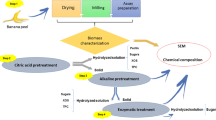
Abstract
In this study, loquat extract was selected as a promising substrate for bacterial cellulose (BC) production. A new BC-producing bacterial strain was isolated from residual loquat and identified as Komagataeibacter rhaeticus. BC production with different carbon sources and with loquat extract was investigated. Among all tested carbon sources, glucose was demonstrated to be the best substrate for BC production by K. rhaeticus, with up to 7.89 g/L dry BC obtained under the optimal initial pH (5.5) and temperature (28 °C) with 10 days of fermentation. The total sugar and individual sugars were investigated in different loquat extracts, in which fructose, glucose, and sucrose were the three main sugars. When loquat extract was prepared with a solid‒liquid (S-L) ratio of 2:1, the concentrations of glucose, fructose, and sucrose were 7.91 g/L, 9.31 g/L, and 2.84 g/L, respectively. The BC production obtained from loquat extract was higher than that of other carbon sources except glucose, and 6.69 g/L dry BC was obtained from loquat extract with an S-L ratio of 2:1. After BC production, all sugars substantially decreased, with the utilization of glucose, fructose, and sucrose reaching 93.9%, 87.9%, and 100%, respectively. These results suggested that the different sugars in loquat extract were all carbon sources participating in BC production by K. rhaeticus. Structural and physicochemical properties were investigated by SEM, TGA, XRD, and FT-IR spectroscopy. The results showed that the structural, chemical group, and water holding capacity of BC obtained from loquat extract were similar to those of BC obtained from glucose, but the crystallinity and thermal stability of BC were higher than those of BC from mannose and lactose but lower than those of BC from glucose and fructose.
Key points
• A new BC-producing strain was isolated and identified as Komagataeibacter rhaeticus.
• Loquat extract is an alternative substrate for BC production.
• The BC obtained from loquat extract owns advanced physicochemical properties.
Graphical Abstract









Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Code availability
The sequence data of this study have been deposited in the NCBI database under accession number OP026093.
References
Barud HS, Ribeiro CA, Crespi MS, Martines MAU, Dexpert-Ghys J, Marques RFC, Messaddeq Y, Ribeiro SJL (2007) Thermal characterization of bacterial cellulose-phosphate composite membranes. J Therm Anal Calorim 87(3):815–818. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-006-8170-5
Barud HS, Barrios C, Regiani T, Marques RFC, Verelst M, Dexpert-Ghys J, Messaddeq Y, Ribeiro SJL (2008) Self-supported silver nanoparticles containing bacterial cellulose membranes. Mat Sci Eng C 28(4):515–518. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msec.2007.05.001
Cai J, Chen T, Zhang Z, Li B, Qin G, Tian S (2019) Metabolic dynamics during loquat fruit ripening and postharvest technologies. Front Plant Sci 10:619. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2019.00619
Cakar F, Ozer I, Aytekin AO, Sahin F (2014) Improvement production of bacterial cellulose by semi-continuous process in molasses medium. Carbohydr Polym 106:7–13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2014.01.103
Campano C, Balea A, Blanco A, Negro C (2016) Enhancement of the fermentation process and properties of bacterial cellulose: a review. Cellulose 23(1):57–91. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-015-0802-0
Castro C, Zuluaga R, Putaux JL, Caro G, Mondragon I, Ganán P (2011) Structural characterization of bacterial cellulose produced by Gluconacetobacter swingsii sp. from Colombian agroindustrial wastes. Carbohyd Polym 84(1):96–102. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2008.09.024
Castro C, Zuluaga R, Alvarez C, Putaux JL, Caro G, Rojas OJ, Mondragon I, Ganan P (2012) Bacterial cellulose produced by a new acid-resistant strain of Gluconacetobacter genus. Carbohydr Polym 89(4):1033–1037. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2012.03.045
Cavka A, Guo X, Tang SJ, Winestrand S, Jonsson LJ, Hong F (2013) Production of bacterial cellulose and enzyme from waste fiber sludge. Biotechnol Biofuels 6(1):25. https://doi.org/10.1186/1754-6834-6-25
Chawla PR, Bajaj IB, Survase SA, Singhal RS (2009) Microbial cellulose: fermentative production and applications. Food Technol Biotechnol 47(2):107–124. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2010.10.072
Cheng Z, Yang R, Liu X, Liu X, Chen H (2017) Green synthesis of bacterial cellulose via acetic acid pre-hydrolysis liquor of agricultural corn stalk used as carbon source. Bioresour Technol 234:8–14. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2017.02.131
Ciechańska D (2004) Multifunctional bacterial cellulose/chitosan composite materials for medical applications. Fibres Text East Eur 12(4):69–72. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dyepig.2003.12.014
Costa AFS, Almeida FCG, Vinhas GM, Sarubbo LA (2017) Production of bacterial cellulose by Gluconacetobacter hansenii using corn steep liquor as nutrient sources. Front Microbiol 8:2027. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2017.02027
Czaja W, Romanovicz D, Brown RM (2004) Structural investigations of microbial cellulose produced in stationary and agitated culture. Cellulose 11(3):403–411
Dellaglio F, Cleenwerck I, Felis GE, Engelbeen K, Janssens D, Marzotto M (2005) Description of Gluconacetobacter swingsii sp. nov. and Gluconacetobacter rhaeticus sp. nov., isolated from Italian apple fruit [J]. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 55(6):2365–2370. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijs.0.63301-0
Ding C, Chachin K, Ueda Y, Imahori Y, Wang CY (2002) Modified atmosphere packaging maintains postharvest quality of loquat fruit. Postharvest Biol Tecchnol 24:341–348. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0925-5214(01)00148-X
Fan X, Gao Y, He W, Hu H, Tian M, Wang K, Pan S (2016) Production of nano bacterial cellulose from beverage industrial waste of citrus peel and pomace using Komagataeibacter xylinus. Carbohydr Polym 151:1068–1072. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2016.06.062
Gomes FP, Silva NHCS, Trovatti E, Serafim LS, Duarte MF, Silvestre AJD, Neto CP, Freire CSR (2013) Production of bacterial cellulose by Gluconacetobacter sacchari using dry olive mill residue. Biomass Bioenerg 55:205–211. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biombioe.2013.02.004
Gorgieva S (2020) Bacterial Cellulose as a versatile platform for research and development of biomedical materials. Processes 8(5):624. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr8050624
Gullo M, La China S, Falcone PM, Giudici P (2018) Biotechnological production of cellulose by acetic acid bacteria: current state and perspectives. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 102(16):6885–6898. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-018-9164-5
Gupte Y, Kulkarni A, Raut B, Sarkar P, Choudhury R, Chawande A, Kumar GRK, Bhadra B, Satapathy A, Das G, Vishnupriya B, Dasgupta S (2021) Characterization of nanocellulose production by strains of Komagataeibacter sp. isolated from organic waste and Kombucha. Carbohydr Polym 266:118176. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2021.118176
Jahan F, Kumar V, Saxena RK (2018) Distillery effluent as a potential medium for bacterial cellulose production: a biopolymer of great commercial importance. Bioresour Technol 250:922–926. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2017.09.094
Keshk SMAS (2014) Vitamin C enhances bacterial cellulose production in Gluconacetobacter xylinus. Carbohyd Polym 99:98–100. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2013.08.060
Khouya T, Ramchoun M, Elbouny H, Hmidani A, Bouhlali EDT, Alem C (2022) Loquat (Eriobotrya japonica (Thunb) Lindl.): evaluation of nutritional value, polyphenol composition, antidiabetic effect, and toxicity of leaf aqueous extract. J Ethnopharmacol 296:115473. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jep.2022.115473
Klemm D, Heublein B, Fink HP, Bohn A (2005) Cellulose: fascinating biopolymer and sustainable raw material. Angew Chem 44(22):3358–3393. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.200460587
Klemm D, Schumann D, Udhardt U, Marsch S (2001) Bacterial synthesized cellulose — artificial blood vessels for microsurgery. Prog Polym Sci 26(9):1561–1603. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0079-6700(01)00021-1
Lin D, Lopez-Sanchez P, Li R, Li Z (2014) Production of bacterial cellulose by Gluconacetobacter hansenii CGMCC 3917 using only waste beer yeast as nutrient source. Bioresour Technol 151:113–119. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2013.10.052
Liu Y, Zhang W, Xu C, Li X (2016) Biological activities of extracts from loquat (Eriobotrya japonica Lindl.): a review. Int J Mol Sci 17(12). https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17121983
Mohite BV, Patil SV (2014) Physical, structural, mechanical and thermal characterization of bacterial cellulose by G. hansenii NCIM 2529. Carbohydr Polym 106:132–141. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2014.02.012
Saowapark T, Chaichana E, Jaturapiree A (2017) Properties of natural rubber latex filled with bacterial cellulose produced from pineapple peels. J Met Mater Miner 12–16.https://doi.org/10.14456/jmmm.2017.xx
Shao X, Zhu Y, Cao S, Wang H, Song Y (2013) Soluble sugar content and metabolism as related to the heat-induced chilling tolerance of loquat fruit during cold storage. Food Bioproc Technol 6:3490–3498. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-012-1011-6
Semjonovs P, Ruklisha M, Paegle L (2017) Cellulose synthesis by Komagataeibacter rhaeticus strain P 1463 isolated from kombucha. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 101:1003–1012. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-016-7761-8
Singhania RR, Patel AK, Tseng YS, Kumar V, Chen CW, Haldar D, Saini JK, Dong CD (2022) Developments in bioprocess for bacterial cellulose production. Bioresour Technol 344(Pt B):126343. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2021.126343
Tsouko E, Kourmentza C, Ladakis D, Kopsahelis N, Mandala I, Papanikolaou S, Paloukis F, Alves V, Koutinas A (2015) Bacterial cellulose production from industrial waste and by-product streams. Int J Mol Sci 16(7):14832–14849. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms160714832
Ul-Islam M, Khan T, Park JK (2012) Water holding and release properties of bacterial cellulose obtained by in situ and ex situ modification. Carbohydr Polym 88(2):596–603. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2012.01.006
Ul-Islam M, Ullah MW, Khan S, Shah N, Park JK (2017) Strategies for cost-effective and enhanced production of bacterial cellulose [J]. Int J Biol Macromol 102:1166–1173. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2017.04.110
Urbina L, Corcuera MÁ, Gabilondo N, Eceiza A, Retegi A (2021) A review of bacterial cellulose: sustainable production from agricultural waste and applications in various fields. Cellulose 28(13):8229–8253. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-021-04020-4
Vazquez A, Foresti ML, Cerrutti P, Galvagno M (2013) Bacterial cellulose from simple and low cost production media by Gluconacetobacter xylinus. J Polym Environ 21(2):545–554. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10924-012-0541-3
Vigentini I, Fabrizio V, Dellaca F, Rossi S, Azario I, Mondin C, Benaglia M, Foschino R (2019) Set-up of bacterial cellulose production from the genus Komagataeibacter and its use in a gluten-free bakery product as a case study. Front Microbiol 10:1953. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2019.01953
Volova TG, Prudnikova SV, Sukovatyi AG, Shishatskaya EI (2018) Production and properties of bacterial cellulose by the strain Komagataeibacter xylinus B-12068. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 102(17):7417–7428. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-018-9198-8
Wang FP, Li B, Sun MY, Wahid F, Zhang HM, Wang SJ, Xie YY, Jia SR, Zhong C (2022) In situ regulation of bacterial cellulose networks by starch from different sources or amylose/amylopectin content during fermentation. Int J Biol Macromol 195:59–66. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2021.11.198
Wei Y, Xu F, Shao X (2017) Changes in soluble sugar metabolism in loquat fruit during different cold storage. J Food Sci Technol 54(5):1043–1051. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-017-2536-5
Xu H, Chen J, Xie M (2010) Effect of different light transmittance paper bags on fruit quality and antioxidant capacity in loquat. J Sci Food Agric 90:1783–1788. https://doi.org/10.1002/jsfa.4012
Ye J, Zheng S, Zhang Z, Yang F, Ma K, Feng Y, Zheng J, Mao D, Yang X (2019) Bacterial cellulose production by Acetobacter xylinum ATCC 23767 using tobacco waste extract as culture medium. Bioresour Technol 274:518–524. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2018.12.028
Zhi C, Ali MM, Zhang J, Shi M, Ma S, Chen F (2021) Effect of paper and aluminum bagging on fruit quality of loquat (Eriobotrya japonica Lindl.). Plants (Basel) 10(12). https://doi.org/10.3390/plants10122704
Zywicka A, Ciecholewska-Jusko D, Drozd R, Rakoczy R, Konopacki M, Kordas M, Junka A, Migdal P, Fijalkowski K (2021) Preparation of Komagataeibacter xylinus inoculum for bacterial cellulose biosynthesis using magnetically assisted external-Loop airlift bioreactor. Polymers-Basel 13(22). https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13223950
Funding
The project was supported in part by the Doctor Support Grants of Putian University (2021068, 2021069) and the Natural Science Foundation of Fujian Province (2021J05242, 2021J05241, 2022J011167).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Study concepts: JY, JX. Study design: JL, QW. Experimental studies: XW, SW. Data acquisition: HW, JL. Data analysis: JL, QW. Manuscript preparation: JY, JX. Manuscript revision: JX, HW.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
This study was conducted without the use of human or animal participants.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ye, J., Li, J., Wang, Q. et al. Bacterial cellulose production by a strain of Komagataeibacter rhaeticus isolated from residual loquat. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 107, 1551–1562 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-023-12407-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-023-12407-5