Abstract
Purpose
To compare the technical success and accuracy of hepatic microwave ablation (MWA) using non-enhanced and enhanced T1-weighted imaging early after ablation. Patients were evaluated with regard to the ablation zone and local tumor progression (LTP).
Methods
This retrospective study conducted between September 2014 and December 2015 which consisted of 56 patients with 56 hepatic malignant lesions who underwent percutaneous MWA. Non-enhanced and contrast-enhanced T1-weighted imagings were performed within 2 days after tumor ablation. The efficacy of ablation assessed according to the hyperintense middle zone on non-enhanced T1-weighted images and the non-enhanced area on contrast-enhanced T1-weighted images were compared. The development of LTP during ≥7 months of follow-up served as the end point.
Results
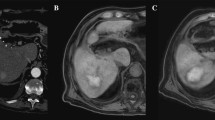
On the non-enhanced T1-weighted images, the ablated region had a characteristic two-zone structure featuring a hyperintense middle zone and a surrounding hypointense band. Among the 56 patients, LTP developed in ten including seven lesions, in which both the non-enhanced T1-weighted and portal-phase images showed incomplete tumor ablation. In two of the remaining three patients, incomplete tumor ablation was detected on the non-enhanced T1-weighted images, whereas the corresponding portal-phase images showed complete ablation. In the remaining patient, no residual tumor was detected on either the non-enhanced T1-weighted or the portal-phase images. In the 46 patients without LTP, there was no evidence of residual tumor on the non-enhanced T1-weighted or portal-phase images obtained early after ablation.
Conclusions
Non-enhanced T1-weighted images are useful in assessing the therapeutic efficacy of MWA of liver tumors early after the procedure.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jiao DC, Zhou Q, Han XW, et al. (2012) Microwave ablation treatment of liver cancer with a 2,450-MHz cooled-shaft antenna: pilot study on safety and efficacy. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev 13:737–742
Liang P, Dong B, Yu X, et al. (2005) Prognostic factors for survival in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma after percutaneous microwave ablation. Radiology 235:299–307
Onishi H, Matsushita M, Murakami T, et al. (2004) MR appearances of radiofrequency thermal ablation region: histopathologic correlation with dog liver models and an autopsy case. Acad Radiol 11:1180–1189
Khankan AA, Murakami T, Onishi H, et al. (2008) Hepatocellular carcinoma treated with radio frequency ablation: an early evaluation with magnetic resonance imaging. J Magn Reson Imaging 27:546–551
Tsuda M, Rikimaru H, Majima K, et al. (2003) Time-related changes of radiofrequency ablation lesion in the normal rabbit liver: findings of magnetic resonance imaging and histopathology. Invest Radiol 38:525–531
Granata V, M Petrillo, R Fusco, et al. (2013) Surveillance of HCC patients after liver RFA: role of MRI with hepatospecific contrast versus three-phase CT scan-experience of High Volume Oncologic Institute. Gastroenterol Res Pract, 469097
Mcghana JP, Dodd GD 3rd (2001) Radiofrequency ablation of the liver: current status. Am J Roentgenol 176:3–16
Koda M, Tokunaga S, Miyoshi K, et al. (2012) Assessment of ablative margin by unenhanced magnetic resonance imaging after radiofrequency ablation for hepatocellular carcinoma. Eur J Radiol 81:2730–2736
Hyodoh H, Hyodoh K, Takahashi K, et al. (1998) Microwave coagulation therapy on hepatomas: CT and MR appearance after therapy. J Magn Reson Imaging 8:451–458
Matsuo Murata KR, Manabe T, et al. (1996) MR imaging of hepatocellular carcinoma following microwave coagulation therapy. Nihon Igaku Hoshasen Gakkai Zasshi 56:940–947
Hoffmann R, H Rempp, DE Kessler, et al. (2016) MR-guided microwave ablation in hepatic tumours: initial results in clinical routine. Eur Radiol
Ringe KI, Wacker F, Raatschen HJ (2015) Is there a need for MRI within 24 hours after CT-guided percutaneous thermoablation of the liver? Acta Radiol 56:10–17
Rossi S, Buscarini E, Garbagnati F, et al. (1998) Percutaneous treatment of small hepatic tumors by an expandable RF needle electrode. Am J Roentgenol 170:1015–1022
Lim HK, Han JK (2002) Hepatocellular carcinoma: evaluation of therapeutic response to interventional procedures. Abdom Imaging 27:168–179
Lazebnik RS, Weinberg BD, Breen MS, Lewin JS, Wilson DL (2003) Sub-acute changes in lesion conspicuity and geometry following MR-guided radiofrequency ablation. J Magn Reson Imaging 18:353–359
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Funding
No funding was received for this study.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
Statement of informed consent was not applicable since the manuscript does not contain any patient data.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jia, ZY., Chen, QF., Yang, ZQ. et al. Early assessment of coagulation necrosis after hepatic microwave ablation: a comparison of non-enhanced and enhanced T1-weighted images. Abdom Radiol 42, 1781–1787 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00261-017-1064-0
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00261-017-1064-0