Abstract
Introduction
This study looks to compare early costs of index surgery and re-operations of robotic-assisted total knee arthroplasties (rTKA) and manual total knee arthroplasty (mTKA) re-operations within 90 days.
Material and methods
The Michigan Arthroplasty Registry Collaborative Quality Initiative (MARCQI) database was queried for patients undergoing rTKA and mTKA at our institution from January 1st, 2018, to March 31st, 2021. Primary outcomes were the day of surgery and overall encounter variable direct costs (VDC). Secondary outcomes included 90-day re-operations and costs.
Results
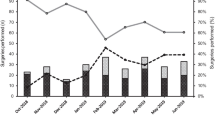
One thousand two hundred seventy-six (21.2%) patients were in the rTKA cohort, while 4740 (78.8%) were in the mTKA cohort. When comparing rTKA to mTKA, rTKA had higher median total encounter costs (p < 0.001) and higher encounter VDC costs (p < 0.001). TKA had higher day of surgery total VDC (p < 0.001), VDC supplies (p < 0.001), and VDC of post-op recovery (p < 0.001). Multivariate linear regression showed no relationship with age, BMI, OR time, or LOS with cost for rTKA or mTKA.
Conclusion
Results from our study show that rTKA is associated with a higher index surgery costs, and no difference in 90-day re-operation costs. The main factor driving increased cost is supply cost, with other variables between too small in difference to make a significant financial impact. Future studies should focus on post-operative costs including readmission and episode of care costs and should consider cost to the payor as opposed to VDC. rTKA will become more common, and other institutions may need to take a closer financial look at this more novel instrumentation before adoption.
Level of evidence: III, retrospective cohort

Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
De-identified data and statistics are available upon request.
References
Bautista M, Manrique J, Hozack WJ (2019) Robotics in total knee arthroplasty. J Knee Surg 32(7):600–606. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0039-1681053
Sousa PL, Sculco PK, Mayman DJ, Jerabek SA, Ast MP, Chalmers BP (2020) Robots in the operating room during hip and knee Arthroplasty. Curr Rev Musculoskelet Med 13(3):309–317. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12178-020-09625-z
Siddiqi A, Mont MA, Krebs VE, Piuzzi NS (2021) Not all robotic-assisted total knee arthroplasty are the same. J Am Acad Orthop Surg 29(2):45–59. https://doi.org/10.5435/JAAOS-D-20-00654
Tompkins GS, Sypher KS, Li HF, Griffin TM, Duwelius PJ (2021) Robotic vs manual total knee arthroplasty in high volume surgeons: a comparison of cost and quality Metrics. J Arthroplasty S0883–5403(21):00953. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arth.2021.12.018
Batailler C, Fernandez A, Swan J, Servien E, Haddad FS, Catani F, Lustig S (2021) MAKO CT-based robotic arm-assisted system is a reliable procedure for total knee arthroplasty: a systematic review. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 29(11):3585–3598. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00167-020-06283-z
Marchand KB, Moody R, Scholl LY, Bhowmik-Stoker M, Taylor KB, Mont MA, Marchand RC (2021) Results of robotic-assisted versus manual total knee arthroplasty at 2-year follow-up. J Knee Surg. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0041-1731349
Ishida K, Shibanuma N, Hayashi S, Kurosaka M, Kuroda R, Matsumoto T (2022) Robotic arm-assisted posterior-stabilised total knee arthroplasty reduces the amount of tibial bone resection thickness without increasing the rate of postoperative flexion contracture in varus knees in the short term: comparison with image-free navigated total knee arthroplasty. Int J Med Robot. https://doi.org/10.1002/rcs.2370
Archer A, Salem HS, Coppolecchia A, Mont MA (2021) Lengths of stay and discharge dispositions after total knee arthroplasty: a comparison of robotic-assisted and manual techniques. J Knee Surg. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0041-1735280
Rajan PV, Khlopas A, Klika A, Molloy R, Krebs V, Piuzzi NS (2022) The cost-effectiveness of robotic-assisted versus manual total knee arthroplasty: a markov model-based evaluation. J Am Acad Orthop Surg 30(4):168–176. https://doi.org/10.5435/JAAOS-D-21-00309
Cotter EJ, Wang J, Illgen RL (2022) Comparative cost analysis of robotic-assisted and jig-based manual primary total knee arthroplasty. J Knee Surg 35(2):176–184. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0040-1713895
Cool CL, Jacofsky DJ, Seeger KA, Sodhi N, Mont MA (2019) A 90-day episode-of-care cost analysis of robotic-arm assisted total knee arthroplasty. J Comp Eff Res 5:327–336. https://doi.org/10.2217/cer-2018-0136
Hughes RE, Hallstrom BR, Zheng H, Kabara J, Cowen M, Igrisan R, Richmond A (2017) Michigan Arthroplasty Registry Collaborative Quality Initiative (MARCQI) report: 2012–2016. University of Michigan, Ann Arbor
Hughes RE, Hallstrom BR, Cowen ME, Igrisan RM, Singal BM, Share DA (2015) Michigan Arthroplasty Registry Collaborative Quality Initiative (MARCQI) as a model for regional registries in the United States. Orthop Res Rev 7:47–56. https://doi.org/10.2147/ORR.S82732
Taheri PA, Butz D, Griffes LC, Morlock DR, Greenfield LJ (2000) Physician impact on the total cost of care. Ann Surg 231(3):432–435. https://doi.org/10.1097/00000658-200003000-00017
Kayani B, Konan S, Tahmassebi J, Pietrzak JRT, Haddad FS (2018) Robotic-arm assisted total knee arthroplasty is associated with improved early functional recovery and reduced time to hospital discharge compared with conventional jig-based total knee arthroplasty: a prospective cohort study. Bone Joint J 100-B(7):930–937. https://doi.org/10.1302/0301-620X.100B7.BJJ-2017-1449.R1.
Agarwal N, To K, McDonnell S, Khan W (2020) Clinical and radiological outcomes in robotic-assisted total knee arthroplasty: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Arthroplasty 35(11):3393-3409.e2. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arth.2020.03.005
Fang CJ, Mazzocco JC, Sun DC et al (2021) Total knee arthroplasty hospital costs by time-driven activity-based costing: robotic vs conventional. Arthroplasty Today 13:43–47. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.artd.2021.11.008
Mont MA, Cool C, Gregory D, Coppolecchia A, Sodhi N, Jacofsky DJ (2021) Health care utilization and payer cost analysis of robotic arm assisted total knee arthroplasty at 30, 60, and 90 Days. J Knee Surg 34(3):328–337. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0039-1695741
Vermue H, Tack P, Gryson T, Victor J (2021) Can robot-assisted total knee arthroplasty be a cost-effective procedure? A Markov decision analysis The Knee 29:345–352. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.knee.2021.02.004
Chen KK, Kim KY, Vigdorchik JM, Meere PA, Bosco JA, Iorio R (2019) Cost-effectiveness analysis of robotic arthroplasty. In: Lonner JH (ed) Robotics in knee and hip arthroplasty. Springer International Publishing, Cham, pp 67–74
St Mart JP, Goh EL (2021) The current state of robotics in total knee arthroplasty. EFORT Open Rev 6(4):270–279. https://doi.org/10.1302/2058-5241.6.200052
Acknowledgements
Pamela Bucki, Director of Finance and Support
Jason Hafron MD, Michigan Institute of Urology, William Beaumont School of Medicine, Beaumont Health
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors whose names appear on the submission:
1.)Made substantial contributions to the conception or design of the work; or the acquisition, analysis, or interpretation of data; or the creation of new software used in the work
2.)Drafted the work or revised it critically for important intellectual content
3.)Approved the version to be published
4.)Agree to be accountable for all aspects of the work in ensuring that questions related to the accuracy or integrity of any part of the work are appropriately investigated and resolved
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
This study was performed in line with the principles of the Declaration of Helsinki. Approval was granted by the Beaumont Health institutional review board (IRB, 2021–122) on 7/1/19.
Consent for publication
As this was a retrospective chart review with minimal risk, the need to obtain individual consents was waived by the institutional review board.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ezeokoli, E.U., John, J., Gupta, R. et al. Index surgery and ninety day re-operation cost comparison of robotic-assisted versus manual total knee arthroplasty. International Orthopaedics (SICOT) 47, 359–364 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00264-022-05674-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00264-022-05674-w