Abstract
Purpose
Our aim was to study the safety and outcomes of posterior instrumentation and transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion (TLIF) for treating pyogenic lumbar spondylodiscitis.
Methods
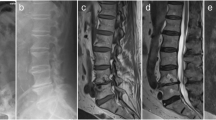
Retrospective analysis was performed on prospectively collected data of 27 consecutive cases of lumbar pyogenic spondylodiscitis treated with posterior instrumentation and TLIF between January 2009 and December 2012. Cases were analysed for safety, radiological and clinical outcomes of transforaminal interbody fusion using bone graft ± titanium cages. Interbody metallic cages with bone graft were used in 17 cases and ten cases used only bone graft. Indications for surgical treatment were failed conservative management in 17, neurodeficit in six and significant bony destruction in four.
Results
There were no cases reporting cage migration, loosening, pseudoarthrosis or recurrence of infection at a mean follow-up of 30 months. Clinical outcomes were assessed using Kirkaldy–Willis criteria, which showed 14 excellent, nine good, three fair and one poor result. Mean focal deformity improved with the use of bone graft ± interbody cages, and the deformity correction was maintained at final follow-up. Mean pre-operative focal lordosis for the graft group was 8.5° (2–16.5°), which improved to 10.9 °(3.3–16°); mean pre-operative focal lordosis in the group treated with cages was 6.7 °(0–15°), which improved to 7°(0–15°) .
Conclusion
TLIFs with cages in patients with pyogenic lumbar spondylodiscitis allows for acceptable clearance of infection, satisfactory deformity correction with low incidence of cage migration, loosening and infection recurrence.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
An KC, Kim JY, Kim TH, Kim JS, Park DH, Kim JG, Sung TW (2012) Posterior lumbar interbody fusion using compressive bone graft with allograft and autograft in the pyogenic discitis. Asian, Spine J 6(1):15–21
Nasto LA, Colangelo D, Mazzotta V, Di Meco E, Neri V, Nasto RA, Pola E (2013) Is posterior percutaneous screw-rod instrumentation a safe and effective alternative approach to TLSO rigid bracing for single-level pyogenic spondylodiscitis? Results of a retrospective cohort analysis. Spine J 14(7):1139–1146
Cheung WY, Luk KD (2012) Pyogenic spondylitis. Int Orthop 36(2):397–404
Kapsalaki E, Gatselis N, Stefos A, Makaritsis K, Vassiou A, Fezoulidis I, Dalekos GN (2009) Spontaneous spondylodiscitis: presentation, risk factors, diagnosis, management, and outcome. Int J Infect Dis 13(5):564–569
Adam D, Papacocea T, Hornea I, Croitoru R (2014) Postoperative spondylodiscitis. A review of 24 consecutive patients. Chirurgia 109:90–94
Moon M S, Kim S S, Lee B J, Moon J L, Sihn J C, & Moon S I (2012). Pyogenic discitis following discectomy. J Orthop Surg 20(1)
Guerado E, Cerván AM (2012) Surgical treatment of spondylodiscitis. An update. Int Orthop 36(2):413–420
Zarghooni K, Röllinghoff M, Sobottke R, Eysel P (2012) Treatment of spondylodiscitis. Int Orthop 36(2):405–411
Lee JS, Suh KT (2006) Posterior lumbar interbody fusion with an autogenous iliac crest bone graft in the treatment of pyogenic spondylodiscitis. J Bone Joint Surg Bri Vol 88(6):765–770
Lin CP, Ma HL, Wang ST, Liu CL, Yu WK, Chang MC (2012) Surgical results of long posterior fixation with short fusion for treating pyogenic spondylodiscitis of the thoracic and lumbar spine: a retrospective study. Spine 37(25):E1572–E1579
Jain AK, Aggarwal A, Dhammi IK, Aggarwal PK, Singh S (2004) Extrapleural anterolateral decompression in tuberculosis of the dorsal spine. J Bone Joint Surg (Br) 86-B:1027–1031
Moon MS, Woo YK, Lee KS et al (1995) Posterior instrumentation and anterior interbody fusion for tuberculous kyphosis of dorsal and lumbar spines. Spine 20:1910–1916
Garg B, Kandwal P, Upendra BN, Goswami A, Jayswal A (2012) Anterior versus posterior procedure for surgical treatment of Thoracolumbar tuberculosis: a retrospective analysis. Ind J Orthop 46:165–170
Sundararaj GD, Amritanand R, Venkatesh K, Arockiaraj J (2011) The use of titanium mesh cages in the reconstruction of anterior column defects in active spinal infections: can we rest the crest? Asian Spine J 5(3):155–161
Hee HT, Majd ME, Holt RT, Pienkowski D (2002) Better treatment of vertebral osteomyelitis using posterior stabilization and titanium mesh cages. J Spinal Disord Tech 15:149–156
Liljenqvist U, Lerner T, Bullmann V, Hackenberg L, Halm H, Winkelmann W (2003) Titanium cages in the surgical treatment of severe vertebral osteomyelitis. Eur Spine J 12:606–612
Frankel HL, Hancock DO, Hyslop G et al (1969) The value of postural reduction in the initial management of the closed injuries of the spine with paraplegia and tetraplegia. Paraplegia 7:179–192
Kirkaldy-Willis WH, Paine KW, Cauchoix J et al (1974) Lumbar spinal stenosis. Clin Orthop 99:30–50
Deininger MH, Unfried MI, Vougioukas VI, Hubbe U (2009) Minimally invasive dorsal percutaneous spondylodesis for the treatment of adult pyogenic spondylodiscitis. Acta Neurochir 151(11):1451–1457
Hadjipavlou AG, Katonis PK, Gaitanis IN, Muffoletto AJ, Tzermiadianos MN, Crow W (2004) Percutaneous transpedicular discectomy and drainage in pyogenic spondylodiscitis. Eur Spine J 13(8):707–713
Bettini N, Girardo M, Dema E, Cervellati S (2009) Evaluation of conservative treatment of non specific spondylodiscitis. Eur Spine J 18(1):143–150
Brase A, Ringel F, Stüer C, Meyer B, Stoffel M (2010) Debridement and fusion with polyetheretherketone implants in purulent spondylodiscitis: a clinical experience with nine patients. Acta Neurochir 152(11):2001–2004
Schomacher M, Finger T, Koeppen D, Süss O, Vajkoczy P, Kroppenstedt S, Cabraja M (2014) Application of titanium and polyetheretherketone cages for treating pyogenic spondylodiscitis. Clin Neurol Neurosurg 127:65–70
Quaile A (2012) Infections associated with spinal implants. Int Orthop 36(2):451–456
Lin Y, Li F, Chen W, Zeng H, Chen A, & Xiong W (2015). Single-level lumbar pyogenic spondylodiscitis treated with mini-open anterior debridement and fusion in combination with posterior percutaneous fixation via a modified anterior lumbar interbody fusion approach. J Neurosurg: Spine 1–7
Lin TY, Tsai TT, Lu ML, Niu CC, Hsieh MK, Fu TS et al (2014) Comparison of two-stage open versus percutaneous pedicle screw fixation in treating pyogenic spondylodiscitis. BMC Musculoskelet Disord 15(1):443
Madhavan K, Vanni S, Williams SK (2014) Direct lateral retroperitoneal approach for the surgical treatment of lumbar discitis and osteomyelitis. Neurosurg Focus 37(2), E5
Sheha AF (2011) Surgical management of post-discectomy spondylodiscitis with transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion (TLIF) and posterior instrumentation. Life Sci J 8(4)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Disclosures
None
Funding
Ganga Orthopaedic Research & Education Foundation (GOREF), Coimbatore.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shetty, A.P., Aiyer, S.N., Kanna, R. et al. Pyogenic lumbar spondylodiscitis treated with transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion: safety and outcomes. International Orthopaedics (SICOT) 40, 1163–1170 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00264-015-3063-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00264-015-3063-5