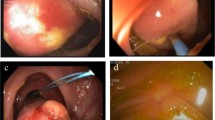
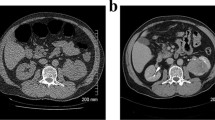
Abstract
Purpose
CT colonography (CTC) is growing in its utilization as a nationally approved colorectal cancer screening test. After colonic polyps, lipomas are the second most common colonic lesions and their accurate and rapid recognition are important.
Methods
This retrospective Institutional Review Board approved study was performed at two large academic university-based institutions. 1044 patients underwent CTC at Institution A from 2010 to 2018 and 1094 patients underwent CTC at Institution B from 2003 to 2015. All CTC examinations with at least one colonic lipoma in their report were evaluated by a fellowship-trained abdominal imaging radiologist. 47 CTC examinations containing 59 colonic lipomas were detected and included. Segmental location, sessile versus pedunculated morphology, multiplicity, average attenuation, and largest lesion diameter were evaluated. A review of the current literature on colonic lipomas is entailed.
Results
The overall incidence of colonic lipoma was 2.2% in women and 2.3% in men. Mean age for detection of colonic lipomas on CTC was 66.9 years. Segmental locations of colonic lipomas include ascending colon (39%), transverse colon (19%), ileocecal valve (12%), cecum (12%), descending colon (10%), and rectosigmoid (8%). 9% of colonic lipomas were multiple, 42% were pedunculated, and 58% were sessile. The mean (range) size of detected lipomas was 19 (6–59) mm. The mean (range) attenuation was − 132 (− 41 to − 258) HU.
Conclusion
Most colonic lipomas are located in the ascending colon. Although they are typically solitary, just under 10% are multiple, and although they are most often sessile, slightly under half are pedunculated mimicking polyps. CTC detects smaller lipomas than optical colonoscopy.
Graphical abstract





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Not applicable.
Code availability
Not applicable.
References
Bardaji, M., et al., Symptomatic colonic lipoma: differential diagnosis of large bowel tumors. International journal of colorectal disease, 1998. 13(1): p. 1-2.
Nallamothu, G. and D.G. Adler, Large colonic lipomas. Gastroenterology & hepatology, 2011. 7(7): p. 490.
Pickhardt, P.J., J. Yee, and C.D. Johnson, CT colonography: over two decades from discovery to practice. Abdominal Radiology, 2018. 43(3): p. 517-522.
USPSTF. Colorectal Cancer: Screening. 2021; Available from: https://www.uspreventiveservicestaskforce.org/uspstf/recommendation/colorectal-cancer-screening.
Rajapaksa, R.C., M. Macari, and E.J. Bini, Prevalence and impact of extracolonic findings in patients undergoing CT colonography. Journal of clinical gastroenterology, 2004. 38(9): p. 767-771.
Yee, J., et al., Extracolonic abnormalities discovered incidentally at CT colonography in a male population. Radiology, 2005. 236(2): p. 519-526.
Pooler, B.D., D.H. Kim, and P.J. Pickhardt, Extracolonic findings at screening CT colonography: prevalence, benefits, challenges, and opportunities. American Journal of Roentgenology, 2017. 209(1): p. 94-102.
Chang, K.J., et al., Fluid tagging for CT colonography: effectiveness of a 2-hour iodinated oral preparation after incomplete optical colonoscopy. Journal of Computer Assisted Tomography, 2011. 35(1): p. 91-95.
Yee, J., Virtual colonoscopy. 2008: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins.
Sapalidis, K., et al., Symptomatic colonic lipomas: report of two cases and a review of the literature. SAGE open medical case reports, 2019. 7: p. 2050313X19830477.
Singh, K., et al., Role of ct colonography in colonic lesions and its correlation with conventional colonoscopic findings. Journal of clinical and diagnostic research: JCDR, 2015. 9(4): p. TC14.
Chehade, H.H.E.H., et al., Large ileocecal submucosal lipoma presenting as hematochezia, a case report and review of literature. International journal of surgery case reports, 2015. 10: p. 1-4.
Dassanayake, S.U., N.P. Dinamithra, and N.M. Nawarathne, Submucosal lipoma of the sigmoid colon as a rare cause of mucoid diarrhea: a case report. Journal of medical case reports, 2016. 10(1): p. 1-3.
Geraci, G., et al., Endoscopic resection of a large colonic lipoma: case report and review of literature. Case reports in gastroenterology, 2010. 4(1): p. 6-11.
Peters Jr, M.B., et al., Laparoscopic management of colonic lipomas: a case report and review of the literature. JSLS: Journal of the Society of Laparoendoscopic Surgeons, 2005. 9(3): p. 342.
Barron, S.L. and R.S. Gonzalez, Clinicopathologic analysis and subclassification of benign lipomatous lesions of the colon. Virchows Archiv, 2019. 474(3): p. 309-313.
Kaltenbach, T., et al., Safe endoscopic treatment of large colonic lipomas using endoscopic looping technique. Digestive and Liver Disease, 2008. 40(12): p. 958-961.
Ivekovic, H., et al., Endoscopic ligation (“Loop-And-Let-Go”) is effective treatment for large colonic lipomas: a prospective validation study. BMC gastroenterology, 2014. 14(1): p. 1-4.
Mantzoros, I., et al., Colonic lipomas: our experience in diagnosis and treatment. Techniques in coloproctology, 2011. 15(1): p. 71-73.
Zhuang, Y., et al., Colonic intussusception caused by an ulcerating lipoma in an adult: A rare case report and literature review. 2018.
Younathan, C.M., P.R. Ros, and S.S. Burton, MR imaging of colonic lipoma. Journal of computer assisted tomography, 1991. 15(3): p. 492-494.
Martin, P., B. Sklow, and D.G. Adler, Large colonic lipoma mimicking colon cancer and causing colonic intussusception. Digestive diseases and sciences, 2008. 53(10): p. 2826-2827.
Cordeiro, J., et al., Intestinal intussusception related to colonic pedunculated lipoma: A case report and review of the literature. International journal of surgery case reports, 2019. 55: p. 206-209.
M’rabet, S., et al., Colonic intussusception caused by a sigmoidal lipoma: A case report. International journal of surgery case reports, 2018. 50: p. 1-4.
Law, Y.Y., et al., A case of colonic intussusception and obstruction secondary to giant colonic lipoma. Journal of Surgical Case Reports, 2020. 2020(10): p. rjaa429.
Moussally, M., et al., Splenic flexure colonic lipoma causing intussusception. JRSM Open, 2021. 12(1): p. 2054270420983088.
Iqbal, R. and P.W. Hamer, Spontaneous expulsion of a giant colonic lipoma. ANZ journal of surgery, 2020. 90(9): p. 1787-1788.
Vishwajeet, V., et al., Giant lipoma of descending colon masquerading as a colonic malignancy. BMJ Case Reports CP, 2021. 14(2): p. e237517.
Narindra, L.H.R.N.O., A. Ahmad, and J.N. Bruneton, Lipomas of the digestive tract: general aspects and imaging. Cureus, 2014. 6(9).
Liu, X., et al., Multiple gastrointestinal stromal tumors and lipomatosis. Archives of pathology & laboratory medicine, 2008. 132(11): p. 1825-1829.
Bilgic, Y., et al., Familial abdominal and intestinal lipomatosis presenting with upper GI bleeding. Case reports in gastrointestinal medicine, 2015. 2015.
Moussa, O.M., et al., Computerized tomography providing definitive diagnosis of colonic lipoma: A case series. Surgical Laparoscopy Endoscopy & Percutaneous Techniques, 2013. 23(6): p. e232-e234.
Mouaqit, O., et al., Pedunculated lipoma causing colo-colonic intussusception: a rare case report. BMC surgery, 2013. 13(1): p. 1-5.
Davis, S. and M. Yoong, Characteristic appearances of colonic lipomas on barium enema: a guide to conservative management. Australasian radiology, 1990. 34(2): p. 131-136.
Bronswijk, M., A.-M. Vandenbroucke, and P. Bossuyt, Endoscopic treatment of large symptomatic colon lipomas: a systematic review of efficacy and safety. United European Gastroenterology Journal, 2020. 8(10): p. 1147-1154.
Mummadi, R. and G.S. Raju, New endoscopic approaches to removing colonic lipomas. Gastroenterology & hepatology, 2007. 3(11): p. 882.
Ejtehadi, F., E. Mohammed, and V. Vijay, Laparoscopic assisted submucosal excision of an intussuscepting colonic lipoma. Journal of Surgical Case Reports, 2020. 2020(8): p. rjaa297.
Funding
Not applicable.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors actively participated in the study and reviewed the paper.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Shima Roknsharifi, Zina Ricci, Mariya Kobi, and Eugene Huo: None. Judy Yee: GE Healthcare, Philips.
Ethics approval
This study was approved by institutional review board (IRB) (IRB #2018-9582).
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Will consent.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Roknsharifi, S., Ricci, Z., Kobi, M. et al. Colonic lipomas revisited on CT colonography. Abdom Radiol 47, 1788–1797 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00261-022-03489-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00261-022-03489-2