Abstract
Purpose
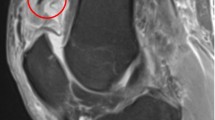
To evaluate the effectiveness of the quadriceps V-Y turndown augmentation for acute quadriceps tendon ruptures in the setting of TKA.
Methods
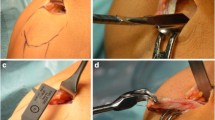
Prospective cohort of 22 patients with quadriceps rupture after TKA were compared with 44 matched patients underwent TKA without quadriceps rupture. Quadriceps ruptures were treated within three weeks after injury by suture augmented with Scuderi quadriceps V-Y turndown flap. Clinical evaluation was performed by the Knee Society Scores (KSS), Western Ontario and McMaster Universities Osteoarthritis Index (WOMAC) and range of motion. Patellar height was assessed by the Blackburne-Peel ratio.
Results
The mean follow-up was 3.3 (range, 3–4) years. At the final follow-up, there were significant improvements in mean KSS scores in both groups (p = 0.001). In the quadriceps group, the mean flexion for all patients, but one with arthrodesis for periprosthetic infection, was 100.1° (range, 90–110°) and mean extensor lag was 7.1° (range, 0–20°). There were significant differences between groups in KSS scores (p = 0.001). Active flexion (p = 0.020) and extension (p = 0.001) were significantly better in the control group. However, there was no significant difference in WOMAC scores (p = 0.252) or patient satisfaction (p = 0.352). There were no quadriceps reruptures. One patient with periprosthetic infection was treated with arthrodesis.
Conclusion
The quadriceps V-Y turndown is an effective and safe procedure for quadriceps ruptures in the setting of TKA. Although the functional outcomes were lower than in TKA patients with no quadriceps rupture, the quality of life and satisfaction were successful in the TKA patients with quadriceps rupture.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dobbs RE, Hanssen AD, Lewallen DG, Pagnano MW (2005) Quadriceps tendon rupture after total knee arthroplasty. Prevalence, complications, and outcomes. J Bone Joint Surg Am 87-A:37–45. https://doi.org/10.2106/JBJS.D.01910
Lynch AF, Rorabeck CH, Bourne RB (1987) Extensor mechanism complications following total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplast 2:135–140. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0883-5403(87)80020-7
Vaishya R, Agarwal AK, Vijay V (2016) Extensor mechanism disruption after total knee arthroplasty: a case series and review of literature. Cureus 8:e479. https://doi.org/10.7759/cureus.479
Wise BT, Erens G, Pour AE, Bradbury TL, Roberson JR (2018) Long-term results of extensor mechanism reconstruction using Achilles tendon allograft after total knee arthroplasty. Int Orthop 42:2367–2373. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00264-018-3848-4
Vajapey SP, Blackwell RE, Maki AJ, Miller TL (2019) Treatment of extensor tendon disruption after total knee arthroplasty: a systematic review. J Arthroplast 34:1279–1286. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arth.2019.02.046
Kim TW, Kamath AF (2011) Israelite CL (2011). Suture anchor repair of quadriceps tendon rupture after total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplast 26:817–820. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arth.2011.01.006
Nodzo SR, Rachala SR (2016) Polypropylene mesh augmentation for complete quadriceps rupture after total knee arthroplasty. Knee 23:177–180. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.knee.2015.09.007
Ormaza A, Moreta J, Mosquera J, de Ugarte OS, Mozos JL (2017) Chronic quadriceps tendon rupture after total knee arthroplasty augmented with synthetic mesh. Orthopedics 40:38–42. https://doi.org/10.3928/01477447-20160915-02
Chhapan J, Sankineani SR, Chiranjeevi T, Reddy MV, Reddy D, Gurava Reddy AV (2018) Early quadriceps tendon rupture after primary total knee arthroplasty. Knee 25:192–194. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.knee.2017.12.002
Soong JW, Silva AN, Andrew TH (2017) Disruption of quadriceps tendon after total knee arthroplasty: case report of four cases. J Orthop Surg 25:2309499017717206. https://doi.org/10.1177/2309499017717206
Sharma P, Maffulli N (2006) Biology of tendon injury: healing, modeling and remodeling. J Musculoskelet Neuronal Interact 6:181–190
Laskin RS (2001) Lateral release rates after total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res 392:88–93. https://doi.org/10.1097/00003086-200111000-00011
Fernandez-Baillo N, Garay EG, Ordonez JM (1993) Rupture of the quadriceps tendon after total knee arthroplasty: a case report. J Arthroplast 8:331–333. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0883-5403(06)80097-5
Shi SM, Shi GG, Laurent EM, Ninomiya JT (2019) Modified V-Y turndown flap augmentation for quadriceps tendon rupture following total knee arthroplasty: a retrospective study. J Bone Joint Surg Am 101-A:1010–1015. https://doi.org/10.2106/JBJS.18.01098
Scuderi C (1958) Ruptures of the quadriceps tendon: study of twenty tendon ruptures. Am J Surg 95:626–634. https://doi.org/10.1016/0002-9610(58)90444-6
Yepes H, Tang M, Morris SF, Stanish WD (2008) Relationship between hypovascular zones and patterns of ruptures of the quadriceps tendon. J Bone Joint Surg Am 90-A:2135–2141. https://doi.org/10.2106/JBJS.G.01200
American Society of Anesthesiologists (2008) Relative value guide. http://www.asahq.org. Accessed 12 January 2020
Insall JN, Dorr LD, Scott RD, Scott WN (1989) Rationale of the Knee Society clinical rating system. Clin Orthop Relat Res 248:13–14
Bellamy N, Buchanan WW, Goldsmith CH, Campbell J, Stitt LW (1988) Validation study of WOMAC: a health status instrument for measuring clinically important patient relevant outcomes to antirheumatic drug therapy in patients with osteoarthritis of the hip or knee. J Rheumatol 15:1833–1840
Bohannon RW (1986) Manual muscle test scores and dynamometer test scores of knee extension strength. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 67:390–392
Blackburne JS, Peel TE (1977) A new method of measuring patellar height. J Bone Joint Surg Br 59:241–242. https://doi.org/10.1302/0301-620X.59B2.873986
Burnett RS, Berger RA, Paprosky WG, Della Valle CJ, Jacobs JJ, Rosenberg AG (2004) Extensor mechanism allograft reconstruction after total knee arthroplasty: a comparison of two techniques. J Bone Joint Surg Am 86-A:2694–2699. https://doi.org/10.2106/00004623-200412000-00016
Lizaur-Utrilla A, Gonzalez-Parreño S, Martinez-Mendez D, Miralles-Muñoz FA, Lopez-Prats FA (2020) Minimal clinically important differences and substantial clinical benefits for knee society scores. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 28:1473–1478. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00167-019-05543-x
Clement ND, Bardgett M, Weir D, Holland J, Gerrand C, Deehan DJ (2018) What is the minimum clinically important difference for the WOMAC index after TKA? Clin Orthop Relat Res 476:2005–2014. https://doi.org/10.1097/CORR.0000000000000444
Pagnano MW (2003) Patellar tendon and quadriceps tendon tears after total knee arthroplasty. J Knee Surg 16:242–247
Papalia R, Vasta S, D’Adamio S, Albo E, Maffulli N, Denaro V (2015) Complications involving the extensor mechanism after total knee arthroplasty. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 23:3501–3515. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00167-014-3189-9
Rasul AT, Fischer DA (1993) Primary repair of quadriceps tendon ruptures. Clin Orthop Relat Res 289:205–207
Boudissa M, Roudet A, Rubens-Duval B, Chaussard C, Saragaglia D (2014) Acute quadriceps tendon ruptures: a series of 50 knees with an average follow-up of more than 6 years. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res 100:213–216. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.otsr.2013.09.014
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Miralles-Muñoz, F.A., Rubio-Morales, M., Ruiz-Lozano, M. et al. V-Y turndown flap augmentation for acute quadriceps rupture after total knee arthroplasty: a prospective matched cohort study. International Orthopaedics (SICOT) 45, 1501–1507 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00264-021-04939-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00264-021-04939-0