Abstract
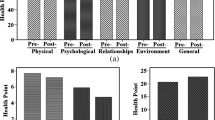
The aim of this study is to analyze the psychological outcomes for patients undergoing non-surgical correction of nasal defects using injections of cross-linked hyaluronic acid. We assessed changes in the subjective perception of nasal appearance after non-surgical rhinoplasty using the Rhinoplasty Outcomes Evaluation (ROE) questionnaire, which is validated and widely used in the literature. One hundred adult subjects without prior history of surgical or non-surgical rhinoplasty underwent non-surgical recontouring using the hyaluronic acid filler from December 2016 to December 2018. The points of inoculation have been standardized by the authors and are divided according to the aesthetic subunits of the nose. A final 74 patients (65 females and 9 males) completed a one-year follow-up and were included in the present study. The ROE questionnaire consists of six questions and assesses the way patients perceive the appearance of their nose and the way they think the people around them view the appearance of their nose. The results of each question were analyzed for each patient, comparing the preoperative results over a 12-month time-frame. Candidates for rhinoplasty, either medical or surgical, are among the most difficult to treat and, interestingly, there is substantial literature showing that among these patients, there is a higher rate of psychiatric disorders. Many of these patients seek aesthetic surgery and are often dissatisfied with the outcome of their surgery. The authors suggest that the use of ROE is not only a valid method of assessing patient satisfaction, but it could also be used as a tool to highlight some of the psychological characteristics of patients long before performing any treatment and could help identify potentially problematic patients.
Level of Evidence IV This journal requires that authors assign a level of evidence to each article. For a full description of these Evidence-Based Medicine ratings, please refer to the Table of Contents or the online Instructions to Authors www.springer.com/00266.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Monreal J (2013) Fat grafting to the nose: personal experience with 36 patients. Aesth Plast Surg 35:916–922
Jasin ME (2013) Nonsurgical rhinoplasty using dermal fillers. Facial Plast Surg Clin N Am 21(2):241–252
Moon H (2016) Use of filler in rhinoplasty. Clin Plast Surg 43(1):307–317
Kurkjian TJ, Ahmad J, Rohrich RJ (2014) Soft-tissue fillers in rhinoplasty. Plast Reconst Surg 133(2):121e–126e
Hedén P (2016) Nasal reshaping with hyaluronic acid: an alternative or complement to surgery. Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open 4(11):e1120 (eCollection 2016)
Bray D, Hopkins C, Roberts DN (2010) Injection rhinoplasty: non-surgical nasal augmentation and correction of post-rhinoplasty contour asymmetries with hyaluronic acid: how we do it. Clin Otolaryngol 35:227–230
Humphrey CD, Arkins JP, Dayan SH (2009) Soft tissue fillers in the nose. Aesthet Surg J 29:477–484
Redaelli A (2008) Medical rhinoplasty with hyaluronic acid and botulinum toxin A: a very simple and quite effective technique. J Cosmet Dermatol 7:210–220
Xue K, Chiang CA, Liu K et al (2012) Multiplane hyaluronic acid rhinoplasty. Plast Reconstr Surg 129:371e–372e
Carruthers J, Cohen SR, Joseph JH et al (2009) The science and art of dermal fillers for soft-tissue augmentation. J Drugs Dermatol 8:335–350
Youn SH, Seo KK (2016) Filler rhinoplasty evaluated by anthropometric analysis. Dermatol Surg 42(9):1071–1081
Alsarraf R (2000) Outcomes research in facial plastic surgery: a review and new directions. Aesth Plast Surg 24:192–197
Izu SC, Kosugi EM, Brandão KV, Lopes AS, Garcia LB, Suguri VM, Gregório LC (2012) Normal values for the rhinoplasty outcome evaluation (ROE) questionnaire. Braz J Otorhinolaryngol 78(4):76–79
Izu SC, Kosugi EM, Lopes AS, Brandão KV, Sousa LB, Suguri VM, Gregório LC (2014) Validation of the rhinoplasty outcomes evaluation (ROE) questionnaire adapted to Brazilian Portuguese. Qual Life Res 23(3):953–958
Barone M, Cogliandro A, Di Stefano N, Tambone V, Persichetti P (2017) A systematic review of patient-reported outcome measures after rhinoplasty. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 274(4):1807–1811
Bulut OC, Plinkert PK, Wallner F, Baumann I (2016) Quality of life in functional rhinoplasty: rhinoplasty outcomes evaluation German version (ROE-D). Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 273(9):2569–2573
Biggs TC, Fraser LR, Ward MJ, Sunkaraneni VS, Harries PG, Salib RJ (2015) Patient reported outcome measures in septorhinoplasty surgery. Ann R Coll Surg Engl 97(1):63–65
Wilkins EG, Lowery JC, Smith DJ Jr (1996) Outcomes research: a primer for plastic surgeons. Ann Plast Surg 37(1):1–11
Edgerton MT, Jacobson WE, Meyer E (1960) Surgical-psychiatric study of patients seeking plastic (cosmetic) surgery: ninety-eight consecutive patients with minimal deformity. Br J Plast Surg 13:136–145
Honigman RJ, Phillips KA, Castle DJ (1999) A review of psychosocial outcomes for patients seeking cosmetic surgery. J Psychosom Res 47(3):277–281
Constantian MB, Lin CP (2014) Why some patients are unhappy: part 1. Relationship of preoperative nasal deformity to number of operations and a history of abuse or neglect. Plast Reconstr Surg 134(4):823–835
Constantian MB, Lin CP (2014) Why some patients are unhappy: part 2. Relationship of nasal shape and trauma history to surgical success. Plast Reconstr Surg 134(4):836–851
Fathololoomi M, Tabrizi A, Bafghi A (2013) Body dysmorphic disorder in aesthetic rhinoplasty candidates. Pak J Med Sci 29(1):197–200
Picavet VA, Gabriëls L, Grietens J, Jorissen M, Prokopakis EP, Hellings PW (2013) Preoperative symptoms of body dysmorphic disorder determine postoperative satisfaction and quality of life in aesthetic rhinoplasty. Plast Reconstr Surg 131(4):861–868
Veale D, Boocock A, Gournay K, Dryden W, Shah F, Willson R, Walburn J (1996) Body dysmorphic disorder. A survey of fifty cases. Br J Psychiatry 169(2):196–201
Lohuis PJ, Hakim S, Duivesteijn W, Knobbe A, Tasman AJ (2013) Benefits of a short, practical questionnaire to measure subjective perception of nasal appearance after aesthetic rhinoplasty. Plast Reconstr Surg 132(6):913e–923e
Aouizerate B, Pujol H, Grabot D, Faytout M, Suire K, Braud C, Auriacombe M, Martin D, Baudet J, Tignol J (2003) Body dysmorphic disorder in a sample of cosmetic surgery applicants. Eur Psychiatry 18(7):365–368
Bellino S, Zizza M, Paradiso E, Rivarossa A, Fulcheri M, Bogetto F (2006) Dysmorphic concern symptoms and personality disorders: a clinical investigation in patients seeking cosmetic surgery. Psychiatry Res 144(1):73–78 (Epub 2006 Aug 17)
Kim SN, Byun DS, Park JH et al (2014) Panophthalmoplegia and vision loss after cosmetic nasal dorsum injection. J Clin Neurosci 21:678–680
Kim EG, Eom TK, Kang SJ (2014) Severe visual loss and cerebral infarction after injection of hyaluronic acid gel. J Craniofac Surg 25:684–686
Kim YJ, Kim SS, Song WK et al (2011) Ocular ischemia with hypotony after injection of hyaluronic acid gel. Ophthal Plast Reconstr Surg 27:e152–e155
He MS, Sheu MM, Huang ZL et al (2013) Sudden bilateral vision loss and brain infarction following cosmetic hyaluronic acid injection. JAMA Ophthalmol 131:1234–1235
Grunebaum LD, Bogdan Allemann I, Dayan S et al (2009) The risk of alar necrosis associated with dermal filler injection. Dermatol Surg 35:1635–1640
Inoue K, Sato K, Matsumoto D et al (2008) Arterial embolization and skin necrosis of the nasal ala following injection of dermal fillers. Plast Reconstr Surg 121:127e–128e
Thomas WW, Bucky L, Friedman O (2016) Injectables in the nose: facts and controversies. Facial Plast Surg Clin N Am 24(3):379–389
Cohen JL, Dayan SH, Brandt FS, Nelson DB, Axford-Gatley RA, Theisen MJ, Narins RS (2013) Systematic review of clinical trials of small- and large-gel-particle hyaluronic acid injectable fillers for aesthetic soft tissue augmentation. Dermatol Surg 39:205–231
Bae IH, Kim MS, Choi H, Na CH, Shin BS (2018) Ischemic oculomotor nerve palsy due to hyaluronic acid filler injection. J Cosmet Dermatol 00:1–3
Khoo C, Tan HJ, Osman SS (2018) A case of Herpes Simplex Virus Type 1 (HSV-1) encephalitis as a possible complication of cosmetic nasal dermal filler injection. Am J Case Rep 2018(19):825–828
Thanasarnaksorn W, Cotofana S, Rudolph C, Kraisak P, Chanasumon N, Suwanchinda A (2018) Severe vision loss caused by cosmetic filler augmentation: case series with review of cause and therapy. J Cosmet Dermatol 17(5):712–718
Ozturk CN, Li Y, Tung R, Parker L, Piliang MP, Zins JE (2013) Complications following injection of soft-tissue fillers. Aesthet Surg J 33(6):862–877
Phillips KA, Siniscalchi JM, McElroy SL (2004) Depression, anxiety, anger, and somatic symptoms in patients with body dysmorphic disorder. Plast Reconstr Surg 113(4):1229–1237
Moon HJ (2016) Use of fillers in rhinoplasty. Clin Plast Surg 43:307–317
Rauso R, Colella G, Zerbinati N, Salti G (2017) Safety and early satisfaction assessment of patients seeking nonsurgical rhinoplasty with filler. J Cutan Aesthet Surg 10(4):207–214
Singh P, Vijayan R, Nikkhah D (2018) Filler rhinoplasty: evidence, outcomes, and complications. Aesthet Surg J 38(11):NP165–NP167
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Ethical Approval
This article does not contain any studies with animal participants performed by any of the authors.
Informed Consent
Informed consent for both filler injections, use of pictures for clinical and scientific studies and psychological questionnaire was obtained for each single patient.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Di Rosa, L., Cerulli, G. & De Pasquale, A. Psychological Analysis of Non-surgical Rhinoplasty. Aesth Plast Surg 44, 131–138 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-019-01538-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-019-01538-8