Plast Surg 20:387–393
Heydenrych I, Kapoor KM, De Boulle K, Goodman G, Swift A, Kumar N, Rahman E (2018) A 10-point plan for avoiding hyaluronic acid dermal filler-related complications during facial aesthetic procedures and algorithms for management. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol 11:603–611
Sykes JM (2009) Applied anatomy of the temporal region and forehead for injectable fillers. J Drug Dermatol 8(Supplement):s24–s27
Tansatit T, Apinuntrum P, Phetudom T (2015) An anatomical study of the middle temporal vein and the drainage vascular networks to assess the potential complications and the preventive maneuver during temporal augmentation using both anterograde and retrograde injections. Aesthet Plast Surg 39:791–799
Kapoor KM, Bertossi D, Li CQ, Saputra DI, Heydenrych I, Yavuzer R (2020) A systematic literature review of the middle temporal vein anatomy: ‘venous danger zone’ in temporal fossa for filler injections. Aesthet Plast Surg 44:1803–1810
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank Editage (www.editage.cn) for English language editing.
Funding
This study was funded by the Science and Technology Program Project of Guangzhou [Grant No. 202102080476 (Dr Xia)].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standard.
Informed consent
The procedure and aim of this study were clearly explained to the patients, who all provided written informed consent.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xia, X., Sun, S., Zou, J. et al. Clinical Application of Stromal Vascular Fraction Gel in Temple Augmentation Using Deep Injection and Shallow Pave Filling. Aesth Plast Surg 46, 1893–1899 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-022-02801-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-022-02801-1