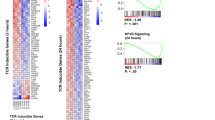
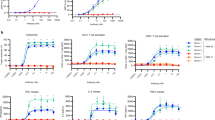
Abstract
Small molecules targeting kinases involved in B cell receptor signaling are showing encouraging clinical activity in chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) patients. Fostamatinib (R406) and entospletinib (GS-9973) are ATP-competitive inhibitors designed to target spleen tyrosine kinase (Syk) that have shown clinical activity with acceptable toxicity in trials with CLL patients. Preclinical studies with these inhibitors in CLL have focused on their effect in patient-derived leukemic B cells. In this work we show that clinically relevant doses of R406 and GS-9973 impaired the activation and proliferation of T cells from CLL patients. This effect could not be ascribed to Syk-inhibition given that we show that T cells from CLL patients do not express Syk protein. Interestingly, ζ-chain-associated protein kinase (ZAP)-70 phosphorylation was diminished by both inhibitors upon TCR stimulation on T cells. In addition, we found that both agents reduced macrophage-mediated phagocytosis of rituximab-coated CLL cells. Overall, these results suggest that in CLL patients treated with R406 or GS-9973 T cell functions, as well as macrophage-mediated anti-tumor activity of rituximab, might be impaired. The potential consequences for CLL-treated patients are discussed.






Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- BCR:
-
B cell receptor
- Btk:
-
Bruton’s tyrosine kinase
- CD40L:
-
CD40 ligand
- CFSE:
-
Carboxyfluorescein succinimidyl ester
- CLL:
-
Chronic lymphocytic leukemia
- ECL:
-
Enhanced chemiluminescence
- Flt3:
-
Fms-like tyrosine kinase 3
- Lck:
-
Lymphocyte-specific protein tyrosine kinase
- M-CSF:
-
Macrophage colony-stimulating factor
- Rx:
-
Rituximab
- pAb:
-
Polyclonal antibodies
- PVDF:
-
Polyvinylidene difluoride
- SEM:
-
Standard error of the mean
- Syk:
-
Spleen tyrosine kinase
- Th:
-
T helper
- ZAP-70 :
-
ζ-chain-associated protein kinase-70
References
Soma LA, Craig FE, Swerdlow SH (2006) The proliferation center microenvironment and prognostic markers in chronic lymphocytic leukemia/small lymphocytic lymphoma. Hum Pathol 37(2):152–159
Rosati S, Kluin PM (2005) Chronic lymphocytic leukaemia: a review of the immuno-architecture. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol 294:91–107
Audrito V, Vaisitti T, Serra S, Bologna C, Brusa D, Malavasi F, Deaglio S (2013) Targeting the microenvironment in chronic lymphocytic leukemia offers novel therapeutic options. Cancer Lett 328(1):27–35. doi:10.1016/j.canlet.2012.08.012
Bagnara D, Kaufman MS, Calissano C, Marsilio S, Patten PE, Simone R, Chum P, Yan XJ, Allen SL, Kolitz JE, Baskar S, Rader C, Mellstedt H, Rabbani H, Lee A, Gregersen PK, Rai KR, Chiorazzi N (2011) A novel adoptive transfer model of chronic lymphocytic leukemia suggests a key role for T lymphocytes in the disease. Blood 117(20):5463–5472. doi:10.1182/blood-2010-12-324210
Ghia P, Strola G, Granziero L, Geuna M, Guida G, Sallusto F, Ruffing N, Montagna L, Piccoli P, Chilosi M, Caligaris-Cappio F (2002) Chronic lymphocytic leukemia B cells are endowed with the capacity to attract CD4+, CD40L+ T cells by producing CCL22. Eur J Immunol 32(5):1403–1413
Granziero L, Ghia P, Circosta P, Gottardi D, Strola G, Geuna M, Montagna L, Piccoli P, Chilosi M, Caligaris-Cappio F (2001) Survivin is expressed on CD40 stimulation and interfaces proliferation and apoptosis in B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood 97(9):2777–2783
Schmid C, Isaacson PG (1994) Proliferation centres in B-cell malignant lymphoma, lymphocytic (B-CLL): an immunophenotypic study. Histopathology 24(5):445–451
Patten PE, Buggins AG, Richards J, Wotherspoon A, Salisbury J, Mufti GJ, Hamblin TJ, Devereux S (2008) CD38 expression in chronic lymphocytic leukemia is regulated by the tumor microenvironment. Blood 111(10):5173–5181. doi:10.1182/blood-2007-08-108605
Crawford DH, Catovsky D (1993) In vitro activation of leukaemic B cells by interleukin-4 and antibodies to CD40. Immunology 80(1):40–44
Buschle M, Campana D, Carding SR, Richard C, Hoffbrand AV, Brenner MK (1993) Interferon gamma inhibits apoptotic cell death in B cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia. J Exp Med 177(1):213–218
Kiaii S, Kokhaei P, Mozaffari F, Rossmann E, Pak F, Moshfegh A, Palma M, Hansson L, Mashayekhi K, Hojjat-Farsangi M, Österborg A, Choudhury A, Mellstedt H (2013) T cells from indolent CLL patients prevent apoptosis of leukemic B cells in vitro and have altered gene expression profile. Cancer Immunol Immunother 62(1):51–63. doi:10.1007/s00262-012-1300-y
Braselmann S, Taylor V, Zhao H, Wang S, Sylvain C, Baluom M, Qu K, Herlaar E, Lau A, Young C, Wong BR, Lovell S, Sun T, Park G, Argade A, Jurcevic S, Pine P, Singh R, Grossbard EB, Payan DG, Masuda ES (2006) R406, an orally available spleen tyrosine kinase inhibitor blocks fc receptor signaling and reduces immune complex-mediated inflammation. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 319(3):998–1008. doi:10.1124/jpet.106.109058
Gobessi S, Laurenti L, Longo PG, Carsetti L, Berno V, Sica S, Leone G, Efremov DG (2009) Inhibition of constitutive and BCR-induced Syk activation downregulates Mcl-1 and induces apoptosis in chronic lymphocytic leukemia B cells. Leukemia 23(4):686–697. doi:10.1038/leu.2008.346
Buchner M, Baer C, Prinz G, Dierks C, Burger M, Zenz T, Stilgenbauer S, Jumaa H, Veelken H, Zirlik K (2010) Spleen tyrosine kinase inhibition prevents chemokine- and integrin-mediated stromal protective effects in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood 115(22):4497–4506. doi:10.1182/blood-2009-07-233692
Suljagic M, Longo PG, Bennardo S, Perlas E, Leone G, Laurenti L, Efremov DG (2010) The Syk inhibitor fostamatinib disodium (R788) inhibits tumor growth in the Emu-TCL1 transgenic mouse model of CLL by blocking antigen-dependent B-cell receptor signaling. Blood 116(23):4894–4905. doi:10.1182/blood-2010-03-275180
Friedberg JW, Sharman J, Sweetenham J, Johnston PB, Vose JM, Lacasce A, Schaefer-Cutillo J, De Vos S, Sinha R, Leonard JP, Cripe LD, Gregory SA, Sterba MP, Lowe AM, Levy R, Shipp MA (2010) Inhibition of Syk with fostamatinib disodium has significant clinical activity in non-Hodgkin lymphoma and chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood 115(13):2578–2585. doi:10.1182/blood-2009-08-236471
Currie KS, Kropf JE, Lee T, Blomgren P, Xu J, Zhao Z, Gallion S, Whitney JA, Maclin D, Lansdon EB, Maciejewski P, Rossi AM, Rong H, Macaluso J, Barbosa J, Di Paolo JA, Mitchell SA (2014) Discovery of GS-9973, a selective and orally efficacious inhibitor of spleen tyrosine kinase. J Med Chem 57(9):3856–3873. doi:10.1021/jm500228a
Sharman J, Hawkins M, Kolibaba K, Boxer M, Klein L, Wu M, Hu J, Abella S, Yasenchak C (2015) An open-label phase 2 trial of entospletinib (GS-9973), a selective spleen tyrosine kinase inhibitor, in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood 125(15):2336–2343. doi:10.1182/blood-2014-08-595934
Dubovsky JA, Beckwith KA, Natarajan G, Woyach JA, Jaglowski S, Zhong Y, Hessler JD, Liu TM, Chang BY, Larkin KM, Stefanovski MR, Chappell DL, Frissora FW, Smith LL, Smucker KA, Flynn JM, Jones JA, Andritsos LA, Maddocks K, Lehman AM, Furman R, Sharman J, Mishra A, Caligiuri MA, Satoskar AR, Buggy JJ, Muthusamy N, Johnson AJ, Byrd JC (2013) Ibrutinib is an irreversible molecular inhibitor of ITK driving a Th1-selective pressure in T lymphocytes. Blood 122(15):2539–2549. doi:10.1182/blood-2013-06-507947
Borge M, Belen Almejun M, Podaza E, Colado A, Fernandez Grecco H, Cabrejo M, Bezares RF, Giordano M, Gamberale R (2015) Ibrutinib impairs the phagocytosis of rituximab-coated leukemic cells from chronic lymphocytic leukemia patients by human macrophages. Haematologica 100(4):e140–e142. doi:10.3324/haematol.2014.119669
Da Roit F, Engelberts PJ, Taylor RP, Breij EC, Gritti G, Rambaldi A, Introna M, Parren PW, Beurskens FJ, Golay J (2014) Ibrutinib interferes with the cell-mediated anti-tumour activities of therapeutic CD20 antibodies: implications for combination therapy. Haematologica 100(1):77–86. doi:10.3324/haematol.2014.107011
Montalvao F, Garcia Z, Celli S, Breart B, Deguine J, Van Rooijen N, Bousso P (2013) The mechanism of anti-CD20-mediated B cell depletion revealed by intravital imaging. J Clin Investig 123(12):5098–5103. doi:10.1172/JCI70972
Uchida J, Hamaguchi Y, Oliver JA, Ravetch JV, Poe JC, Haas KM, Tedder TF (2004) The innate mononuclear phagocyte network depletes B lymphocytes through Fc receptor-dependent mechanisms during anti-CD20 antibody immunotherapy. J Exp Med 199(12):1659–1669
Leonhardt F, Zirlik K, Buchner M, Prinz G, Hechinger AK, Gerlach UV, Fisch P, Schmitt-Graff A, Reichardt W, Zeiser R (2012) Spleen tyrosine kinase (Syk) is a potent target for GvHD prevention at different cellular levels. Leukemia 26(7):1617–1629. doi:10.1038/leu.2012.10
Platt AM, Benson RA, McQueenie R, Butcher JP, Braddock M, Brewer JM, McInnes IB, Garside P (2015) The active metabolite of spleen tyrosine kinase inhibitor fostamatinib abrogates the CD4(+) T cell-priming capacity of dendritic cells. Rheumatology 54(1):169–177. doi:10.1093/rheumatology/keu273
Chattopadhyay PK, Yu J, Roederer M (2006) Live-cell assay to detect antigen-specific CD4+ T-cell responses by CD154 expression. Nat Protoc 1(1):1–6. doi:10.1038/nprot.2006.1
Borge M, Nannini PR, Galletti JG, Morande PE, Avalos JS, Bezares RF, Giordano M, Gamberale R (2010) CXCL12-induced chemotaxis is impaired in T cells from patients with ZAP-70-negative chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Haematologica 95(5):768–775. doi:10.3324/haematol.2009.013995
Geginat J, Sallusto F, Lanzavecchia A (2003) Cytokine-driven proliferation and differentiation of human naive, central memory and effector memory CD4+ T cells. Pathol Biol 51(2):64–66
Geginat J, Lanzavecchia A, Sallusto F (2003) Proliferation and differentiation potential of human CD8 + memory T-cell subsets in response to antigen or homeostatic cytokines. Blood 101(11):4260–4266. doi:10.1182/blood-2002-11-3577
Palacios EH, Weiss A (2007) Distinct roles for Syk and ZAP-70 during early thymocyte development. J Exp Med 204(7):1703–1715. doi:10.1084/jem.20070405
Feldman AL, Sun DX, Law ME, Novak AJ, Attygalle AD, Thorland EC, Fink SR, Vrana JA, Caron BL, Morice WG, Remstein ED, Grogg KL, Kurtin PJ, Macon WR, Dogan A (2008) Overexpression of Syk tyrosine kinase in peripheral T-cell lymphomas. Leukemia 22(6):1139–1143. doi:10.1038/leu.2008.77
Noraz N, Schwarz K, Steinberg M, Dardalhon V, Rebouissou C, Hipskind R, Friedrich W, Yssel H, Bacon K, Taylor N (2000) Alternative antigen receptor (TCR) signaling in T cells derived from ZAP-70-deficient patients expressing high levels of Syk. J Biol Chem 275(21):15832–15838. doi:10.1074/jbc.M908568199
Krishnan S, Juang YT, Chowdhury B, Magilavy A, Fisher CU, Nguyen H, Nambiar MP, Kyttaris V, Weinstein A, Bahjat R, Pine P, Rus V, Tsokos GC (2008) Differential expression and molecular associations of Syk in systemic lupus erythematosus T cells. J Immunol 181(11):8145–8152
Hauck F, Blumenthal B, Fuchs S, Lenoir C, Martin E, Speckmann C, Vraetz T, Mannhardt-Laakmann W, Lambert N, Gil M, Borte S, Audrain M, Schwarz K, Lim A, Schamel WW, Fischer A, Ehl S, Rensing-Ehl A, Picard C, Latour S (2015) SYK expression endows human ZAP70-deficient CD8 T cells with residual TCR signaling. Clin Immunol 161(2):103–109. doi:10.1016/j.clim.2015.07.002
Buchner M, Fuchs S, Prinz G, Pfeifer D, Bartholome K, Burger M, Chevalier N, Vallat L, Timmer J, Gribben JG, Jumaa H, Veelken H, Dierks C, Zirlik K (2009) Spleen tyrosine kinase is overexpressed and represents a potential therapeutic target in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Cancer Res 69(13):5424–5432. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-08-4252
Hallek M (2015) Chronic lymphocytic leukemia: 2015 Update on diagnosis, risk stratification, and treatment. Am J Hematol 90(5):446–460. doi:10.1002/ajh.23979
Mocsai A, Ruland J, Tybulewicz VL (2010) The SYK tyrosine kinase: a crucial player in diverse biological functions. Nat Rev Immunol 10(6):387–402. doi:10.1038/nri2765
Bojarczuk K, Siernicka M, Dwojak M, Bobrowicz M, Pyrzynska B, Gaj P, Karp M, Giannopoulos K, Efremov DG, Fauriat C, Golab J, Winiarska M (2014) B-cell receptor pathway inhibitors affect CD20 levels and impair antitumor activity of anti-CD20 monoclonal antibodies. Leukemia 28(5):1163–1167. doi:10.1038/leu.2014.12
Jain N, O’Brien S (2015) Targeted therapies for CLL: practical issues with the changing treatment paradigm. Blood Rev 30(3):233–244. doi:10.1016/j.blre.2015.12.002
Kohrt HE, Sagiv-Barfi I, Rafiq S, Herman SE, Butchar JP, Cheney C, Zhang X, Buggy JJ, Muthusamy N, Levy R, Johnson AJ, Byrd JC (2014) Ibrutinib antagonizes rituximab-dependent NK cell-mediated cytotoxicity. Blood 123(12):1957–1960. doi:10.1182/blood-2014-01-547869
Herman SE, Gordon AL, Wagner AJ, Heerema NA, Zhao W, Flynn JM, Jones J, Andritsos L, Puri KD, Lannutti BJ, Giese NA, Zhang X, Wei L, Byrd JC, Johnson AJ (2010) Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-delta inhibitor CAL-101 shows promising preclinical activity in chronic lymphocytic leukemia by antagonizing intrinsic and extrinsic cellular survival signals. Blood 116(12):2078–2088. doi:10.1182/blood-2010-02-271171
Ravandi F, O’Brien S (2006) Immune defects in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Cancer Immunol Immunother 55(2):197–209
Weinblatt ME, Kavanaugh A, Genovese MC, Musser TK, Grossbard EB, Magilavy DB (2010) An oral spleen tyrosine kinase (Syk) inhibitor for rheumatoid arthritis. N Engl J Med 363(14):1303–1312. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1000500
Barr PM, Saylors GB, Spurgeon SE, Cheson BD, Greenwald DR, O’Brien SM, Liem AK, Mclntyre RE, Joshi A, Abella-Dominicis E, Hawkins MJ, Reddy A, Di Paolo J, Lee H, He J, Hu J, Dreiling LK, Friedberg JW (2016) Phase 2 study of idelalisib and entospletinib: pneumonitis limits combination therapy in relapsed refractory CLL and NHL. Blood 127(20):2411–2415. doi:10.1182/blood-2015-12-683516
Okkenhaug K, Burger JA (2016) PI3 K Signaling in Normal B Cells and Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (CLL). Curr Top Microbiol Immunol 393:123–142. doi:10.1007/82_2015_484
Kiefer F, Brumell J, Al-Alawi N, Latour S, Cheng A, Veillette A, Grinstein S, Pawson T (1998) The Syk protein tyrosine kinase is essential for Fc gamma receptor signaling in macrophages and neutrophils. Mol Cell Biol 18(7):4209–4220
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by grants from Fondo para la Investigación Científica y Tecnológica (PICT 1074/2013 and PICT 1310/2012), Ministry of Science, Technology and Innovation, Argentina. We are indebted to Beatriz Loria, María Tejeda and Federico Fuentes for their technical assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Romina Gamberale had received compensation as speaker for Janssen and Bristol-Myers Squibb, as speaker and consultant for Roche, and as a member of the advisory board of AbbVie. Raimundo Fernando Bezares had received compensation as speaker from Novartis, Varifarma and Roche. All the other authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Colado, A., Almejún, M.B., Podaza, E. et al. The kinase inhibitors R406 and GS-9973 impair T cell functions and macrophage-mediated anti-tumor activity of rituximab in chronic lymphocytic leukemia patients. Cancer Immunol Immunother 66, 461–473 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00262-016-1946-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00262-016-1946-y