Abstract
Objective
Rhinoplasty is a constant challenge for the surgeon, where the correct evaluation of facial aesthetic parameters allows harmonic changes appropriate for each patient. The aim of this study was to compare the preoperative and postoperative results of nasofacial analysis, performed by Rhinobase ® software (indirect anthropometry) compared with direct anthropometry (caliper), in patients undergoing aesthetic rhinoplasty.
Methods
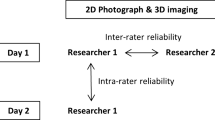
The authors assessed the reliability of using Rhinobase ® software for measuring nasofacial characteristics in 20 individuals (18 F, 2 M). In each patient, the nasofacial analysis was performed before and after surgery. Two raters performed indirect anthropometry on each image on two separate occasions.
Results
Intrarater and interrater reliability for most indirect anthropometric measurements had intraclass correlation coefficients greater than 0.8. Regarding intermethod reliability, Pearson correlation coefficients ranged from 0.6 to 0.9 for most measurements. The highest correlation was found in interalar width, chin vertical, and lower facial height. The Cronbach’s α coefficient calculated for all measurements was 0.8.
Conclusions
The Rhinobase ® software is an easy and safe method for facial analysis. This study provides evidence of high reliability for several nasofacial measurements. The nasofacial analysis allows an accurate preoperative evaluation, surgical planning, and analysis of outcomes in rhinoplasty and may be a useful tool for both novice and experienced surgeons.
Level of Evidence IV
This journal requires that authors assign a level of evidence to each article. For a full description of these Evidence-Based Medicine ratings, please refer to the Table of Contents or the online Instructions to Authors www.springer.com/00266.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bull TR (1983) Rhinoplasty: aesthetics, ethics and airway. J Laryngol Otol 97:901–916
Farkas LG, Hreczko TA, Kolar JC, Munro IR (1985) Vertical and horizontal proportions of the face in young adult North American Caucasians: revision of neoclassical canons. Plast Reconstr Surg 75:328–338
Leong SC, White PS (2006) A comparison of aesthetic proportions between the healthy Caucasian nose and the aesthetic ideal. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg 59:248–252
Byrd HS, Hobar PC (1993) Rhinoplasty: a practical guide for surgical planning. Plast Reconstr Surg 91:642–654; discussion 655-646
Steiger JD, Baker SR (2009) Nuances of profile management: the radix. Facial Plast Surg Clin North Am 17:15–28
Hormozi AK, Toosi AB (2008) Rhinometry: an important clinical index for evaluation of the nose before and after rhinoplasty. Aesthetic Plast Surg 32:286–293
Guyuron B (1988) Precision rhinoplasty. Part I: the role of life-size photographs and soft-tissue cephalometric analysis. Plast Reconstr Surg 81:489–499
Guyuron B (1988) Precision rhinoplasty. Part II: prediction. Plast Reconstr Surg 81:500–505
Yavuzer R, Smirnes S, Jackson IT (2001) Guidelines for standard photography in plastic surgery. Ann Plast Surg 46:293–300
Galdino GM, DaSilva D, Gunter JP (2002) Digital photography for rhinoplasty. Plast Reconstr Surg 109:1421–1434
Henderson JL, Larrabee WF Jr., Krieger BD (2005) Photographic standards for facial plastic surgery. Arch Facial Plast Surg 7:331–333
Punthakee X, Rival R, Solomon P (2009) Digital imaging in rhinoplasty. Aesthetic Plast Surg 33:635–638
Mahajan AY, Shafiei M, Marcus BC (2009) Analysis of patient-determined preoperative computer imaging. Arch Facial Plast Surg 11:290–295
Gode S, Tiris FS, Akyildiz S, Apaydin F (2011) Photogrammetric analysis of soft tissue facial profile in Turkish rhinoplasty population. Aesthetic Plast Surg 35:1016–1021
Apaydin F, Akyildiz S, Hecht DA, Toriumi DM (2009) Rhinobase: a comprehensive database, facial analysis, and picture-archiving software for rhinoplasty. Arch Facial Plast Surg 11:209–211
Sedgwick P (2014) Spearman's rank correlation coefficient. BMJ 349:g7327
Ulijaszek SJ, Kerr DA (1999) Anthropometric measurement error and the assessment of nutritional status. Br J Nutr 82:165–177
Saito Y, Sozu T, Hamada C, Yoshimura I (2006) Effective number of subjects and number of raters for inter-rater reliability studies. Stat Med 25:1547–1560
Woodard CR, Park SS (2010) Nasal and facial analysis. Clin Plast Surg 37:181–189
Meningaud JP, Lantieri L, Bertrand JC (2008) Rhinoplasty: an outcome research. Plast Reconstr Surg 121:251–257
Han K, Kwon HJ, Choi TH, Kim JH, Son D (2010) Comparison of anthropometry with photogrammetry based on a standardized clinical photographic technique using a cephalostat and chair. J Craniomaxillofac Surg 38:96–107
Rohrich RJ, Ahmad J (2011) Rhinoplasty. Plast Reconstr Surg 128:49e–73e
Streiner DL, Norman GR (1989) From health measurement scales a practical guide to their development and use. Oxford University Press, New York
Armijo BS, Brown M, Guyuron B (2012) Defining the ideal nasolabial angle. Plast Reconstr Surg 129:759–764
Brown M, Guyuron B (2013) Redefining the ideal nasolabial angle: part 2. Expert analysis. Plast Reconstr Surg 132:221e–225e
Tollefson TT, Sykes JM (2007) Computer imaging software for profile photograph analysis. Arch Facial Plast Surg 9:113–119
Rohrich RJ, Adams WPJ, Ahmad J, Gunter JP (2014) Dallas rhinoplasty: nasal surgery by the masters, vol 1, 3rd edn. QMP Press, St. Louis
Heike CL, Cunningham ML, Hing AV, Stuhaug E, Starr JR (2009) Picture perfect? Reliability of craniofacial anthropometry using three-dimensional digital stereophotogrammetry. Plast Reconstr Surg 124:1261–1272
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Ethical Approval
Not required.
Funding
There is no funding for this article.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Meruane, M., Ayala, M.F., García-Huidobro, M.A. et al. Reliability of Nasofacial Analysis Using Rhinobase ® Software. Aesth Plast Surg 40, 149–156 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-015-0569-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-015-0569-6