Abstract
Objective
To compare the diagnostic performance of a conventional metal artifact suppression sequence MAVRIC-SL (multi-acquisition variable-resonance image combination selective) and a novel 2.6-fold faster sequence employing robust principal component analysis (RPCA), in the MR evaluation of hip implants at 3 T.
Materials and methods
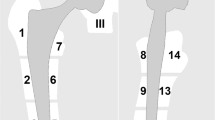
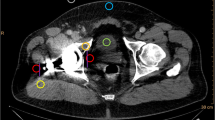
Thirty-six total hip implants in 25 patients were scanned at 3 T using a conventional MAVRIC-SL proton density-weighted sequence and an RPCA MAVRIC-SL proton density-weighted sequence. Comparison was made of image quality, geometric distortion, visualization around acetabular and femoral components, and conspicuity of abnormal imaging findings using the Wilcoxon signed-rank test and a non-inferiority test. Abnormal findings were correlated with subsequent clinical management and intraoperative findings if the patient underwent subsequent surgery.
Results
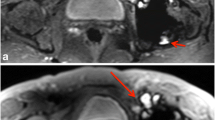
Mean scores for conventional MAVRIC-SL were better than RPCA MAVRIC-SL for all qualitative parameters (p < 0.05), although the probability of RPCA MAVRIC-SL being clinically useful was non-inferior to conventional MAVRIC-SL (within our accepted 10% difference, p < 0.05), except for visualization around the acetabular component. Abnormal imaging findings were seen in 25 hips, and either equally visible or visible but less conspicuous on RPCA MAVRIC-SL in 21 out of 25 cases. In 4 cases, a small joint effusion was queried on MAVRIC-SL but not RPCA MAVRIC-SL, but the presence or absence of a small effusion did not affect subsequent clinical management and patient outcome.
Conclusion
While the overall image quality is reduced, RPCA MAVRIC-SL allows for significantly reduced scan time and maintains almost equal diagnostic performance.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hargunani R, Madani H, Khoo M, et al. Imaging of the painful hip arthroplasty. Can Assoc Radiol J. 2016;67(4):345–55.
Fritz J, Lurie B, Miller TT, Potter HG. MR imaging of hip arthroplasty implants. Radiographics. 2014;34(4):E106-132.
Potter HG, Nestor BJ, Sofka CM, Ho ST, Peters LA, Salvati EA. Magnetic resonance imaging after total hip arthroplasty: evaluation of periprosthetic soft tissue. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2004;86(9):947–54.
Walde TA, Weiland DE, Leung SB, et al. Comparison of CT, MRI, and radiographs in assessing pelvic osteolysis: a cadaveric study. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2005;437:138–44.
Talbot BS, Weinberg EP. MR imaging with metal-suppression sequences for evaluation of total joint arthroplasty. Radiographics. 2016;36(1):209–25.
Chang KJ, Kamel IR. Body MR imaging at 3T: basic considerations about artifacts and safety. In: Kamel IR, Merkle, EM, eds. Body MR Imaging at 3 Tesla. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. 2011:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1017/CBO9780511978968.
Olsen RV, Munk PL, Lee MJ, et al. Metal artifact reduction sequence: early clinical applications. Radiographics. 2000;20(3):699–712.
Koch KM, Brau AC, Chen W, et al. Imaging near metal with a MAVRIC-SEMAC hybrid. Magn Reson Med. 2011;65(1):71–82.
Koch KM, Lorbiecki JE, Hinks RS, King KF. A multispectral three-dimensional acquisition technique for imaging near metal implants. Magn Reson Med. 2009;61(2):381–90.
Lu W, Pauly KB, Gold GE, Pauly JM, Hargreaves BA. SEMAC: slice encoding for metal artifact correction in MRI. Magn Reson Med. 2009;62(1):66–76.
Hargreaves BA, Worters PW, Pauly KB, Pauly JM, Koch KM, Gold GE. Metal-induced artifacts in MRI. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2011;197(3):547–55.
Harris CA, White LM. Metal artifact reduction in musculoskeletal magnetic resonance imaging. Orthop Clin North Am. 2006;37(3):349-359,vi.
Kretzschmar M, Nardo L, Han MM, et al. Metal artefact suppression at 3 T MRI: comparison of MAVRIC-SL with conventional fast spin echo sequences in patients with Hip joint arthroplasty. Eur Radiol. 2015;25(8):2403–11.
Otazo R, Nittka M, Bruno M, et al. Sparse-SEMAC: rapid and improved SEMAC metal implant imaging using SPARSE-SENSE acceleration. Magn Reson Med. 2017;78(1):79–87.
Wiens CN, Artz NS, Jang H, McMillan AB, Reeder SB. Externally calibrated parallel imaging for 3D multispectral imaging near metallic implants using broadband ultrashort echo time imaging. Magn Reson Med. 2017;77(6):2303–9.
Nardo L, Han M, Kretzschmar M, et al. Metal artifact suppression at the hip: diagnostic performance at 3.0 T versus 1.5 Tesla. Skeletal Radiol. 2015;44(11):1609–16.
Liebl H, Heilmeier U, Lee S, et al. In vitro assessment of knee MRI in the presence of metal implants comparing MAVRIC-SL and conventional fast spin echo sequences at 1.5 and 3 T field strength. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2015;41(5):1291–9.
Hargreaves BA, Chen W, Lu W, et al. Accelerated slice encoding for metal artifact correction. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2010;31(4):987–96.
Levine E, Stevens K, Beaulieu C, Hargreaves B. Accelerated three-dimensional multispectral MRI with robust principal component analysis for separation of on- and off-resonance signals. Magn Reson Med. 2018;79(3):1495–505.
Fritz J, Ahlawat S, Demehri S, et al. Compressed sensing SEMAC: 8-fold accelerated high resolution metal artifact reduction MRI of cobalt-chromium knee arthroplasty implants. Invest Radiol. 2016;51(10):666–76.
Worters PW, Sung K, Stevens KJ, Koch KM, Hargreaves BA. Compressed-sensing multispectral imaging of the postoperative spine. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2013;37(1):243–8.
Gwet KL. Computing inter-rater reliability and its variance in the presence of high agreement. Br J Math Stat Psychol. 2008;61(Pt 1):29–48.
Hayter CL, Koff MF, Shah P, Koch KM, Miller TT, Potter HG. MRI after arthroplasty: comparison of MAVRIC and conventional fast spin-echo techniques. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2011;197(3):W405–11.
Choi SJ, Koch KM, Hargreaves BA, Stevens KJ, Gold GE. Metal artifact reduction with MAVRIC SL at 3-T MRI in patients with hip arthroplasty. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2015;204(1):140–7.
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr. Evan Levine for assistance in the design and preliminary work on the RPCA MAVRIC-SL sequence.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Institutes of Health (R01 EB017739) and GE Medical Systems.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
B.A.H. received NIH grant support, R01 EB017739 (MRI Near Metal). These sponsors provided funding for the study but were not involved in the study design, collection, analysis or interpretation of data, or preparation of the article. All other authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Doyle, Z., Yoon, D., Lee, P.K. et al. Clinical utility of accelerated MAVRIC-SL with robust-PCA compared to conventional MAVRIC-SL in evaluation of total hip arthroplasties. Skeletal Radiol 51, 549–556 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00256-021-03848-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00256-021-03848-y