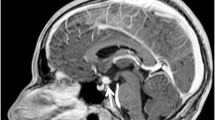
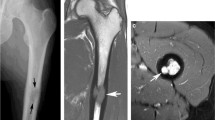
Abstract
This is, to our knowledge, the first case report with in-depth analysis of bone marrow and bone lesions with diffusion-weighted imaging and dynamic contrast-enhanced MRI in Erdheim-Chester disease to date. We present a case of a 70-year-old woman who was referred for an X-ray of the pelvis, right femur and right knee after complaints of migratory arthralgia in hip and knee five months after an initial hip and knee trauma. Bone lesions on X-ray were identified. This case report highlights the strength and complementary use of modern multimodality multiparametric imaging techniques in the clinical radiological manifestations of Erdheim-Chester disease, in the differential diagnosis and in treatment response assessment, which is classically performed using 18FDG PET-CT. Erdheim-Chester disease is a rare form of non-Langerhans’ cell histiocytosis, mainly affecting individuals in their fifth-seventh decade of life and without sex predominance. Apart from the typical bilateral symmetric lesions in long bone diaphyseal and metaphyseal regions and classically sparing the epiphyses, this multisystemic disease causes significant morbidity by infiltrating critical organs (the central nervous system, cardiovascular system, retroperitoneum, lungs and skin). With non-traumatic bone pain being the most common complaint, Erdheim-Chester disease is diagnosed most often in an incidental setting on imaging. The imaging workup classically consists of a multimodality approach using conventional radiography, CT, MRI, bone scintigraphy and 18FDG PET-CT. This case report extends this evaluation with diffusion-weighted imaging and dynamic contrast-enhanced imaging techniques.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Data (imaging and anonimyzed patient information from the electronic patient record) can be obtained at the data protection officer’s office of the data provider (Ghent University Hospital, Ghent, Corneel Heymanslaan 10, 9000 Ghent, Belgium), in close collaboration with the Institutional Ethical Review Board.
References
Haroche J, Cohen-Aubart F, Amoura Z. Erdheim-Chester disease. Blood. 2020;135(16):1311–8.
Mazor RD, Manevich-Mazor M, Shoenfeld Y. Erdheim-Chester disease: a comprehensive review of the literature. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2013;8:137.
Goyal G, Heaney ML, Collin M, et al. Erdheim-Chester disease: consensus recommendations for evaluation, diagnosis, and treatment in the molecular era. Blood. 2020;135(22):1929–45.
Diamond EL, Dagna L, Hyman DM, et al. Consensus guidelines for the diagnosis and clinical management of Erdheim-Chester disease. Blood. 2014;124(4):483–92.
Abdelfattah AM, Arnaout K, Tabbara IA. Erdheim-Chester disease: a comprehensive review. Anticancer Res. 2014;34(7):3257–61.
Haroche J, Charlotte F, Arnaud L, et al. High prevalence of BRAF V600E mutations in Erdheim-Chester disease but not in other non-Langerhans cell histiocytoses. Blood. 2012;120(13):2700–3.
Dutoit JC, Claus E, Offner F, Noens L, Delanghe J, Verstraete KL. Combined evaluation of conventional MRI, dynamic contrast-enhanced MRI and diffusion weighted imaging for response evaluation of patients with multiple myeloma. Eur J Radiol. 2016;85(2):373–82.
Dutoit JC, Verstraete KL. Whole-body MRI, dynamic contrast-enhanced MRI, and diffusion-weighted imaging for the staging of multiple myeloma. Skeletal Radiol. 2017;46(6):733–50.
Van Den Berghe T, Verstraete KL, Lecouvet FE, Lejoly M, Dutoit J. Review of diffusion-weighted imaging and dynamic contrast-enhanced MRI for multiple myeloma and its precursors (monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance and smouldering myeloma). Skeletal Radiol. 2022;51(1):101–22.
Joshua DE, Bryant C, Dix C, Gibson J, Ho J. Biology and therapy of multiple myeloma. Med J Aust. 2019;210(8):375–80.
Starkebaum G, Hendrie P. Erdheim-Chester disease. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol. 2020;34(4):101510.
Garg N, Lavi ES. Clinical and neuroimaging manifestations of Erdheim-Chester disease: a review. J Neuroimaging. 2021;31(1):35–44.
Cives M, Simone V, Rizzo FM, et al. Erdheim-Chester disease: a systematic review. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2015;95(1):1–11.
Knitza J, Kampylafka E, Wacker J, Schett G, Manger B. Erdheim-Chester disease: an important differential diagnosis and its main symptoms. Z Rheumatol. 2019;78(1):66–71.
Campochiaro C, Tomelleri A, Cavalli G, Berti A, Dagna L. Erdheim-Chester disease. Eur J Intern Med. 2015;26(4):223–9.
Munoz J, Janku F, Cohen PR, Kurzrock R. Erdheim-Chester disease: characteristics and management. Mayo Clin Proc. 2014;89(7):985–96.
Antunes C, Graça B, Donato P. Thoracic, abdominal and musculoskeletal involvement in Erdheim-Chester disease: CT, MR and PET imaging findings. Insights Imaging. 2014;5(4):473–82.
Haroche J, Papo M, Cohen-Aubart F, et al. Erdheim-Chester disease (ECD), an inflammatory myeloid neoplasia. Presse Med. 2017;46(1):96–106.
Choraria A, Andrei V, Rajakulasingam R, Saifuddin A. Musculoskeletal imaging features of non-Langerhans cell histiocytoses. Skeletal Radiol. 2021;50(10):1921–40.
Wang F, Cao X, Niu N, et al. Multisystemic imaging findings in Chinese patients with Erdheim-Chester disease. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2019;213(6):1179–86.
Kumar P, Singh A, Gamanagatti S, Kumar S, Chandrashekhara SH. Imaging findings in Erdheim-Chester disease: what every radiologist needs to know. Pol J Radiol. 2018;83:e54–62.
Moulis G, Sailler L, Bonneville F, Wagner T. Imaging in Erdheim-Chester disease: classic features and new insights. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2014;32(3):410–4.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in the study involving human participants are in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from the subject described in this report.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Van Den Berghe, T., Candries, E., Everaert, N. et al. Erdheim-Chester disease: diffusion-weighted imaging and dynamic contrast-enhanced MRI provide useful information. Skeletal Radiol 52, 1605–1618 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00256-022-04265-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00256-022-04265-5