Abstract
Background
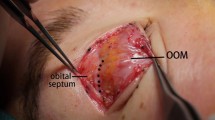
Our objective is to evaluate the evidence on the aesthetic effect and complications of skin-OOM strip resection compared to skin only upper blepharoplasty.
Methods
A systematic search of EMBASE, PubMed, Cochrane and Google Scholar databases was performed using our search strategy through to 31 December 2019. Only comparative studies of the two upper blepharoplasty techniques were included. Three reviewers performed study selection process, data extraction, and quality assessment.
Results
A total of six articles were eligible for final inclusion. The included studies consist of two controlled retrospective cohorts and four small randomized controlled studies (RCT). Three of which, were double blinded. Those RCTs were assigned level 2 evidence due to small size and methodological limitations. The sample size of included was studies 407 in the two retrospective studies and 57 in the four RCTs. The outcomes showed that resection of OOM along with skin in upper blepharoplasty showed no difference in long-term aesthetic outcome when skin only procedure is performed. Muscle strip resection was associated with initially higher ophthalmological morbidity (edema, bruising, pain, dry eye, sluggish eye closure and lagopthalmos). Those resolved a few weeks later with conservative treatment.
Conclusion
The resection of OOM along with skin in upper blepharoplasty showed no difference in long-term aesthetic outcome and was associated with initially higher ophthalmological morbidity compared to skin only procedure. While we are not suggesting that OOM resection is never required, the evidence strongly support its preservation during standard upper blepharoplasty.
Level of Evidence III
This journal requires that authors assign a level of evidence to each article. For a full description of these Evidence-Based Medicine ratings, please refer to Table of Contents or the online Instructions to Authors www.springer.com/00266.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rohrich RJ, Coberly DM, Fagien S, Stuzin JM (2004) Current concepts in aesthetic upper blepharoplasty. Plast Reconstr Surg 113:32e–42e
Gradinger GP (1988) Cosmetic upper blepharoplasty. Clin Plast Surg 15:289–297
D’ Assumpca o EA (1999) Blepharoplasty: a personal tactical approach. Aesthetic Plast Surg 23:28–31
Bosniak SL, McDevitt TF (1991) Cosmetic blepharoplasty. Curr Opin Ophthalmol 2:601–606
Carroll RP, Mahanti RL (1992) En bloc resection in upper eyelid blepharoplasty. Ophthal Plast Reconstr Surg 8:47–49
Furnas DW (1981) The orbicularis oculi muscle management in blepharoplasty. Clin Plast Surg 8:687–715
Loeb R (1977) Necessity for partial resection of the orbicularis oculi muscle in blepharoplasties in some young patients. Plast Reconstr Surg 60:176–178
Widgerow AD (2003) Upper blepharoplasty with lateral segmental orbicularis excision. Ann Plast Surg 50:471–474
Fagien S (2002) Advanced rejuvenative upper blepharoplasty: enhancing aesthetics of the upper periorbita. Plast Reconstr Surg 110:278–291
Hoorntje LE, Lei B, Stollenwerck GA, Kon M (2010) Resecting orbicularis oculi muscle in upper eyelid blepharoplasty–a review of theliterature. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg 63:787–792
Damasceno RW, Cariello AJ, Cardoso EB, Viana GA, Osaki MH (2011) Upper blepharoplasty with or without resection of the orbicularis oculi muscle: a randomized double-blind left-right study. Ophthal Plast Reconstr Surg 27(3):195–197
Liberati A, Altman DG, Tetzlaff J et al (2009) The PRISMA statement for reporting systematic reviews and meta-analyses of studies that evaluate health care interventions: explanation and elaboration. PLoS Med 6(7):253–255
Slim K, Nini E, Forestier D, Kwiatkowski F, Panis Y, Chipponi J (2003) Methodological index for non-randomized studies (Minors): development and validation of a new instrument. ANZ J Surg 73(9):712–716
Higgins JPT, Altman DG, Gøtzsche PC et al (2011) The cochrane collaboration’s tool for assessing risk of bias in randomised trials. BMJ 343:7829
Shea BJ, Reeves BC, Wells G et al (2017) AMSTAR 2 A critical appraisal tool for systematic reviews that include randomised or non-randomised studies of healthcare interventions, or both. BMJ 3:358
Nguyen A, Mahabir RC (2016) An update on the level of evidence for plastic surgery research published in plastic and reconstructive surgery. Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open 4(7):153–157
Van Meer N, Backaert T, Verhaert P, Raus P (2017) Upper lid blepharoplasty without cutting the orbicularis muscle. Int J Ophthalmol Eye Sci 5:308–312
Lopiccolo MC, Mahmoud BH, Liu A, Sage RJ, Kouba DJ (2013) Evaluation of orbicularis oculi muscle stripping on the cosmetic outcome of upper lid blepharoplasty: a randomized, controlled study. Dermatologic Surg 39(5):739–743
Kiang L, Deptula P, Mazhar M, Murariu D, Parsa FD (2014) Muscle-sparing blepharoplasty: a prospective left-right comparative study. Arch Plast Surg 41(5):576–583
Mohammed MF (2018) Impact of orbicularis oculi muscle strip excision during upper lid blepharoplasty on tear film break up time and postoperative dry eye. Al-Azhar Med J 47(3):539–549
Saalabian AA, Liebmann P, Deutinger M (2017) Which tissue should be removed in upper blepharoplasty? Analysis and evaluation of satisfaction. World J Plast Surg 6(3):324–331
Mustarde JC (1975) Problems and possibilities in ptosis surgery. Plast Reconstr Surg 56:3818
Brennan HG, Joseph BA (1979) Delineating the cleft in upper blepharoplasty. Arch Otolaryngol 105:5158
Paul MD (1989) The surgical management of upper eyelid hooding. Aesthetic Plast Surg 13:120
Furnas DW (1978) Festoons of orbicularis muscle as a cause of baggyeyelids. Plast Reconstr Surg 16:52
Saadat D, Dresner SC (2004) Safety of blepharoplasty in patients with preoperative dry eyes. Arch Facial Plast Surg 6:1014
Gulyas G (2006) Improving the lateral fullness of the upper eyelid. Aesthetic Plast Surg 30:6418
Zide BM (1981) Anatomy of the eyelids. Clin Plast Surg 8(4):623–634
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Human Participants and Animals Rights
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Informed Consent
For this type of study, informed consent is not required.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Samargandi, O.A., Prabhu, N., Boudreau, C. et al. Is Orbicularis Oculi Muscle Resection Necessary in Upper Blepharoplasty? A Systematic Review. Aesth Plast Surg 45, 2190–2198 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-021-02131-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-021-02131-8