Abstract
Introduction
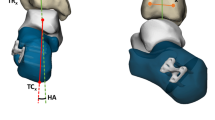
Pes planus is a common three-dimensional (3D) deformity characterised by forefoot abduction, the collapse of the medial longitudinal arch, and hindfoot valgus. Several radiological measurements such as anteroposterior talocalcaneal angle (Kite’s) and ‘Calcaneal pitch angle’ (CPA) exist to calculate the degree of hindfoot alignment in these patients with variable intra- and interobserver reliability.
Objective
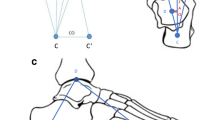
To describe a new radiological ancillary method of measuring hindfoot alignment, the calcaneal offset index (COI).
Material and Methods
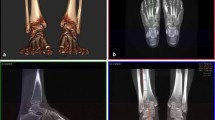
Anteroposterior (mortise) and lateral view weight-bearing (WB) ankle radiographs of 200 consecutive patients referred for foot and ankle pain were reviewed. Demographic details, clinical indication, and COI calculation were undertaken on the mortise view along with the measurement of CPA for each patient. A one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) was performed. Intraclass correlation coefficient (ICC) analysis was evaluated to assess the intraclass reliability between observers.
Results
There was a female preponderance of 2:1 in the study population with a mean age of 51.21 years (13–86 years). The calcaneal offset was increased in pes planus (hindfoot valgus). The p-value was 0.00023 on ANOVA. The COI gave an excellent interobserver correlation with ICC of 0.9 and moderate intraobserver reliability on the ICC analysis of 0.55.
Conclusion
The COI can be an additional index of measuring hindfoot alignment in patients with pes planus. Contrary to the traditional angular measurements, this linear transverse plane measure is easier to calculate and reproducible. COI measurement has shown moderate intraobserver reliability but excellent interobserver reliability.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Michaudet C, Edenfield KM, Nicolette GW, Carek PJ. Foot and ankle conditions: pes planus. FP Essent. 2018;465:18–23.
Deland JT. Adult-acquired flatfoot deformity. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2008;16(7):399–406. https://doi.org/10.5435/00124635-200807000-00005.
Smyth NA, Aiyer AA, Kaplan JR, Carmody CA, Kadakia AR. Adult-acquired flatfoot deformity. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2017;27(4):433–9. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00590-017-1945-5.
Ling SK, Lui TH. Posterior tibial tendon dysfunction: an overview. Open Orthop J. 2017;31(11):714–23. https://doi.org/10.2174/1874325001711010714.
Abousayed MM, Alley MC, Shakked R, Rosenbaum AJ. Adult-acquired flatfoot deformity: etiology, diagnosis, and management. JBJS Rev. 2017;5(8): e7. https://doi.org/10.2106/JBJS.RVW.16.00116.
Abousayed MM, Tartaglione JP, Rosenbaum AJ, Dipreta JA. Classifications in brief: Johnson and Strom classification of adult-acquired flatfoot deformity. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2016;474(2):588–93. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11999-015-4581-6.
Yoshioka N, Ikoma K, Kido M, Imai K, Maki M, Arai Y, Fujiwara H, Tokunaga D, Inoue N, Kubo T. Weight-bearing three-dimensional computed tomography analysis of the forefoot in patients with flatfoot deformity. J Orthop Sci. 2016;21(2):154–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jos.2015.12.001.
Flores DV, Mejía Gómez C, Fernández Hernando M, Davis MA, Pathria MN. Adult Acquired flatfoot deformity: anatomy, biomechanics, staging, and imaging findings. Radiographics. 2019;39(5):1437–60. https://doi.org/10.1148/rg.2019190046.
Strash WW, Berardo P. Radiographic assessment of the hindfoot and ankle. Clin Podiatr Med Surg. 2004;21(3):295–304. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cpm.2004.03.004.
Thomas JL, Kunkel MW, Lopez R, Sparks D. Radiographic values of the adult foot in a standardized population. J Foot Ankle Surg. 2006;45(1):3–12. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.jfas.2005.10.014.
Lamm BM, Stasko PA, Gesheff MG, Bhave A. Normal foot and ankle radiographic angles, measurements, and reference points. J Foot Ankle Surg. 2016;55(5):991–8. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.jfas.2016.05.005.
Donovan A, Rosenberg ZS. Extraarticular lateral hindfoot impingement with posterior tibial tendon tear: MRI correlation. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2009;193(3):672–8. https://doi.org/10.2214/AJR.08.2215.
Reilingh ML, Beimers L, Tuijthof GJ, Stufkens SA, Maas M, van Dijk CN. Measuring hindfoot alignment radiographically: the long axial view is more reliable than the hindfoot alignment view. Skeletal Radiol. 2010;39(11):1103–8. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00256-009-0857-9.
Sensiba PR, Coffey MJ, Williams NE, Mariscalco M, Laughlin RT. Inter- and intraobserver reliability in the radiographic evaluation of adult flatfoot deformity. Foot Ankle Int. 2010;31(2):141–5. https://doi.org/10.3113/FAI.2010.0141.
Arunakul M, Amendola A, Gao Y, Goetz JE, Femino JE, Phisitkul P. Tripod index: a new radiographic parameter assessing foot alignment. Foot Ankle Int. 2013;34(10):1411–20. https://doi.org/10.1177/1071100713488761.
Pilania K, Jankharia B, Monoot P. Role of the weight-bearing cone-beam CT in evaluation of flatfoot deformity. Indian J Radiol Imaging. 2019;29(4):364–71. https://doi.org/10.4103/ijri.IJRI_288_19.
Ohuchi H, Chavez JS, Alvarez CAD. Changes in calcaneal pitch and heel fat pad thickness in static weight bearing radiographs while wearing shoes with arch support and heel cup orthotics. Asia Pac J Sports Med Arthrosc Rehabil Technol. 2019;31(17):21–4. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asmart.2019.07.001.
Kaschak TJ, Laine W. Surgical radiology. Clin Podiatr Med Surg. 1988;5(4):797–829.
Koo TK, Li MY. A guideline of selecting and reporting intraclass correlation coefficients for reliability research. J Chiropr Med. 2016;15(2):155–63. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcm.2016.02.012 (Erratum in: J Chiropr Med. 2017 Dec;16(4):346).
Yalçin N, Esen E, Kanatli U, Yetkin H. Evaluation of the medial longitudinal arch: a comparison between the dynamic pressure measurement system and radiographic analysis. Acta Orthop Traumatol Turc. 2010;44(3):241–5. https://doi.org/10.3944/AOTT.2010.2233.
Saltzman CL, El-Khoury GY. The hindfoot alignment view. Foot Ankle Int. 1995;16(9):572–6. https://doi.org/10.1177/107110079501600911.
Choi JY, Lee HI, Kim JH, Suh JS. Radiographic measurements on hindfoot alignment view in 1128 asymptomatic subjects. Foot Ankle Surg. 2021;27(4):366–70. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fas.2020.04.010.
de Cesar Netto C, Kunas GC, Soukup D, Marinescu A, Ellis SJ. Correlation of clinical evaluation and radiographic hindfoot alignment in stage ii adult-acquired flatfoot deformity. Foot Ankle Int. 2018;39(7):771–9. https://doi.org/10.1177/1071100718762113.
de Cesar Netto C, Shakoor D, Roberts L, Chinanuvathana A, Mousavian A, Lintz F, Schon LC, Demehri S, Weight Bearing CT International Study Group. Hindfoot alignment of adult acquired flatfoot deformity: a comparison of clinical assessment and weightbearing cone beam CT examinations. Foot Ankle Surg. 2019;25(6):790–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fas.2018.10.008.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Iyengar, K.P., Azzopardi, C.A., Fitzpatrick, J. et al. Calcaneal offset index to measure hindfoot alignment in pes planus. Skeletal Radiol 51, 1631–1637 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00256-022-04011-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00256-022-04011-x