Abstract
Introduction
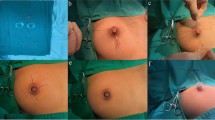
Nipple inversion is defined as a non-projectile nipple. It is a frequent pathologic condition, in which the whole nipple, or a portion of its, is buried inward towards the lactiferous duct and lies below the plane of the areola. Numerous strategies have been described to correct nipple inversion. All the procedures have the purpose to give a good shape to the nipple, preserving its function and sensitivity, when it is possible. To avoid recurrences and to obtain good aesthetic results, we present a modified percutaneous technique.
Method
We performed a retrospective study between 2011 and 2016 and included all the cases of inverted nipples treated in our department. Our modified percutaneous technique consists of a minimal incision supported by a percutaneous suture as a temporary spacer to fill the defect caused by releasing the fibro-ductal bands.
Results
A total of 41 cases of inverted nipples were corrected in 32 patients. After 1 year of follow-up, no recurrence was observed and all nipples maintained complete eversion. There was only one case of partial unilateral necrosis in a patient who underwent tumorectomy and radiotherapy. All patients were satisfied with the aesthetic outcomes.
Conclusion
This is a simple, safe and cheap technique that should be considered as a reliable method for long-term correction of nipple inversion.
Level of Evidence IV
This journal requires that authors assign a level of evidence to each article. For a full description of these Evidence-Based Medicine ratings, please refer to the Table of Contents or the online Instructions to Authors www.springer.com/00266.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cooper A (1840) Anatomy of the breast. Brown and Longman’s, London
Schwager RG, Smith JW, Gray GF et al (1974) Inversion of the human female nipple, with a simple method of treatment. Plast Reconstr Surg 54:564e9
McG Taylor D, Lahiri A, Laitung JK (2011) Correction of the severely inverted nipple: areola- based dermoglandular rhomboid advancement. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg 64(12):e297–e302. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bjps.2011.05.002 Epub 2011 Jun 8
Kim DY, Jeong EC (2003) Correction of inverted nipple: an alternative method using two triangular areolar dermal flaps. Ann Plast Surg 51:636–640
Cabalag MS, Chui CH, Tan BK (2010) Correction of nipple inversion using a micro-knife and transverse to longitudinal skin closure. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg 63(8):e627–e630. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bjps.2010.03.021 Epub 2010 Apr 3
Han S, Hong YG (1999) The inverted nipple: its grading and surgical correction. Plast Reconstr Surg 104:389–395
Peeters G, Decloedt J, Nagels H, Cambier B (2010) Treatment of the severe or recurrent inverted nipple by interposition of a resorbable polydioxanone sheet. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg 63(2):e175–e176
Kolker AR, Torina PJ (2009) Minimally invasive correction of inverted nipples: a safe and simple technique for reliable, sustainable projection. Ann Plast Surg 62(5):549–553. https://doi.org/10.1097/SAP.0b013e31819fb190
Scholten E (2001) A contemporary correction of inverted nipples. Plast Reconstr Surg 107:511
Michael G (2003) Tal correction of inverted nipple using piercing. Plast Reconstr Surg 112(4):1178–1179
Kesaree N, Banapurmath CR, Banapurmath S et al (1993) Treatment of inverted nipples using a disposable syringe. J Hum Lact 9:27–29
Chakrabarti K, Basu S (2011) Management of flat or inverted nipples with simple rubber bands. Breastfeed Med. 6(4):215–219. https://doi.org/10.1089/bfm.2010.0028 Epub 2011 Jan 8
Lee HB, Roh TS, Chung YK et al (1998) Correction of inverted nipple using strut reinforcement with deepithelialized triangular flaps. Plast Reconstr Surg 102:1253–1258
Zhou H, Tan Q, Wu J, Zheng DF, Zhou HR, Xu P, Wang SQ, Ge HQ (2011) Correction of inverted nipple with bilateral areolar rhomboid dermal flaps. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg 64(6):e159–e161. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bjps.2011.01.022 Epub 2011 Mar 4
Chen SH, Gedebou T, Chen PH (2007) The endoscope as an adjunct to correction of nipple inversion deformity. Plast Reconstr Surg 119:1178–1182
Peled IJ (1999) Purse-string suture for nipple projection. Plast Reconstr Surg 103(5):1480–1482
Serra-Renom J, Fontdevila J, Monner J (2004) Correction of the inverted nipple with an internal 5-point star suture. Ann Plast Surg 53(3):293–296
Pribaz JJ, Pousti T (1998) Correction of recurrent nipple inversion with cartilage graft. Ann Plast Surg 40:14e7
Bracaglia R, Tambasco D, Gentileschi S, D’Ettorre M (2012) Recurrent inverted nipple: a reliable technique for the most difficult cases. Ann Plast Surg 69(1):24–26. https://doi.org/10.1097/SAP.0b013e318221b52f
Hwang K, Kim DH (2013) Half Z-plasty, band release, and cavity filling for correction of inverted nipple. J Plast Surg Hand Surg. 47(2):93–96. https://doi.org/10.3109/2000656X.2012.738606 Epub 2013 Feb 26
Sakai S, Sakai Y, Izawa H (1999) A new surgical procedure for the very severe inverted nipple. Aesthetic Plast Surg 23:139
Pompei S, Tedesco M (1999) A new surgical technique for the correction of the inverted nipple. Aesthet Plast Surg 23(5):371–374
Lee MJ, DePolli PA, Casas LA (2003) Aesthetic and predictable correction of the inverted nipple. Aesthet Surg J 23:353–356
Min KH, Park SS (2010) Scar-free technique for inverted-nipple correction. Aesthetic Plastic Surgery 34:116–119
Long X, Zhao R (2011) Nipple retractor to correct inverted nipples. Breast Care (Basel) 6(6):463–465 Epub 2011 Dec 15
Pereira Filho OJ, Bins-Ely J, Granemann AS, Bertelli JA, Abdalla SC (2001) Closed inverted nipple treatment through a microincision procedure. Plast Reconstr Surg 108(4):1000–1005
Wong RK, Wichterman L, Parson SD (2008) Skin sparing nipple reconstruction with polytetrafluoroethylene implant. Ann Plast Surg 61(3):256–258. https://doi.org/10.1097/SAP.0b013e31815d5bfa
Kim JT, Lim YS, Oh JG (2006) Correction of inverted nipples with twisting and locking principles. Plast Reconstr Surg 118(7):1526–1531
Andrade MG, Weissman R, Reis SR (2006) Tissue reaction and surface morphology of absorbable sutures after in vivo exposure. J Mater Sci Mater Med 17(10):949–961
Nary Filho H, Matsumoto MA, Batista AC, Lopes LC, de Góes FC, Consolaro A (2002) Comparative study of tissue response to polyglecaprone 25, polyglactin 910 and polytetrafluorethylene suture materials in rats. Braz Dent J 13(2):86–91
Pavan A, Bosio M, Longo T (1979) A comparative study of poly (glicolic acid) and catgut as suture materials. Histomorphology and mechanical properties. J Biomed Mater Res 13:477–496
Beswada RS, Jamiolkowski DD, Lee IY, Agarwal V, Persivale J, Trenka-Benthin S, Erneta M, Suryadevara J, Yang A, Liu S (1995) Monocryl suture, a new ultra-pliable absorbable monofilament suture. Biomaterials 16:1141–1148
de Melo F, Marijnissen-Hofsté J (2012) Investigation of physical properties of a polycaprolactone dermal filler when mixed with lidocaine and lidocaine/epinephrine. Dermatol Ther (Heidelb) 2(1):13. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13555-012-0013-7
Evaluation of the local tolerance and neocollagenesis of AQTIS Medical Dermal Filler Ellansé-S and AQTIS Medical dermal filler Ellansé-M (2010) Seven months after subdermal and intradermal injection in the rabbit. Dept. Pathobiology, Faculty of Veterinary Medicine, Utrecht University, The Netherlands
Sihna VR, Bansal K, Kaushik R, Kumria R et al (2004) Polye-caprolactone microspheres and nanospheres: an overview. Int J Pharm 278:1–23
Sun H, Mei L, Song C, Cui X, Wang P (2006) The in vivo degradation, absorption and excretion of PCL-based implant. Biomat 27:1735–1740
Funding
The author received no financial support for the research, authorship or publication of this article.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary material 1 (MP4 132177 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dessena, L., Dast, S., Perez, S. et al. Inverted Nipple Treatment and Poliglecaprone Spacer. Aesth Plast Surg 42, 958–963 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-018-1139-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-018-1139-5