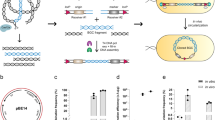
Abstract
Cloning of large DNA fragments from microorganisms becomes increasingly important but remains seriously challenging due to the complexity and diversity of genetic background. In particular, the methods with high precision and efficiency are in great need for obtaining intact biosynthetic gene clusters (BGCs) of microbial natural products. Here, we report a new strategy for targeted cloning of large DNA fragments (TCLD) from different bacteria. Using this method, precise cloning of desired E. coli chromosomal fragments up to 201 kb was achieved with 53% positive rate. Moreover, its application in cloning of large BGCs with high G + C content and multiple repetitive sequences was also demonstrated, including the 98 kb tylosin BGC (tyl), 128 kb daptomycin BGC (dpt), and 127 kb salinomycin BGC (sal). Subsequently, heterologous expression of the cloned tyl BGC in Streptomyces coelicolor M1146 led to the production of tylosins in the resulting recombinant strains. And also, its introduction into Streptomyces fradiae ATCC 19609, a native producer of tylosin, effectively increased tylosin yield to 230%. Hence, TCLD is a powerful tool for cloning large BGCs and would facilitate the discovery of bioactive substances from microbial resources.
Key points
• TCLD is an efficient method for cloning large DNA fragments.
• Repeat sequence-mediated intra-molecular cyclization improves the cloning efficiency.
• TCLD combined with scarless editing allows unlimited modifications on BGCs.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Datsenko K, Wanner B (2000) One step inactivation of chromosomal genes in Escherichia coli K-12 using PCR products. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97:6640–6645. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.120163297
Du D, Wang L, Tian Y, Liu H, Tan H, Niu G (2015) Genome engineering and direct cloning of antibiotic gene clusters via phage ϕ BT1 integrase-mediated site-specific recombination in Streptomyces. Sci Rep 5:8740. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep08740
Enghiad B, Huang C, Guo F, Jiang G, Wang B, Tabatabaei SK, Martin TA, Zhao H (2021) Cas12a-assisted precise targeted cloning using in vivo Cre-lox recombination. Nat Commun 12:1171. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-021-21275-4
Fu J, Bian X, Hu S, Wang H, Huang F, Seibert PM, Plaza A, Xia L, Müller R, Stewart AF, Zhang Y (2012) Full-length RecE enhances linear-linear homologous recombination and facilitates direct cloning for bioprospecting. Nat Biotechnol 30:440–446. https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt.2183
Gibson DG, Benders GA, Axelrod KC, Zaveri J, Algire MA, Moodie M, Montague MG, Venter JC, Smith HO, Hutchison CA III (2008) One-step assembly in yeast of 25 overlapping DNA fragments to form a complete synthetic Mycoplasma genitalium genome. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105:20404–20409. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0811011106
Gibson DG, Young L, Chuang RY, Venter JC, Hutchison CA III, Smith HO (2009) Enzymatic assembly of DNA molecules up to several hundred kilobases. Nat Methods 6:343–345. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.1318
Gomez-Escribano JP, Bibb MJ (2011) Engineering Streptomyces coelicolor for heterologous expression of secondary metabolite gene clusters. Microb Biotechnol 4:207–215. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1751-7915.2010.00219.x
Grenier F, Matteau D, Baby V, Rodrigue S (2014) Complete genome sequence of Escherichia coli BW25113. Genome Announc 2:e01038-e1114. https://doi.org/10.1128/genomeA.01038-14
Gust B, Challis G, Fowler K, Kieser T, Chater KF (2003) PCR-targeted Streptomyces gene replacement identifies a protein domain needed for biosynthesis of the sesquiterpene odor geosmin. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100:1541–1546. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0337542100
Jiang C, Wang H, Kang Q, Liu J, Bai L (2012) Cloning and characterization of the polyether salinomycin biosynthesis gene cluster of Streptomyces albus XM211. Appl Environ Microbiol 78:994–1003. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.06701-11
Jiang W, Zhao X, Gabrieli T, Lou C, Ebenstein Y, Zhu T (2015) Cas9-assisted targeting of chromosome segments CATCH enables onestep targeted cloning of large gene clusters. Nat Commun 6:8101. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms9101
Kieser T, Bibb MJ, Buttner MJ, Chater KF, Hopwood DA (2000) Practical Streptomyces Genetics. John Innes Foundation, Norwich, UK
Kim E, Song MC, Kim MS, Beom JY, Lee EY, Kim DM, Nam SJ, Yoon YJ (2016) Characterization of the two methylation steps involved in the biosynthesis of mycinose in tylosin. J Nat Prod 79:2014–2021. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jnatprod.6b00267
Kouprina N, Larionov V (2019) TAR cloning: perspectives for functional genomics, biomedicine, and biotechnology. Mol Ther Methods Clin Dev 14:16–26. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.omtm.2019.05.006
Kouprina N, Noskov V, Larionov V (2020) Selective isolation of large segments from individual microbial genomes and environmental DNA samples using transformation-associated recombination cloning in Yeast. Nat Protoc 15:734–749. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41596-019-0280-1
Laureti L, Song L, Huang S, Corre C, Leblond P, Challis GL, Aigle B (2011) Identification of a bioactive 51-membered macrolide complex by activation of a silent polyketide synthase in Streptomyces ambofaciens. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 108:6258–6263. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1019077108
Li D, Zhang J, Tian Y, Tan H (2019) Enhancement of salinomycin production by ribosome engineering in Streptomyces albus. Sci China Life Sci 62:276–279. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11427-018-9474-7
Liang M, Liu L, Xu F, Zeng X, Wang R, Yang J, Wang W, Karthik L, Liu J, Yang Z, Zhu G, Wang S, Bai L, Tong Y, Liu X, Wu M, Zhang L, Tan G (2022) Activating cryptic biosynthetic gene cluster through a CRISPR–Cas12a-mediated direct cloning approach. Nucleic Acids Res 50:3581–3592. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkac181
Liao G, Li J, Li L, Yang H, Tian Y, Tan H (2010) Cloning, reassembling and integration of the entire nikkomycin biosynthetic gene cluster into Streptomyces ansochromogenes lead to an improved nikkomycin production. Microb Cell Fact 9:6. https://doi.org/10.1186/1475-2859-9-6
Liu G, Chater KF, Chandra G, Niu G, Tan H (2013) Molecular regulation of antibiotic biosynthesis in Streptomyces. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 77:112–143. https://doi.org/10.1128/MMBR.00054-12
Lu C, Liao G, Zhang J, Tan H (2015) Identification of novel tylosin analogues generated by a wblA disruption mutant of Streptomyces ansochromogenes. Microb Cell Fact 14:173. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12934-015-0359-5
MacNeil DJ, Gewain KM, Ruby CL, Dezeny G, Gibbons PH, MacNeil T (1992) Analysis of Streptomyces avermitilis genes required for avermectin biosynthesis utilizing a novel integration vector. Gene 111:61–68. https://doi.org/10.1016/0378-1119(92)90603-m
Miao V, Coeffet-Legal MF, Brian P, Brost R, Penn J, Whiting A, Martin S, Ford R, Parr I, Bouchard M, Silva CJ, Wrigley SK, Baltz RH (2005) Daptomycin biosynthesis in Streptomyces roseosporus: cloning and analysis of the gene cluster and revision of peptide stereochemistry. Microbiology 151(1507):1523. https://doi.org/10.1099/mic.0.27757-0
Murakami T, Burian J, Yanai K, Bibb MJ, Thompson CJ (2011) A system for the targeted amplification of bacterial gene clusters multiplies antibiotic yield in Streptomyces coelicolor. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 108:16020–16025. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1108124108
Muth G (2018) The pSG5-based thermosensitive vector family for genome editing and gene expression in actinomycetes. Appl Environ Microbiol 102:9067–9080. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-018-9334-5
Nah HJ, Woo MW, Choi SS, Kim ES (2015) Precise cloning and tandem integration of large polyketide biosynthetic gene cluster using Streptomyces artificial chromosome system. Microb Cell Fact 14:140. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12934-015-0325-2
Noskov VN, Karas BJ, Young L, Chuang RY, Gibson DG, Lin YC, Stam J, Yonemoto IT, Suzuki Y, Andrews-Pfannkoch A, Glass JI, Smith HO, Hutchison CA III, Venter JC, Weyman PD (2012) Assembly of large, high G+C bacterial DNA fragments in yeast. ACS Synth Biol 1:267–273. https://doi.org/10.1021/sb3000194
Nguyen KT, Kau D, Gu JQ, Brian P, Wrigley SK, Baltz RH, Miao V (2006) A glutamic acid 3-methyltransferase encoded by an accessory gene locus important for daptomycin biosynthesis in Streptomyces roseosporus. Mol Microbiol 61:1294–1307. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2958.2006.05305.x
Paget MS, Chamberlin L, Atrih A, Foster SJ, Buttner MJ (1999) Evidence that the extracytoplasmic function sigma factor σE is required for normal cell wall structure in Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2). J Bacteriol 181:204–211. https://doi.org/10.1128/JB.181.1.204-211.1999
Palazzotto E, Tong Y, Lee S, Weber T (2019) Synthetic biology and metabolic engineering of actinomycetes for natural product discovery. Biotechnol Adv 37:107366. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biotechadv.2019.03.005
Pigac J, Vujaklija D, Toman Z, Gamulin V, Schrempf H (1988) Structural instability of a bifunctional plasmid pZG1 and single-stranded DNA formation in Streptomyces. Plasmid 19:222–230. https://doi.org/10.1016/0147-619x(88)90040-6
Sambrook J, Russell DW (2001) Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual, 3rd edn. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, New York
Stratigopoulos G, Cundliffe E (2002) Expression analysis of the tylosin biosynthetic gene cluster: pivotal regulatory role of the tylQ product. Chem Biol 9:71–78. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1074-5521(01)00095-3
Tan G, Deng K, Liu X, Tao H, Chang Y, Chen J, Chen K, Sheng Z, Deng Z, Liu T (2017) Heterologous biosynthesis of spinosad: an omics-guided large polyketide synthase gene cluster reconstitution in Streptomyces. ACS Synth Biol 6:995–1005. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssynbio.6b00330
Wang H, Li Z, Jia R, Yin J, Li A, Xia L, Yin Y, Müller R, Fu J, Stewart AF, Zhang Y (2018) ExoCET: exonuclease in vitro assembly combined with RecET recombination for highly efficient direct DNA cloning from complex genomes. Nucleic Acids Res 46:e28. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkx1249
Yamanaka K, Reynolds KA, Kersten RD, Ryan KS, Gonzalez DJ, Nizet V, Dorrestein PC, Moore BS (2014) Direct cloning and refactoring of a silent lipopeptide biosynthetic gene cluster yields the antibiotic taromycin A. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 111:1957–1962. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1319584111
Yin J, Hoffmann M, Bian X, Tu Q, Yan F, Xia L, Ding X, Stewart AF, Müller R, Fu J, Zhang Y (2015) Direct cloning and heterogenous expression of the salinomycin biosynthetic gene cluster from Streptomyces albus DSM41398 in Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2). Sci Rep 5:15081. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep15081
Zheng J, Li Y, Guan H, Zhang J, Tan H (2019) Enhancement of neomycin production by engineering the entire biosynthetic gene cluster and feeding key precursors in Streptomyces fradiae CGMCC 4.576. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 103:2263–2275. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-018-09597-8
Zhuo J, Ma B, Xu J, Hu W, Zhang J, Tan H, Tian Y (2017) Reconstruction of a hybrid nucleoside antibiotic gene cluster based on scarless modification of large DNA fragments. Sci China Life Sci 60:968–979. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11427-017-9119-1
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to Dr. Wenzhao Wang (Institute of Microbiology, Chinese Academy of Sciences) for his assistance in the analysis of mass spectrometry.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (grant number 2018YFA0901900), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant numbers 32270055 and 82173720), and Beijing Natural Science Foundation (grant number 7212153).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
JL, JZ, and YT conceived and designed the research. YT, DL, KW, and BW conducted experiments. YT, JL, and JZ analyzed data. The manuscript was written by JL, JZ, YT, and DL. All the authors read and approved the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with animals performed by any of the authors.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Tian, Y., Li, D., Wang, K. et al. An efficient method for targeted cloning of large DNA fragments from Streptomyces. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 107, 5749–5760 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-023-12685-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-023-12685-z