Abstract
Purpose
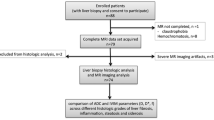
To evaluate the diagnostic accuracy of intravoxel incoherent motion (IVIM) model parameters for the diagnosis and staging of liver fibrosis and inflammation in patients with chronic hepatitis B.
Methods
Fifty-four patients with chronic hepatitis B and 42 healthy volunteers were included in the study. All subjects were examined by 3 T magnetic resonance imaging. Diffusion-weighted imaging was undertaken with sixteen b values. IVIM parameters [D (true diffusion coefficient), D* (pseudo-diffusion coefficient), f (perfusion fraction)] were calculated. Histological evaluation of biopsy samples was considered the reference standard for the staging of liver fibrosis and inflammation. Differences in IVIM parameters between patient and control groups were analyzed. In the patient group, fibrosis stage and inflammation grade groups were analyzed with respect to IVIM parameters. The correlation was assessed between IVIM parameters and Ishak-modified scale of fibrosis stages and inflammation grades.
Results
The D was significantly lower in the patient group than the control group, p = 0.038 with Cohen’s d effect size of 0.452. D was significantly different between fibrosis stage levels. D values decreased in fibrosis stages from the minimal to moderate to marked fibrosis. Fibrosis grades significantly negatively correlated with D and D* values, p = 0.001, and 0.021, respectively. In addition, inflammation grades negatively correlated with f values, p = 0.047.
Conclusion
D values measured with IVIM imaging may help to diagnose liver fibrosis. IVIM imaging could be an alternative to liver biopsy for the staging of liver fibrosis.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
. Gutierrez-Reyes G1, Gutierrez-Ruiz MC, Kershenobich D. Liver Fibrosis and Chronic Viral Hepatitis. Arch Med Res. 2007;38(6):644-51. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arcmed.2006.10.001.
Smith AD, Porter KK, Elkassem AA, Sanyal R, Lockhart ME. Current Imaging Techniques for Noninvasive Staging of Hepatic Fibrosis. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2019;11:1-13. https://doi.org/10.2214/ajr.19.21144.
Martinez SM, Foucher J, Combis JM, et al. Longitudinal liver stiffness assessment in patients with chronic hepatitis C undergoing antiviral therapy. PLoS One 2012;7:e47715. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0047715.
Shayesteh M, Shayesteh AA, Motamedfar A, Tahmasebi M, Bagheri S et al. The clinical value of the apparent diffusion coefficient of liver magnetic resonance images in patients with liver fibrosis compared to healthy subjects. J Family Med Prim Care. 2018;7(6):1501-1505.https://doi.org/10.4103/jfmpc.jfmpc_299_18.
Mallet V, Gilgenkrantz H, Serpaggi J, Verkarre V, Vallet-Pichard A, Fontaine H, et al. Brief communication: The relationship of regression of cirrhosis to outcome in chronic hepatitis C. Ann Intern Med 2008;149:399-403.
Dolman GE, Koffas A, Mason WS, Kennedy PT. Why, who and when to start treatment for chronic hepatitis B infection. Curr Opin Virol 2018; 30: 39-47 [PMID: 29655092 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.coviro.2018.03.006]
Tapper EB, Lok ASF. Use of Liver Imaging and Biopsy in Clinical Practice. N Engl J Med 2017; 377: 2296-2297 [PMID: 29211669 https://doi.org/10.1056/nejmc1712445]
Liaw, Y.F., Kao, J.H., Piratvisuth, T. et al. Asian-Pacific consensus statement on the management of chronic hepatitis B: a 2012 update. Hepatol Int. 2012; 6: 531–561.
Le Bihan D, Breton E, Lallemand D, Aubin M L, Vignaud J and Laval-Jeantet M. Separation of diffusion and perfusion in intravoxel incoherent motion MR imaging. Radiology. 1988; 168 497–505.
Liang J, Song X, Xiao Z, Chen H, Shi C, et al.Using IVIM-MRI and R2⁎ Mapping to Differentiate Early Stage Liver Fibrosis in a Rat Model of Radiation-Induced Liver Fibrosis. Biomed Res Int. 2018; 3;2018:4673814. https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/4673814. eCollection 2018.
Ishak K, Baptista A, Bianchi L, Callea F, De Groote J, Gudat F, et al. Histological grading and staging of chronic hepatitis. J Hepatol 1995;22: 696-699.
Li YT, Cercueil JP, Yuan J, Chen W, Loffroy R, Wang YX. Liver intravoxel incoherent motion (IVIM) magnetic resonance imaging: A comprehensive review of published data on normal values and applications for fibrosis and tumor evaluation. Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2017; 7:59–78.
Yoon JH, Lee JM, Baek JH, Shin CI, Kiefer B, et al. Evaluation of hepatic fibrosis using intravoxel incoherent motion in diffusion-weighted liver MRI. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 2014;38: 110–116. https://doi.org/10.1097/rct.0b013e3182a589be.
Li T, Che-Nordin N, Wáng YXJ, Rong PF, Qiu SW. Intravoxel incoherent motion derived liver perfusion/diffusion readouts can be reliable biomarker for the detection of viral hepatitis B induced liver fibrosis. Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2019;9(3):371-385. https://doi.org/10.21037/qims.2019.02.11.
Wu CH, Ho MC, Jeng YM, Liang PC, Hu RH, Lai HS, et al. Assessing hepatic fibrosis: comparing the intravoxel incoherent motion in MRI with acoustic radiation force impulse imaging in US. Eur Radiol. 2015; 25:3552–9. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-015-3774-4 PMID: 25991478.
Leporq B, Saint-Jalmes H, Rabrait C, Pilleul F, Guillaud O, Dumortier J, et al. Optimization of intra-voxel incoherent motion imaging at 3.0 Tesla for fast liver examination. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2015; 41: 1209–1217. https://doi.org/10.1002/jmri.24693 PMID: 25044653.
Jalnefjord O, Andersson M, Montelius M, Starck G, Elf AK, et al. Comparison of methods for estimation of the intravoxel incoherent motion (IVIM) diffusion coefficient (D) and perfusion fraction (f). MAGMA. 2018; 31(6):715-723. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10334-018-0697-5.
Tosun M, Inan N, Sarisoy HT, et al. (2013) Diagnostic performance of conventional diffusion weighted imaging and diffusion tensor imaging for the liver fibrosis and inflammation. Eur J Radiol. 2013;82:203–207. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejrad.2012.09.009
Chow AM, Gao DS, Fan SJ, Qiao Z, Lee FY, Yang J, Man K, Wu EX. Liver fibrosis: an intravoxel incoherent motion (IVIM) study. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2012; 36(1):159-67. https://doi.org/10.1002/jmri.23607.
Chevallier O, Zhou N, He J, Loffroy R, Wáng YX. Removal of evidential motion-contaminated and poorly fitted image data improves IVIM diffusion MRI parameter scan-rescan reproducibility. Acta Radiol. 2018; 59:1157-67.
Wáng YXJ, Deng M, Li YT, Huang H, Leung JCS et al. A Combined Use of Intravoxel Incoherent Motion MRI Parameters Can Differentiate Early-Stage Hepatitis-b Fibrotic Livers from Healthy Livers. SLAS Technol. 2018;23(3):259-268. https://doi.org/10.1177/2472630317717049.
Barbieri S, Donati OF, Froehlich JM, Thoeny HC. Impact of the calculation algorithm on biexponential fitting of diffusion-weighted MRI in upper abdominal organs. Magn Reson Med. 2016; 75:2175-84.
Park HJ, Sung YS, Lee SS, Lee Y, Cheong H,et al. Intravoxel incoherent motion diffusion-weighted MRI of the abdomen: The effect of fitting algorithms on the accuracy and reliability of the parameters. J Magn Reson Imaging 2017;45: 1637–1647.
Wáng YX, Li YT, Chevallier O, Huang H, Leung JCS, et al. Dependence of intravoxel incoherent motion diffusion MR threshold b-value selection for separating perfusion and diffusion compartments and liver fibrosis diagnostic performance. Acta Radiol. 2019; 60:3-12. https://doi.org/10.1177/0284185118774913.
Zhang Y, Jin N, Deng J, Guo Y, White SB, Yang GY, et al (2013). Intra-voxel incoherent motion MRI in rodent model of diethylnitrosamine-induced liver fibrosis. Magn Reson Imaging. 2013; 31: 1017–1021. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mri.2013.03.007 PMID: 23598061.
Lee EY, Yu X, Chu MM, Ngan HY, Siu SW, Soong IS, et al. Perfusion and diffusion characteristics of cervical cancer based on intraxovel incoherent motion MR imaging-a pilot study. Eur Radiol .2014; 24:1506–1513. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-014-3160-7 PMID: 24744198.
Andreou A, Koh DM, Collins DJ,Blackledge M, Wallace T, et al. Measurement reproducibility of perfusion fraction and pseudodiffusion coefficient derived by intravoxel incoherent motion diffusion-weighted MR imaging in normal liver and metastases. Eur Radiol. 2013; 23:428–434. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-012-2604-1.
Kakite S, Dyvorne, HA, Besa C,Cooper N, Facciuto M, et al. Hepatocellular carcinoma: short-term reproducibility of apparent diffusion coefficient and intravoxel incoherent motion parameters at 3.0T. J Magn Reson imaging. 2015; 41:149–156.https://doi.org/10.1002/jmri.24538.
ter Voert EE, Delso G, Porto M, Huellner M, VeitHaibach P. Intravoxel Incoherent Motion Protocol Evaluation and Data Quality in Normal and Malignant Liver Tissue and Comparison to the Literature. Invest Radiol. 2016; 51:90-9.
Yamada I, Aung W, Himeno Y, Nakagawa T, Shibuya H. Diffusion coefficients in abdominal organs and hepatic lesions: evaluation with intravoxel incoherent motion echo-planar MR imaging. Radiology. 1999;210(3):617-23.
Moteki T, Horikoshi H. Evaluation of hepatic lesions and hepatic parenchyma using diffusion-weighted echo-planar MR with three values of gradient b-factor. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2006; 24(3):637-45.
Jing Zhang, Yihao Guo, Xiangliang Tan, Zeyu Zheng, Mengqi He.MRI-based Estimation of Liver Function by Intravoxel Incoherent Motion Diffusion-weighted Imaging.Magn Reson Imaging. 2016; 34(8):1220-5. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mri.2016.05.013.
Anderson SW, Jara H, Ozonoff A, O’Brien M, Hamilton JA,et al. Effect of disease progression on liver apparent diffusion coefficient and T2 values in a murine model of hepatic fibrosis at 11.7 Tesla MRI, J. Magn. Reson. Imaging. 2012;35(1): 140–146. https://doi.org/10.1002/jmri.22807.
Lu PX, Huang H, Yuan J, et al. (2014) Decreases in molecular diffusion, perfusion fraction and perfusion-related diffusion in fibrotic livers: a prospective clinical intravoxel incoherent motion MR imaging study. PLoS ONE 9:e113846.
Hu F, Yang R, Huang Z, Wang M, Zhang H, et al. Liver fibrosis: in vivo evaluation using intravoxel incoherent motion-derived histogram metrics with histopathologic findings at 3.0 T. Abdom Radiol (NY). 2017 Dec;42(12):2855-2863. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00261-017-1208-2.
França M, Martí-Bonmatí L, Alberich-Bayarri Á, Oliveira P, Guimaraes S, et al. Evaluation of fibrosis and inflammation in diffuse liver diseases using intravoxel incoherent motion diffusion-weighted MR imaging. Abdom Radiol (NY). 2017; 42 (2):468-477. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00261-016-0899-0.
Maksan SM1, Ryschich E, Ulger Z, Gebhard MM, Schmidt J. Disturbance of hepatic and intestinal microcirculation in experimental liver cirrhosis. World J Gastroenterol. 2005;14;11(6):846–849.
Dyvorne HA1, Galea N, Nevers T, Fiel MI, Carpenter D, et al. Diffusion-weighted imaging of the liver with multiple b values: effect of diffusion gradient polarity and breathing acquisition on image quality and intravoxel incoherent motion parameters-A pilot study. Radiology. 2013; 266(3):920-9. https://doi.org/10.1148/radiol.12120686.
Wang QB, Zhu H, Liu HL, Zhang B. Performance of magnetic resonance elastography and diffusion-weighted imaging for the staging of hepatic fibrosis: A meta-analysis. Hepatology. 2012; 56:239–247.
Ghany MG, Strader DB, Thomas DL, Seeff LB. Diagnosis, management, and treatment of hepatitis C: an update. Hepatology. 2009; 49:1335–1374.
Yoon JH, Lee JM, Yu MH, Kiefer B, Han JK, et al. Evaluation of hepatic focal lesions using diffusion-weighted MR imaging: comparison of apparent diffusion coefficient and intravoxel incoherent motion-derived parameters. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging. 2014; 39:276–285.
Cui Y, Dyvorne H, Besa C, Cooper N, Taouli B. IVIM Diffusion-weighted Imaging of the Liver at 3.0T: Comparison with 1.5T. Eur J Radiol Open. 2015;2:123-128.
Zhu J, Zhang J, Gao J, Li JN, Yang DW, et al. Apparent diffusion coefficient normalization of normal liver: Will it improve the reproducibility of diffusion-weighted imaging at different MR scanners as a new biomarker? Medicine (Baltimore). 2017; 96:3: e5910. https://doi.org/10.1097/md.0000000000005910.
Jiang H, Chen J, Gao R, Huang Z, Wu M, et al.Liver fibrosis staging with diffusion-weighted imaging: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Abdom Radiol (NY). 2017; 42(2):490-501. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00261-016-0913-6.
Lemke A, Stieltjes B, Schad LR, Laun FB. Toward an optimal distribution of b values for intravoxel incoherent motion imaging. J Magn Reson Imaging.2011; 29:766–776.
Ichikawa S, Motosugi U, Morisaka H, Sano K, Ichikawa T, Enomoto N, et al. MRI-Based Staging of Hepatic Fibrosis: Comparison of Intravoxel Incoherent Motion Difusion-Weighted Imaging with Magnetic Resonance Elastography. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2015;42(1):204-210. https://doi.org/10.1002/jmri.24760.
Yoon JH, Lee JM, Joo I, Lee ES, Sohn JY, Jang SK, et al. (2014) Hepatic Fibrosis: Prospective Comparison of MR Elastography and US Shear-Wave Elastography for Evaluation. Radiology 2014;273(3):772-782. https://doi.org/10.1148/radiol.14132000.
Chen J, Talwalkar JA, Yin M, Glaser KJ, Sanderson SO, Ehman RL. Early detection of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease by using MR elastography. Radiology 2011; 259:749–756.
Funding
The authors declared that this study has received no financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
MT: concept, acquisition of data, literature review, manuscript draft, revision, final approval. TO: acquisition of data, data analysis, literature review, manuscript draft, editing, final approval. HU: acquisition of data, literature review, final approval. BA: acquisition of data, literature review, final approval. SA: clinical care of patients, literature review, final approval.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
No conflict of interest was declared by the authors.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tosun, M., Onal, T., Uslu, H. et al. Intravoxel incoherent motion imaging for diagnosing and staging the liver fibrosis and inflammation. Abdom Radiol 45, 15–23 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00261-019-02300-z
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00261-019-02300-z