Abstract
Objective
To determine whether ultrasound-guided percutaneous sural nerve needle biopsy yields sufficient tissue for analysis in a patient with suspected vasculitis-related peripheral neuropathy.
Materials and methods
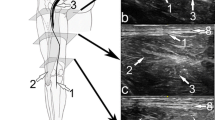
With real-time ultrasound guidance, a hydrodissection of the sural nerve from the adjacent small saphenous vein was first performed. A 14-gauge biopsy needle was then manipulated under real-time ultrasound guidance to obtain two transverse samples of the sural nerve at the lateral distal calf.
Results
The biopsy was technically successful and yielded adequate tissue for routine processing. The specimen showed mild epineurial perivascular chronic inflammation with marked loss of myelinated axons. These histologic findings are not diagnostically definitive for vasculitis-related peripheral neuropathy but were supportive of the diagnosis in combination with the patient’s physical examination, laboratory, and electromyography findings. The patient suffered no immediate complications after the procedure.
Conclusions
This ultrasound-guided sural nerve needle biopsy, like many surgical biopsies, did not yield a definitive result in a patient with suspected vasculitis-related peripheral neuropathy; however, the procedure was technically successful. Given that percutaneous needle procedures offer many advantages over surgical procedures, we believe that this procedure warrants further investigation.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gwathmey KG, Burns TM, Collins MP, Dyck PJ. Vasculitic neuropathies. Lancet Neurol. 2014;13(1):67–82.
Gorson KC. Vasculitic neuropathies: An update. Neurologist. 2007;13(1):12–9.
Schaublin GA, Michet CJ Jr, Dyck PJ, Burns TM. An update on the classification and treatment of vasculitic neuropathy. Lancet Neurol. 2005;4(12):853–65.
Wees SJ, Sunwoo IN. Oh SJ. Sural nerve biopsy in systemic necrotizing vasculitis. Am J Med. 1981;71(4):525–32.
Dyck PJ, Lofgren EP. Nerve biopsy. Choice of nerve, method, symptoms, and usefulness. Med Clin North Am. 1968;52(4):885–93.
Dyck PJ, Lofgren EP. Method of fascicular biopsy of human peripheral nerve for electrophysiologic and histologic study. Mayo Clin Proc. 1966;41(11):778–84.
Bevilacqua NJ, Rogers LC, Malik RA, Armstrong DG. Technique of the sural nerve biopsy. J Foot Ankle Surg. 2007;46(2):139–42.
Pollock M, Nukada H, Taylor P, Donaldson I, Carroll G. Comparison between fascicular and whole sural nerve biopsy. Ann Neurol. 1983;13(1):65–8.
Vital C, Vital A, Canron MH, et al. Combined nerve and muscle biopsy in the diagnosis of vasculitic neuropathy. A 16-year retrospective study of 202 cases. J Peripher Nerv Syst. 2006;11(1):20–9.
Rappaport WD, Valente J, Hunter GC, et al. Clinical utilization and complications of sural nerve biopsy. Am J Surg. 1993;166(3):252–6.
Collins MP, Mendell JR, Periquet MI, et al. Superficial peroneal nerve/peroneus brevis muscle biopsy in vasculitic neuropathy. Neurology. 2000;55(5):636–43.
Prayson RA, Sedlock DJ. Clinicopathologic study of 43 patients with sural nerve vasculitis. Hum Pathol. 2003;34(5):484–90.
Chen CH, Shen CC, Lan HHC, Lee SK. Ultrasound-assisted sural nerve biopsy: technical note and correlation of ultrasound imaging with operative findings. J Med Ultrasound. 2013;21(1):43–5.
Dahlin LB, Eriksson KF, Sundkvist C. Persistent postoperative complaints after whole sural nerve biopsies in diabetic and non-diabetic subjects. Diabet Med. 1997;14(5):353–6.
Hilton DA, Jacob J, Househam L, Tengah C. Complications following sural and peroneal nerve biopsies. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2007;78(11):1271–2.
Solders G. Discomfort after fascicular sural nerve biopsy. Acta Neurol Scand. 1988;77(6):503–4.
Gabriel CM, Howard R, Kinsella N, et al. Prospective study of the usefulness of sural nerve biopsy. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2000;69(4):442–6.
Sahni V, Qi Y, Frostick S. Peripheral nerve regeneration. Eur Surg. 2005;37(4):187–92.
Lundborg G, Dahlin LB, Danielsen N, et al. Nerve regeneration in silicone chambers: influence of gap length and of distal stump components. Exp Neurol. 1982;76(2):361–75.
Theriault M, Dort J, Sutherland G. Zochodne DW. A prospective quantitative study of sensory deficits after whole sural nerve biopsies in diabetic and nondiabetic patients. Surgical approach and the role of collateral sprouting. Neurology. 1998;50(2):480–4.
Schoeller T, Huemer GM, Shafighi M, Gurunluoglu R, Wechselberger G, Piza-Katzer H. Microsurgical repair of the sural nerve after nerve biopsy to avoid associated sensory morbidity: a preliminary report. Neurosurgery. 2004;54(4):897–901.
Kennedy WR, Navarro X, Kamal H. Reinnervation of sweat glands in the mouse: axonal regeneration versus collateral sprouting. Muscle Nerve. 1988;11(6):603–9.
Acknowledgements
We greatly appreciate the help of Megan Griffiths, MA, in the preparation and submission of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Forney, M.C., Li, X., Prayson, R. et al. Technically successful ultrasound-guided percutaneous sural nerve needle biopsy in a patient with indeterminate peripheral neuropathy. Skeletal Radiol 48, 1105–1109 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00256-018-3109-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00256-018-3109-z