Abstract
Background
Treatment of a sunken appearance of the temporal region using injectable fillers is a popular procedure. The temporal fossa has very complex anatomy due to multiple vessels running in the different tissue layers. A severe complication in the form of non-thrombotic pulmonary embolism (NTPE) can occur as a result of an inadvertent injection in the middle temporal vein (MTV) while performing temporal fossa filler procedures. Therefore, in-depth knowledge and understanding of the MTV anatomy are essential for successful and safer injectable procedures of the temporal fossa.
Objectives
While there have been many studies to describe the arteries in this region, there is limited information about the location and course of the middle temporal vein. This literature review is aimed at providing detailed information about the course, depth, and size of the MTV to help aesthetic practitioners in performing safer temporal fossa filler injections. This information is imperative to delineate the ‘venous danger zone’ in the temple region.
Methods
The preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses guidelines were used for this review. A literature search was performed to find the articles providing details about the MTV anatomy and the measurements related to its course and size.
Results
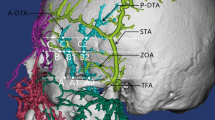
A review of the literature showed that the MTV displays a consistent course and depth in the temporal region, with high variability in its diameter. The middle temporal vein width varied between 0.5 and 9.1 mm in various studies. The middle temporal vein receives many subfascial tributaries from the surface of the temporalis muscle, and for most of its course runs in the fat pad enclosed between superficial and deep layers of the deep temporal fascia. A ‘venous danger zone,’ in the interfascial planes of the temporal fossa, which contain the main part of the MTV and its tributaries, has been proposed in this paper.
Conclusions
The temporal fossa filler procedures need great caution, and knowledge of the depth and course of the MTV is essential for avoiding NTPE.
Level of Evidence III
This journal requires that authors assign a level of evidence to each article. For a full description of these Evidence-Based Medicine ratings, please refer to the Table of Contents or the online Instructions to Authors www.springer.com/00266.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- MTV:
-
Middle temporal vein
- MTA:
-
Middle temporal artery
- IFV:
-
Interfascial vein
- TFP:
-
Temporal fat pad
- STF:
-
Superficial temporal fascia
- DTF:
-
Deep temporal fascia
- NTPE:
-
Nonthrombotic pulmonary embolism
- PRISMA:
-
Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses
References
Sykes JM (2009) Applied anatomy of the temporal region and forehead for injectable fillers. J Drugs Dermatol JDD 8(10):s24–s27
Moradi A, Shirazi A, Perez V (2011) A guide to temporal fossa augmentation with small gel particle hyaluronic acid dermal filler. J Drugs Dermatol 10:673–676
Houseman ND, Taylor GI, Pan WR (2000) The angiosomes of the head and neck: anatomic study and clinical applications. Plast Reconstr Surg 105(7):2287–2313. https://doi.org/10.1097/00006534-200006000-00001
Onishi S, Imanishi N, Yoshimura Y et al (2017) Venous drainage of the face, vol 70. Elsevier, Amsterdam. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bjps.2016.11.023
Lopez R, Benouaich V, Chaput B, Dubois G, Jalbert F (2013) Description and variability of temporal venous vascularization: clinical relevance in temporoparietal free flap technique. Surg Radiol Anat 35(9):831–836. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00276-013-1087-3
Fang M, Rahman E, Kapoor KM (2018) Managing complications of submental artery involvement after hyaluronic acid filler injection in chin region. Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open 6(5):1–4. https://doi.org/10.1097/GOX.0000000000001789
Loh KTD, Phoon YS, Phua V, Kapoor KM (2018) Successfully managing impending skin necrosis following hyaluronic acid filler injection, using high-dose pulsed hyaluronidase. Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open 2018:1. https://doi.org/10.1097/gox.0000000000001639
Wibowo A, Kapoor KM, Philipp-Dormston WG (2019) Reversal of post-filler vision loss and skin ischaemia with high-dose pulsed hyaluronidase injections. Aesth Plast Surg 43:1337–1344. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-019-01421-6
Kapoor KM, Kapoor P, Heydenrych I, Bertossi D (2019) Vision loss associated with hyaluronic acid fillers: a systematic review of literature. Aesthet Plast Surg. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-019-01562-8
Kim SG, Kim YJ, Lee SIL, Lee CJ (2011) Salvage of nasal skin in a case of venous compromise after hyaluronic acid filler injection using prostaglandin E. Dermatol Surg 37(12):1817–1819. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1524-4725.2011.02188.x
Jiang X, Liu DL, Chen B (2014) Middle temporal vein: a fatal hazard in injection cosmetic surgery for temple augmentation. JAMA Facial Plast Surg 16(3):227–229. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamafacial.2013.2565
Longmore RB (1980) Middle temporal veins—a potential hazard in the gillies’ operation. Br J Oral Surg 1981(19):129–131
Abul-Hassan HS, von Drasek AG, Acland RD (1986) Surgical anatomy and blood supply of the fascia layers of the temporal region. Plast Reconstr Surg 77:17–28
Beheiry EE, Abdel-Hamid FAM (2007) An anatomical study of the temporal fascia and related temporal pads of fat. Plast Reconstr Surg 119(1):136–144. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.prs.0000245068.04942.a8
Yano T, Tanaka K, Iida H, Kishimoto S, Okazaki M (2012) Usability of the middle temporal vein as a recipient vessel for free tissue transfer in skull-base reconstruction. Ann Plast Surg 68(3):286–289. https://doi.org/10.1097/SAP.0b013e3182198c55
Yano T, Okazaki M, Yamaguchi K, Akita K (2014) Anatomy of the middle temporal vein. Plast Reconstr Surg 134(1):92e–101e. https://doi.org/10.1097/prs.0000000000000283
Jung W, Youn KH, Won SY, Park JT, Hu KS, Kim HJ (2014) Clinical implications of the middle temporal vein with regard to temporal fossa augmentation. Dermatol Surg 40(6):618–623. https://doi.org/10.1111/dsu.0000000000000004
Jang JG, Hong KS, Choi EY (2014) A case of nonthrombotic pulmonary embolism after facial injection of hyaluronic acid in an illegal cosmetic procedure. Tuberc Respir Dis (Seoul) 77(2):90–93. https://doi.org/10.4046/trd.2014.77.2.90
Jorens PG, Van Marck E, Snoeckx A, Parizel PM (2008) Nonthrombotic pulmonary embolism. Eur Respir J 34(2):452–474. https://doi.org/10.1183/09031936.00141708
Bhagat R, Forteza RM, Calcote CB, Williams WT, Bigler AS, Dwyer TM (2012) Pulmonary emboli from therapeutic sodium hyaluronate. Respir Care. https://doi.org/10.4187/respcare.01666
Park HJ, Jung KH, Kim SY, Lee JH, Jeong JY, Kim JH (2010) Hyaluronic acid pulmonary embolism: a critical consequence of an illegal cosmetic vaginal procedure. Thorax. https://doi.org/10.1136/thx.2009.128272
Heydenrych I, Kapoor KM, De Boulle K et al (2018) A 10-point plan for avoiding hyaluronic acid dermal filler-related complications during facial aesthetic procedures and algorithms for management. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol 11:603–611. https://doi.org/10.2147/CCID.S180904
Kumar N, Rahman E (2017) Effectiveness of teaching facial anatomy through cadaver dissection on aesthetic physicians’ knowledge. Adv Med Educ Pract 2017:475–480. https://doi.org/10.2147/amep.s139893
Trinei FA, Januszkiewicz J, Nahai F (1998) The sentinel vein: an important reference point for surgery in the temporal region. Plast Reconstr Surg. https://doi.org/10.1097/00006534-199801000-00006
Tansatit T, Apinuntrum P, Phetudom T (2015) An anatomical study of the middle temporal vein and the drainage vascular networks to assess the potential complications and the preventive maneuver during temporal augmentation using both anterograde and retrograde injections. Aesthet Plast Surg 39(5):791–799. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-015-0529-1
Campero A, Ajler P, Paíz M, Elizalde RL (2017) Microsurgical anatomy of the interfascial vein. Its significance in the interfascial dissection of the pterional approach. Oper Neurosurg 13(5):622–625. https://doi.org/10.1093/ons/opx047
Wang L, Shi X (2019) Letter: microsurgical anatomy of the interfascial vein. Its significance in the interfascial dissection of the pterional approach. Oper Neurosurg. https://doi.org/10.1093/ons/opz005
Campero A, Ajler P (2019) In reply: microsurgical anatomy of the interfascial vein. Its significance in the interfascial dissection of the pterional approach. Oper Neurosurg. https://doi.org/10.1093/ons/opz008
Sokolovska S, Grinsell DG, Shayan R (2018) Microsurgical reconstruction using the middle temporal vein: a case report. ANZ J Surg 2018:1–2. https://doi.org/10.1111/ans.14698
Cheung LK (1996) The vascular anatomy of the human temporalis muscle: implications for surgical splitting techniques. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg 25(6):414–421. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0901-5027(96)80074-9
Patil J, Kumar N, Swamy RS, D’Souza MR, Guru A, Nayak SB (2014) Absence of retromandibular vein associated with atypical formation of external jugular vein in the parotid region. Anat Cell Biol 47(2):135. https://doi.org/10.5115/acb.2014.47.2.135
Cvetko E (2013) A case of an unusual arrangement of numerous tributaries to the middle temporal vein and its fenestration. Surg Radiol Anat 35(4):355–357. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00276-012-1032-x
Carruthers J, Humphrey S, Beleznay K, Carruthers A (2017) Suggested injection zone for soft tissue fillers in the temple? Dermatol Surg. https://doi.org/10.1097/dss.0000000000001057
Funding
No financial disclosure with respect to this paper from all the authors as no financial support/Grant received by any author for writing and publishing this review paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest to disclose with regard to this review paper. No funding or grant has been received by any author for this paper.
Human and Animal Rights
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Informed Consent
For this type of study, informed consent is not required.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kapoor, K.M., Bertossi, D., Li, C.Q. et al. A Systematic Literature Review of the Middle Temporal Vein Anatomy: ‘Venous Danger Zone’ in Temporal Fossa for Filler Injections. Aesth Plast Surg 44, 1803–1810 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-020-01791-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-020-01791-2