Abstract
Purpose
Fibroblast activation protein (FAP) is a pan-cancer target and now the state-of-the-art to develop radiopharmaceuticals. FAP inhibitors have been of great success in developing imaging tracers. Yet, the overly rapid clearance cannot match with the long half-lives of regular therapeutic radionuclides. Though strategies that aim to elongate the circulation of FAPIs are being developed, here we describe an innovation that uses α-emitters of short half-lives (e.g., 213Bi) to pair the rapid pharmacokinetics of FAPIs.
Methods
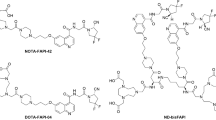
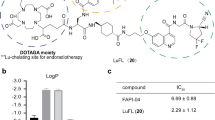
An organotrifluoroborate linker is engineered to FAPIs to give two advantages: (1) selectively increases tumor uptake and retention; (2) facile 18F-radiolabeling for positron emission tomography to guide radiotherapy with α-emitters, which can hardly be traced in general.
Results
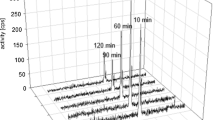
The organotrifluoroborate linker helps to improve the internalization in cancer cells, resulting in notably higher tumor uptake while the background is clean. In FAP-expressed tumor-bearing mice, this FAPI labeled with 213Bi, a short half-life α-emitter, exhibits almost complete suppression to tumor growth while the side effect is negligible. Additional data shows that this strategy is generally applicable to guide other α-emitters, such as 212Bi, 212Pb, and 149Tb.
Conclusion
The organotrifluoroborate linker may be of importance to optimize FAP-targeted radiopharmaceuticals, and the short half-lived α-emitters may be of choice for the rapid-cleared small molecule-based radiopharmaceuticals.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Gill MR, Falzone N, Du Y, Vallis KA. Targeted radionuclide therapy in combined-modality regimens. Lancet Oncol. 2017;18:e414–23.
Sartor O, de Bono J, Chi KN, et al. Lutetium-177-PSMA-617 for metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer. N Engl J Med. 2021;385:1091–103.
Gafita A, Calais J, Grogan TR, et al. Nomograms to predict outcomes after 177Lu-PSMA therapy in men with metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer: an international, multicentre, retrospective study. Lancet Oncol. 2021;22:1115–25.
Langbein T, Weber WA, Eiber M. Future of theranostics: an outlook on precision oncology in nuclear medicine. J Nucl Med. 2019;60:13S-19S.
de Swart J, Chan HS, Goorden MC, et al. Utilizing high-energy γ-photons for high-resolution 213Bi SPECT in mice. J Nucl Med. 2016;57:486–92.
Kratochwil C, Flechsig P, Lindner T, et al. (68)Ga-FAPI PET/CT: tracer uptake in 28 different kinds of cancer. J Nucl Med. 2019;60:801–5.
Wei Y, Zheng J, Ma L, et al. [18F]AlF-NOTA-FAPI-04: FAP-targeting specificity, biodistribution, and PET/CT imaging of various cancers. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2022;49:2761–73.
Loktev A, Lindner T, Burger EM, et al. Development of fibroblast activation protein-targeted radiotracers with improved tumor retention. J Nucl Med. 2019;60:1421–9.
Loktev A, Lindner T, Mier W, et al. A tumor-imaging method targeting cancer-associated fibroblasts. J Nucl Med. 2018;59:1423–9.
Lindner T, Loktev A, Altmann A, et al. Development of quinoline-based theranostic ligands for the targeting of fibroblast activation protein. J Nucl Med. 2018;59:1415–22.
Liu Y, Watabe T, Kaneda-Nakashima K, et al. Fibroblast activation protein targeted therapy using [177Lu]FAPI-46 compared with [225Ac]FAPI-46 in a pancreatic cancer model. Euro J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2022;49:871–80.
Watabe T, Liu Y, Kaneda-Nakashima K, et al. Theranostics targeting fibroblast activation protein in the tumor stroma: 64Cu- and 225Ac-Labeled FAPI-04 in pancreatic cancer xenograft mouse models. J Nucl Med. 2020;61:563–9.
Ahenkorah S, Cassells I, Deroose CM, et al. Bismuth-213 for targeted radionuclide therapy: from atom to bedside. Pharmaceutics. 2021;13:599.
Altmann A, Haberkorn U, Siveke J. The latest developments in imaging of fibroblast activation protein. J Nucl Med. 2021;62:160–7.
Kratochwil C, Giesel FL, Rathke H, et al. [153Sm]Samarium-labeled FAPI-46 radioligand therapy in a patient with lung metastases of a sarcoma. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2021;48:3011–3.
Liu Z, Pourghiasian M, Radtke MA, et al. An organotrifluoroborate for broadly applicable one-step 18F-labeling. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2014;53:11876–80.
Liu Z, Lin KS, Benard F, et al. One-step 18F labeling of biomolecules using organotrifluoroborates. Nat Protoc. 2015;10:1423–32.
Xu M, Zhang P, Ding J, Chen J, Huo L, Liu Z. Albumin binder-conjugated fibroblast activation protein inhibitor radiopharmaceuticals for cancer therapy. J Nucl Med. 2022;63:952–8.
Morgenstern A, Apostolidis C, Bruchertseifer F. Supply and clinical application of Actinium-225 and Bismuth-213. Semin Nucl Med. 2020;50:119–23.
Kuyumcu S, Kovan B, Sanli Y, et al. Safety of fibroblast activation protein-targeted radionuclide therapy by a low-dose dosimetric approach using 177Lu-FAPI04. Clin Nucl Med. 2021;46:641–6.
Price EW, Orvig C. Matching chelators to radiometals for radiopharmaceuticals. Chem Soc Rev. 2014;43:260–90.
Wurzer A, Di Carlo D, Schmidt A, et al. Radiohybrid ligands: a novel tracer concept exemplified by 18F- or 68Ga-labeled rhPSMA inhibitors. J Nucl Med. 2020;61:735–42.
Rohrich M, Loktev A, Wefers AK, et al. IDH-wildtype glioblastomas and grade III/IV IDH-mutant gliomas show elevated tracer uptake in fibroblast activation protein-specific PET/CT. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2019;46:2569–80.
Meyer C, Dahlbom M, Lindner T, et al. Radiation dosimetry and biodistribution of 68Ga-FAPI-46 PET imaging in cancer patients. J Nucl Med. 2020;61:1171–7.
Ferdinandus J, Fragoso Costa P, Kessler L, et al. Initial clinical experience with 90Y-FAPI-46 radioligand therapy for advanced stage solid tumors: a case series of nine patients. J Nucl Med. 2022;63:727–34.
Jung HJ, Nam EH, Park JY, Ghosh P, Kim IS. Identification of BR102910 as a selective fibroblast activation protein (FAP) inhibitor. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2021;37:127846.
Younis MH, Malih S, Lan X, Rasaee MJ, Cai W. Enhancing fibroblast activation protein (FAP)-targeted radionuclide therapy with albumin binding, and beyond. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2022;49:1773–7.
Hasan M. Fundamentals of radiation oncology, 3rd ed. Academic Press; 2019. p. 57–87. https://doi.org/10.1016/C2018-0-04417-5
Thomas IK, Chris O. Radioactive main group and rare earth metals for imaging and therapy. Chem Rev. 2019;119:902–56.
Dolgin E. Drugmakers go nuclear, continuing push into radiopharmaceuticals. Nat Biotechnol. 2021;39:647–9.
Kratochwil C, Schmidt K, Afshar-Oromieh A, et al. Targeted alpha therapy of mCRPC: dosimetry estimate of 213Bismuth-PSMA-617. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2018;45:31–7.
Chappell LL, Dadachova E, Milenic DE, Garmestani K, Wu C, Brechbiel MW. Synthesis, characterization, and evaluation of a novel bifunctional chelating agent for the lead isotopes 203Pb and 212Pb. Nucl Med Biol. 2000;27:93–100.
Acknowledgements
We acknowledge the facility support from the Analytical Instrumentation Center of Peking University.
Funding
We gratefully acknowledge the Beijing Municipal Natural Science Foundation (Grant No. Z200018), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. U1867209), the Ministry of Science and Technology of the People’s Republic of China (Grant Nos. 2021YFA1601400 and 2017YFA0506300), the Special Foundation of Beijing Municipal Education Commission (Grant No. 3500–12020123), and the Li Ge-Zhao Ning Life Science Youth Research Foundation (LGZNQN202004) to Z.L.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Y.L. participated in all the experiments. H.T. and T.S. assisted in cell and animal experiments. M.X. and J.C. provided radionuclides and guided the radiolabeling. Y.L. and XY.C. wrote the manuscipt. Y.H. and Z.L. helped analyze the experimental data. Z.L. designed the study and revised the manuscipt. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.”
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
The ethics approval was granted by the Ethics Committee of Peking University (CCME-LiuZB-2).
Competing interests
The authors declare competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
This article is part of the Topical Collection on Theragnostic.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, Y., Tang, H., Song, T. et al. Organotrifluoroborate enhances tumor targeting of fibroblast activation protein inhibitors for targeted radionuclide therapy. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 50, 2636–2646 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00259-023-06230-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00259-023-06230-3