Abstract
Background
There are inherent limitations with previously reported inframammary fold (IMF) recreation methods. The IMF is firmly fixed to the chest wall, but not physiologically, and it is difficult to determine the correct IMF position in the supine position and in the absence of an implant.
Methods
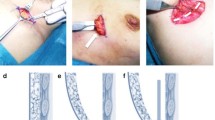
With our new IMF reconstruction method (i.e., drawstring method), the IMF is recreated by drawing a barbed suture, penetrating the dermis, along the IMF. The barbed suture is fixed to the costal cartilage at the medial IMF, and the head is drawn and cut externally at the lateral IMF. The IMF level and depth can be finely adjusted by the tension, in a seated position after implant insertion. Furthermore, the approach can be from a small incision, and a smooth IMF curve is reconstructed.
Results
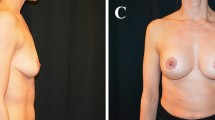
Our drawstring method was performed in 102 patients who underwent reconstruction using a breast implant (n = 95) or flap (n = 7). The mean patient age was 52.0 years (range 33–77 years) and the follow-up period was 12 months (range 3–18 months). Suture or implant infection or exposure did not occur. Suture slack occurred in ten patients with implant-based reconstruction; their IMF became shallow. Insufficient skin expansion (P < 0.005) and strong traction of the barbed suture from the caudal side (P < 0.05) were related to IMF slack. The total revision rate was 2.9 %.
Conclusions
With sufficient skin expansion, the drawstring method using a barbed suture enables smooth and symmetrical IMF reconstruction.
Level of Evidence IV
This journal requires that authors assign a level of evidence to each article. For a full description of these Evidence-Based Medicine ratings, please refer to the Table of Contents or the online Instructions to Authors www.springer.com/00266.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Pennisi VR (1977) Making a definite inframammary fold under a reconstructed breast. Plast Reconstr Surg 60:523–525
Ryan JJ (1982) A lower thoracic advancement flap in breast reconstruction after mastectomy. Plast Reconstr Surg 70:153–160
May JW Jr, Attwood J, Bartlett S (1987) Staged use of soft-tissue expansion and lower thoracic advancement flap in breast reconstruction. Plast Reconstr Surg 79:272–277
Wechselberger G, Del Frari B, Pϋlzl P, Schoeller T (2003) Inframammary fold reconstruction with a deepithelialized skin flap. Ann Plast Surg 50:433–436
Versaci AD (1987) A method of reconstructing a pendulous breast utilizing the tissue expander. Plast Reconstr Surg 80:387–395
Pinella JW (1989) Creating an inframammary crease with a liposuction cannula. Plast Reconstr Surg 83:925
Dowden RV (1987) Achieving a natural inframammary fold and ptotic effect in the reconstructed breast. Ann Plast Surg 19:524–529
Handel N, Jensen JA (1992) An improved technique for creation of the inframammary fold in silicone implant breast reconstruction. Plast Reconstr Surg 89:558–562
Nava M, Quattrone P, Riggio E (1998) Focus on the breast fascial system: a new approach for inframammary fold reconstruction. Plast Reconstr Surg 102:1034–1045
Bogetti P, Cravero L, Spagnoli G, Devalle L, Boriani F, Bocchiotti MA, Renditorre S, Baglioni E (2007) Aesthetic role of the surgically rebuilt inframammary fold for implant-based breast reconstruction after mastectomy. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg 60:1225–1232
Carlson GW, Grossl N, Lewis MM, Temple JR, Styblo TM (1996) Preservation of the inframammary fold: what are we leaving behind? Plast Reconstr Surg 98:447–450
Behranwala KA, Gui GP (2002) Breast cancer in the inframammary fold: is preserving the inframammary fold during mastectomy justified? Breast 11:340–342
Gui GP, Behranwala KA, Abdullah N, Seet J, Osin P, Nerurkar A, Lakhani SR (2004) The inframammary fold: contents, clinical significance and implications for immediate breast reconstruction. Br J Plast Surg 57:146–149
Lockwood TE (1991) Superficial fascial system (SFS) of the trunk and extremities: a new concept. Plast Reconstr Surg 87:1009–1018
Muntan CD, Sundine MJ, Rink RD, Acland RD (2000) Inframammary fold: a histologic reappraisal. Plast Reconstr Surg 105:549–557
Hirsch EM, Seth AK, Fine NA (2014) Reconstruction of the inframammary fold using barbed suture. Ann Plast Surg 72:388–390
Acknowledgments
We used V-LocTM barbed sutures from Covidien (Mansfield, Massachusetts, USA).
Conflict of interest
There is no financial interest in this study.
Ethical standards
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary material 1 (MP4 22294 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Terao, Y., Taniguchi, K. & Tomita, S. A New Method for Inframammary Fold Recreation Using a Barbed Suture. Aesth Plast Surg 39, 379–385 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-015-0479-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-015-0479-7