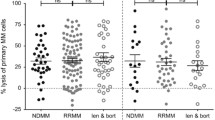
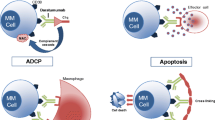
Abstract
CD38, an adenine dinucleotide phosphate (ADP) ribose cyclase and a cyclic ADP ribose hydrolase, is widely expressed on the surface of multiple myeloma (MM) cells. It is known to play a pivotal role in the downstream pathways that mediate MM cell growth, signal transduction, and adhesion. The clinical use of CD38 monoclonal antibodies (MoAbs), such as daratumumab, either as monotherapy or in combination with other anti-MM agents, has produced impressive results in patients who have failed standard MM therapy. CD38 MoAbs exhibit several cytotoxic mechanisms on MM cells. In addition to the classical effector mechanisms associated with antibody therapy, CD38 MoAbs induce MM apoptosis and clonal T-cell expansion. Here, we summarize the results of some pivotal clinical studies using a human CD38 MoAb, daratumumab, in patients with MM, discuss the anti-MM effector mechanisms induced by CD38 MoAbs, and review the potential tumor antigens that may be suitable targets for immunotherapy of MM. Finally, we present a paradigm of immunotherapy for MM patients using CD38 MoAbs followed by GM-CSF and an immune checkpoint inhibitor in patients who have undergone high dose chemotherapy and autologous stem cell transplant. CD38 MoAbs have emerged as a novel and ultimately very promising immunotherapeutic agent for MM because of its ability to induce MM cytotoxicity through both arms of the adaptive immune responses.

Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ADCC:
-
Antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity
- ADCP:
-
Antibody-dependent cellular phagocytosis
- ADP:
-
Adenine dinucleotide phosphate
- ADPR:
-
Adenine dinucleotide phosphate ribose
- APC:
-
Antigen presenting cell
- cADPR:
-
Cyclic adenine dinucleotide phosphate ribose
- CDC:
-
Complement-dependent cytotoxicity
- CDR:
-
Complementarity determining region
- CTA:
-
Cancer-testis antigen
- DC:
-
Dendritic cell
- FcγR:
-
Fcγ receptor
- FDA:
-
Food and drug administration
- GM-CSF:
-
Granulocyte–macrophage colony stimulating factor
- HLA:
-
Human leukocyte antigen
- Id:
-
Idiotypic protein
- MDSC:
-
Myeloid-derived suppressor cell
- MM:
-
Multiple myeloma
- MoAb:
-
Monoclonal antibody
- NAADP:
-
Nicotinic acid adenine dinucleotide phosphate
- NAD:
-
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide
- NK:
-
Natural killer
- PD1:
-
Programmed death 1
- PD-L1:
-
Programmed death ligand 1
- PFS:
-
Progression-free survival
- PR:
-
Partial response
- Rd:
-
Lenalidomide and dexamethasone
- SCT:
-
Stem cell transplant
- Treg :
-
T regulatory
- Vd:
-
Bortizomib and dexamethasone
- VH:
-
Variable region of the immunoglobulin heavy chain
References
Palumbo A, Cavallo F, Gay F, Di Raimondo F, Yehuda DB, Petrucci MT, Pezzatti S, Caravita T, Cerrato C, Ribakovsky E, Genuardi M, Cafro A, Marcatti M, Catalano L, Offidani M, Carella AM, Zamagni E, Patriarca F, Musto P, Evangelista A, Ciccone G, Omedé P, Crippa C, Corradini P, Nagler A, Boccadoro M, Cavo M (2014) Autologous transplantation and maintenance therapy in multiple myeloma. N Engl J Med 371:895–905
Malavasi F, Funaro A, Roggero S, Horenstein A, Calosso L, Mehta K (1994) Human CD38: a glycoprotein in search of a function. Immunol Today 15:95–97
Howard M, Grimaldi JC, Bazan JF, Lund FE, Santos-Argumedo L, Parkhouse RM, Walseth TF, Lee HC (1993) Formation and hydrolysis of cyclic ADP-ribose catalyzed by lymphocyte antigen CD38. Science 262:1056–1059
Muñoz P, Mittelbrunn M, de la Fuente H, Pérez-Martínez M, García-Pérez A, Ariza-Veguillas A, Malavasi F, Zubiaur M, Sánchez-Madrid F, Sancho J (2008) Antigen-induced clustering of surface CD38 and recruitment of intracellular CD38 to the immunologic synapse. Blood 111: 3653–3664.
Guse AH, da Silva CP, Berg I, Skapenko AL, Weber K, Heyer P, Hohenegger M, Ashamu GA, Schulze-Koops H, Potter BV, Mayr GW (1999) Regulation of calcium signalling in T lymphocytes by the second messenger cyclic ADP-ribose. Nature 398:70–73
Gasser A, Bruhn S, Guse AH (2006) Second messenger function of nicotinic acid adenine dinucleotide phosphate revealed by an improved enzymatic cycling assay. J Biol Chem 281:16906–16913
Partida-Sánchez S, Cockayne DA, Monard S, Jacobson EL, Oppenheimer N, Garvy B, Kusser K, Goodrich S, Howard M, Harmsen A, Randall TD, Lund FE (2001) Cyclic ADP-ribose production by CD38 regulates intracellular calcium release, extracellular calcium influx and chemotaxis in neutrophils and is required for bacterial clearance in vivo. Nat Med 7:1209–1216
van de Donk NW, Janmaat ML, Mutis T, Lammerts van Bueren JJ, Ahmadi T, Sasser AK, Lokhorst HM, Parren PW (2016) Monoclonal antibodies targeting CD38 in hematological malignancies and beyond. Immunol Rev 270:95–112
Lokhorst HM, Plesner T, Laubach JP, Nahi H, Gimsing P, Hansson M, Minnema MC, Lassen U, Krejcik J, Palumbo A, van de Donk NW, Ahmadi T, Khan I, Uhlar CM, Wang J, Sasser AK, Losic N, Lisby S, Basse L, Brun N, Richardson PG (2015) Targeting CD38 with daratumumab monotherapy in multiple myeloma. N Engl J Med 373:1207–1219
Lonial S, Weiss BM, Usmani SZ, Singhal S, Chari A, Bahlis NJ, Belch A, Krishnan A, Vescio RA, Mateos MV, Mazumder A, Orlowski RZ, Sutherland HJ, Bladé J, Scott EC, Oriol A, Berdeja J, Gharibo M, Stevens DA, LeBlanc R, Sebag M, Callander N, Jakubowiak A, White D, de la Rubia J, Richardson PG, Lisby S, Feng H, Uhlar CM, Khan I, Ahmadi T, Voorhees PM (2016) Daratumumab monotherapy in patients with treatment-refractory multiple myeloma (SIRIUS): an open-label, randomised, phase 2 trial. Lancet 387:1551–1560
Plesner T, Arkenau HT, Gimsing P, Krejcik J, Lemech C, Minnema MC, Lassen U, Laubach JP, Palumbo A, Lisby S, Basse L, Wang J, Sasser AK, Guckert ME, de Boer C, Khokhar NZ, Yeh H, Clemens PL, Ahmadi T, Lokhorst HM, Richardson PG (2016) Phase 1/2 study of daratumumab, lenalidomide, and dexamethasone for relapsed multiple myeloma. Blood 128:1821–1828
Dimopoulos MA, Oriol A, Nahi H, San-Miguel J, Bahlis NJ, Usmani SZ, Rabin N, Orlowski RZ, Komarnicki M, Suzuki K, Plesner T, Yoon SS, Ben Yehuda D, Richardson PG, Goldschmidt H, Reece D, Lisby S, Khokhar NZ, O’Rourke L, Chiu C, Qin X, Guckert M, Ahmadi T, Moreau P, POLLUX Investigators (2016) Daratumumab, lenalidomide, and dexamethasone for multiple myeloma. N Engl J Med 375:1319–1331
Palumbo A, Chanan-Khan A, Weisel K, Nooka AK, Masszi T, Beksac M, Spicka I, Hungria V, Munder M, Mateos MV, Mark TM, Qi M, Schecter J, Amin H, Qin X, Deraedt W, Ahmadi T, Spencer A, Sonneveld P (2016) CASTOR Investigators Daratumumab, bortezomib and dexamethasone for multiple myeloma. N Engl J Med 375:754–766
de Weers M, Tai YT, van der Veer MS, Bakker JM, Vink T, Jacobs DC, Oomen LA, Peipp M, Valerius T, Slootstra JW, Mutis T, Bleeker WK, Anderson KC, Lokhorst HM, van de Winkel JG, Parren PW (2011) Daratumumab, a novel therapeutic human CD38 monoclonal antibody, induces killing of multiple myeloma and other hematological tumors. J Immunol 186: 1840–1848
Nijhof IS, Groen RW, Noort WA, van Kessel B, de Jong-Korlaar R, Bakker J, van Bueren JJ, Parren PW, Lokhorst HM, van de Donk NW, Martens AC, Mutis T (2015) Preclinical evidence for the therapeutic potential of CD38-targeted immuno-chemotherapy in multiple myeloma patients refractory to lenalidomide and bortezomib. Clin Cancer Res 21:2802–2810
Overdijk MB, Verploegen S, Bögels M, van Egmond M, Lammerts van Bueren JJ, Mutis T, Groen RW, Breij E, Martens AC, Bleeker WK, Parren PW (2015) Antibody-mediated phagocytosis contributes to the anti-tumor activity of the therapeutic antibody daratumumab in lymphoma and multiple myeloma. mAbs 7:311–320
Zheng Y, Cai Z, Wang S, Zhang X, Qian J, Hong S, Li H, Wang M, Yang J, Yi Q (2009) Macrophages are an abundant component of myeloma microenvironment and protect myeloma cells from chemotherapy drug–induced apoptosis. Blood 114:3625–3628
Leidi M, Gotti E, Bologna L, Miranda E, Rimoldi M, Sica A, Roncalli M, Palumbo GA, Introna M, Golay J (2009) M2 macrophages phagocytose rituximab-opsonized leukemic targets more efficiently than M1 cells in vitro. J Immunol 182: 4415–4422
Overdijk MB, Jansen JH, Nederend M, Lammerts van Bueren JJ, Groen RW, Parren PW, Leusen JH, Boross P (2016) The therapeutic CD38 monoclonal antibody daratumumab induces programmed cell death via Fcγ receptor-mediated cross-linking. J Immunol 197:807–813
Deckert J, Wetzel MC, Bartle LM, Skaletskaya A, Goldmacher VS, Vallée F, Zhou-Liu Q, Ferrari P, Pouzieux S, Lahoute C, Dumontet C, Plesa A, Chiron M, Lejeune P, Chittenden T, Park PU, Blanc V (2014) SAR650984, a novel humanized CD38-targeting antibody, demonstrates potent antitumor activity in models of multiple myeloma and other CD38+ hematologic malignancies. Clin Cancer Res 20:4574–4583
Davies FE, Raje N, Hideshima T, Lentzsch S, Young G, Tai YT, Lin B, Podar K, Gupta D, Chauhan D, Treon SP, Richardson PG, Schlossman RL, Morgan GJ, Muller GW, Stirling DI, Anderson KC (2001) Thalidomide and immunomodulatory derivatives augment natural killer cell cytotoxicity in multiple myeloma. Blood 98:210–216
Hayashi T, Hideshima T, Akiyama M, Podar K, Yasui H, Raje N, Kumar S, Chauhan D, Treon SP, Richardson P, Anderson KC (2005) Molecular mechanisms whereby immunomodulatory drugs activate natural killer cells: clinical application. Br J Haematol 128:192–203
van der Veer MS, de Weers M, van Kessel B, Bakker JM, Wittebol S, Parren PW, Lokhorst HM, Mutis T (2011) Towards effective immunotherapy of myeloma: enhanced elimination of myeloma cells by combination of lenalidomide with the human CD38 monoclonal antibody daratumumab. Haematologica 96:284–290
Krejcik J, Casneuf T, Nijhof IS, Verbist B, Bald J, Plesner T, Syed K, Liu K, van de Donk NW, Weiss BM, Ahmadi T, Lokhorst HM, Mutis T, Sasser AK (2016) Daratumumab depletes CD38+ immune regulatory cells, promotes T-cell expansion, and skews T-cell repertoire in multiple myeloma. Blood 128:384–394
Qu P, Wang LZ, Lin PC (2016) Expansion and functions of myeloid-derived suppressor cells in the tumor microenvironment. Cancer Lett 380:253–256
Lokhorst HM, Schattenberg A, Cornelissen JJ, van Oers MH, Fibbe W, Russell I, Donk NW, Verdonck LF (2000) Donor lymphocyte infusions for relapsed multiple myeloma after allogeneic stem-cell transplantation: predictive factors for response and long-term outcome. J Clin Oncol 18:3031–3037
Chiriva-Internati M, Wang Z, Bumm K, Xue Y, Hahn AB, Lim SH (2001) Sperm protein 17 (Sp17) in multiple myeloma: opportunity for myeloma-specific donor T cell infusion to enhance graft-versus-myeloma effect without increasing graft-versus-host disease risk. Eur J Immunol 31:2277–2283
Chiriva-Internati M, Wang Z, Salati E, Bumm K, Barlogie B, Lim SH (2002) Sperm protein 17 (Sp17) is a suitable target for immunotherapy of multiple myeloma. Blood 100:961–965
Lim SH, Badros A, Lue C, Barlogie B (2001) Distinct T-cell clonal expansion in the vicinity of tumor cells in plasmacytoma. Cancer 91:900–908
Brown RD, Spencer A, Ho PJ, Kennedy N, Kabani K, Yang S, Sze DM, Aklilu E, Gibson J, Joshua DE (2009) Prognostically significant cytotoxic T cell clones are stimulated after thalidomide therapy in patients with multiple myeloma. Leuk Lymphoma 50:1860–1864
Wen YJ, Ling M, Bailey-Wood R, Lim SH (1998) Id-pulsed adherent PBMC-derived dendritic cells prime immune system in multiple myeloma. Clin Cancer Res 4:957–962
Lim SH, Bailey-Wood R (1999) Idiotypic protein-pulsed dendritic cell vaccination in multiple myeloma. Int J Cancer 83:215–222
Wen YJ, Ling M, Lim SH (1998) Immunogenicity and cross-reactivity with idiotypic IgA of VH CDR3 peptide in multiple myeloma. Br J Haematol 100:464–468
Batchu RB, Moreno AM, Szmania SM, Bennett G, Spagnoli GC, Ponnazhagan S, Barlogie B, Tricot G, van Rhee F (2005) Protein transduction of dendritic cells for NY-ESO-1-based immunotherapy of myeloma. Cancer Res 65: 10041–10049
Jungbluth AA, Ely S, DiLiberto M, Niesvizky R, Williamson B, Frosina D, Chen YT, Bhardwaj N, Chen-Kiang S, Old LJ, Cho HJ (2005) The cancer-testis antigens CT7 (MAGE-C1) and MAGE-A3/6 are commonly expressed in multiple myeloma and correlate with plasma-cell proliferation. Blood 106:167–174
Lim SH, Wang Z, Chiriva-Internati M, Xue Y (2001) Sperm protein 17 is a novel cancer-testis antigen in multiple myeloma. Blood 97:1508–1510
Wang Z, Zhang J, Zhang Y, Lim SH (2006) SPAN-Xb expression in myeloma cells is dependent on promoter hypomethylation and can be upregulated pharmacologically. Int J Cancer 118:1436–1444
Zhang R, Wang Z, Liu H, Giles FJ, Lim SH (2003) Pattern of gene expression and immune responses to Semenogelin 1 in chronic hematologic malignancies. J Immunother 26:461–467
Wang Z, Zhang Y, Mandal A, Zhang J, Giles FJ, Herr JC, Lim SH (2004) The Spermatozoa Protein, SLLP1, is a Novel Cancer–Testis Antigen in Hematologic Malignancies. Clin Cancer Res 10:6544–6550
Li Z, Li W, Meklat F, Wang Z, Zhang J, Zhang Y, Lim SH (2007) A yeast two-hybrid system using Sp17 identified Ropporin as a novel cancer–testis antigen in hematologic malignancies. Int J Cancer 121:1507–1511
Guillaume T, Rubinstein DB, Symann M (1998) Immune reconstitution and immunotherapy after autologous hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Blood 92:1471–1490
Nair JR, Carlson LM, Koorella C, Rozanski CH, Byrne GE, Bergsagel PL, Shaughnessy JP Jr, Boise LH, Chanan-Khan A, Lee KP (2011) CD28 expressed on malignant plasma cells induces a prosurvival and immunosuppressive microenvironment. J Immunol 187:1243–1253
Inaba K, Steinman RM, Pack MW, Aya H, Inaba M, Sudo T, Wolpe S, Schuler G (1992) Identification of proliferating dendritic cell precursors in mouse blood. J Exp Med 175:1157–1167
Sallusto F, Lanzavecchia A (1994) Efficient presentation of soluble antigen by cultured human dendritic cells is maintained by granulocyte/macrophage colony-stimulating factor plus interleukin 4 and downregulated by tumor necrosis factor alpha. J Exp Med 179:1109–1118
Caux C, Vanbervliet B, Massacrier C, Dezutter-Dambuyant C, de Saint-Vis B, Jacquet C, Yoneda K, Imamura S, Schmitt D, Banchereau J (1996) CD34 hematopoietic progenitors from human cord blood differentiate along two independent dendritic cell pathways in response to GM-CSF+ TNF alpha. J Exp Med 184:695–706
Ahlers JD, Dunlop N, Alling DW, Nara PL, Berzofsky JA (1997) Cytokine-in-adjuvant steering of the immune response phenotype to HIV-1 vaccine constructs: granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor and TNF-alpha synergize with IL-12 to enhance induction of cytotoxic T lymphocytes. J Immunol 158:3847–3958
Wang Z, Zhang Y, Ramsahoye B, Bowen D, Lim SH (2004) Sp17 gene expression in tumor cells is regulated by promoter methylation. Br J Cancer 91:1597–1603
Zhang Y, Wang Z, Zhang J, Farmer B, Lim SH (2008) Semenogelin I expression in myeloma cells can be upregulated pharmacologically. Leuk Res 32:1889–1894
Yousef S, Marvin J, Steinbach M, Langemo A, Kovacsovics T, Binder M, Kröger N, Luetkens T, Atanackovic D (2015) Immunomodulatory molecule PD-L1 is expressed on malignant plasma cells and myeloma-propagating pre-plasma cells in the bone marrow of multiple myeloma patients. Blood Cancer J 5:e285
Liu J, Hamrouni A, Wolowiec D, Coiteux V, Kuliczkowski K, Hetuin D, Saudemont A, Quesnel B (2007) Plasma cells from multiple myeloma patients express B7-H1 (PD-L1) and increase expression after stimulation with IFN-{gamma} and TLR ligands via a MyD88-, TRAF6-, and MEK-dependent pathway. Blood 110:296–304
Hallett WHD, Jing W, Drobyski WR, Johnson BD (2011) Immunosuppressive effects of multiple myeloma are overcome by PD-L1 blockade. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 17:1133–1145
Tamura H, Ishibashi M, Yamashita T, Tanosaki S, Okuyama N, Kondo A, Hyodo H, Shinya E, Takahashi H, Dong H, Tamada K, Chen L, Dan K, Ogata K (2013) Marrow stromal cells induce B7-H1 expression on myeloma cells, generating aggressive characteristics in multiple myeloma. Leukemia 27:464–472
Paiva B, Azpilikueta A, Puig N, Ocio EM, Sharma R, Oyajobi BO, Labiano S, San-Segundo L, Rodriguez A, Aires-Mejia I, Rodriguez I, Escalante F, de Coca AG, Barez A, San Miguel JF, Melero I (2015) PD-L1/PD-1 presence in the tumor microenvironment and activity of PD-1 blockade in multiple myeloma. Leukemia 29:2110–2113
Kearl TJ, Jing W, Gershan JA, Johnson BD (2013) PD-1/PD-L1 Blockade after transient lymphodepletion to treat myeloma. J Immunol 190:5620–5628
Zelle-Rieser C, Thangavadivel S, Biedermann R, Brunner A, Stoitzner P, Willenbacher E, Greil R, Jöhrer K (2016) T cells in multiple myeloma display features of exhaustion and senescence at the tumor site. J Hematol Oncol 9:116
Suen H, Brown R, Yang S, Ho PJ, Gibson J, Joshua D (2015) The failure of immune checkpoint blockade in multiple myeloma with PD-1 inhibitors in a phase I study. Leukemia 29:1621–2622
Lesokhin AM, Ansell SM, Armand P, Scott EC, Halwani A, Gutierrez M, Millenson MM, Cohen AD, Schuster SJ, Lebovic D, Dhodapkar M, Avigan D, Chapuy B, Ligon AH, Freeman GJ, Rodig SJ, Cattry D, Zhu L, Grosso JF, Bradley Garelik MB, Shipp MA, Borrello I, Timmerman J (2016) Nivolumab in patients with relapsed or refractory hematologic malignancy: preliminary results of a phase Ib study. J Clin Oncol 34:2698–2704
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors confirm that there is no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shallis, R.M., Terry, C.M. & Lim, S.H. The multi-faceted potential of CD38 antibody targeting in multiple myeloma. Cancer Immunol Immunother 66, 697–703 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00262-017-1990-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00262-017-1990-2