Abstract
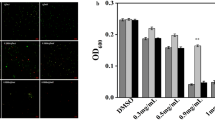
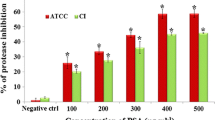
Shigella flexneri (Sh. flexneri), a common foodborne pathogen, has become one of the main threats to food safety and human health due to its high pathogenicity and persistent infection. The objective of this study was to explore the antimicrobial and anti-biofilm activities and the possible mechanism of thymoquinone (TQ) against Sh. flexneri. The minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) and minimal bactericidal concentration (MBC) of TQ against Sh. flexneri were 0.4 and 0.5 mg/mL, respectively. TQ showed bactericidal activity against Sh. flexneri in culture medium and milk system. Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and confocal laser scanning microscopy (CLSM) observations demonstrated that TQ could induce abnormal cell morphology and destroy cell membrane. Sodium dodecyl sulfate polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE) analysis suggested that TQ could inhibit protein synthesis in Sh. flexneri. Also, at sub-inhibitory concentrations (SICs), TQ exhibited an inhibitory effect on Sh. flexneri biofilm formation, which was confirmed by crystal violet quantitative analysis and SEM observation. Real-time quantitative PCR (RT-qPCR) analyses revealed that TQ downregulated the expression of genes involved in Sh. flexneri biofilm formation. Thus, TQ has potential as a natural antimicrobial and anti-biofilm agent to address the contamination and infection caused by Sh. flexneri.
Key points
• Antimicrobial and anti-biofilm activity of TQ on Shigella flexneri were investigated.
• TQ inhibited biofilm formation by Shigella flexneri.
• TQ provided a new strategy for Shigella flexneri control.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are available in the manuscript.
References
Adnan M, Patel M, Deshpande S, Alreshidi M, Siddiqui AJ, Reddy MN, Emira N, De FV (2020) Effect of Adiantum philippense extract on biofilm formation, adhesion with its antibacterial activities against foodborne pathogens, and characterization of bioactive metabolites: an in vitro-in silico approach. Front Microbiol 11:823. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2020.00823
Ahmed AM, Shimamoto T (2015) Molecular characterization of multidrug-resistant Shigella spp. of food origin. Int J Food Microbiol 194:78–82. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2014.11.013
Al-Majed AA, Al-Omar FA, Nagi MN (2006) Neuroprotective effects of thymoquinone against transient forebrain ischemia in the rat hippocampus. Eur J Pharmacol 543(1-3):40–47. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejphar.2006.05.046
Bridier A, Sanchez-Vizuete P, Guilbaud M, Piard JC, Naitali M, Briandet R (2015) Biofilm-associated persistence of food-borne pathogens. Food Microbiol 45(Pt B):167–178. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fm.2014.04.015
Chimnoi N, Reuk-Ngam N, Chuysinuan P, Khlaychan P, Khunnawutmanotham N, Chokchaichamnankit D, Thamniyom W, Klayraung S, Mahidol C, Techasakul S (2018) Characterization of essential oil from Ocimum gratissimum leaves: antibacterial and mode of action against selected gastroenteritis pathogens. Microb Pathog 118:290–300. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micpath.2018.03.041
Costa JG, Keser V, Jackson C, Saraiva N, Guerreiro I, Almeida N, Camoes SP, Manguinhas R, Castro M, Fernandes AS, Oliveira NG (2020) A multiple endpoint approach reveals potential in vitro anticancer properties of thymoquinone in human renal carcinoma cells. Food Chem Toxicol 136:111076. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2019.111076
Coughlan LM, Cotter PD, Hill C, Alvarez-Ordonez A (2016) New weapons to fight old enemies: novel strategies for the (bio)control of bacterial biofilms in the food industry. Front Microbiol 7:1641. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2016.01641
Diao WR, Hu QP, Zhang H, Xu JG (2014) Chemical composition, antibacterial activity and mechanism of action of essential oil from seeds of fennel (Foeniculum vulgare Mill.). Food Control 35(1):109–116. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodcont.2013.06.056
El Gazzar M, El Mezayen R, Marecki JC, Nicolls MR, Canastar A, Dreskin SC (2006) Anti-inflammatory effect of thymoquinone in a mouse model of allergic lung inflammation. Int Immunopharmacol 6(7):1135–1142. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intimp.2006.02.004
Frankova A, Marounek M, Mozrova V, Weber J, Kloucek P, Lukesova D (2014) Antibacterial activities of plant-derived compounds and essential oils toward Cronobacter sakazakii and Cronobacter malonaticus. Foodborne Pathog Dis 11(10):795–797. https://doi.org/10.1089/fpd.2014.1737
Gu H, Fan D, Gao J, Zou W, Peng Z, Zhao Z, Ling J, LeGeros RZ (2012) Effect of ZnCl2 on plaque growth and biofilm vitality. Arch Oral Biol 57(4):369–375. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.archoralbio.2011.10.001
Halawani E (2009) Antibacterial activity of thymoquinone and thymohydroquinone of Nigella sativa L. and their interaction with some antibiotics.Advan. Biol Res 3(5-6):148–152
Hirudkar JR, Parmar KM, Prasad RS, Sinha SK, Jogi MS, Itankar PR, Prasad SK (2020) Quercetin a major biomarker of Psidium guajava L. inhibits SepA protease activity of Shigella flexneri in treatment of infectious diarrhoea. Microb. Pathogenesis 138:103807. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micpath.2019.103807
Huang JF, Yang LY, Zou Y, Luo SC, Wang X, Liang YJ, Du YH, Feng RZ, Wei Q (2021) Antibacterial activity and mechanism of three isomeric terpineols of Cinnamomum longepaniculatum leaf oil. Folia Microbiol 66(1):59–67. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12223-020-00818-0
Kalus U, Pruss A, Bystron J, Jurecka M, Smekalova A, Lichius JJ, Kiesewetter H (2003) Effect of Nigella sativa (black seed) on subjective feeling in patients with allergic diseases. Phytother Res 17(10):1209–1214. https://doi.org/10.1002/ptr.1356
Kang J, Liu L, Liu M, Wu X, Li J (2018a) Antibacterial activity of gallic acid against Shigella flexneri and its effect on biofilm formation by repressing mdoH gene expression. Food Control 94:147–154. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodcont.2018.07.011
Kang J, Liu L, Liu Y, Wang X (2020) Ferulic acid inactivates Shigella flexneri through cell membrane destruction, biofilm retardation, and altered gene expression. J Agric Food Chem 68(27):7121–7131. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.0c01901
Kang J, Liu L, Wu X, Sun Y, Liu Z (2018b) Effect of thyme essential oil against Bacillus cereus planktonic growth and biofilm formation. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 102(23):10209–10218. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-018-9401-y
Liu F, Wang F, Du L, Zhao T, Doyle MP, Wang D, Zhang X, Sun Z, Xu W (2018) Antibacterial and antibiofilm activity of phenyllactic acid against Enterobacter cloacae. Food Control 84:442–448. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodcont.2017.09.004
Livio S, Strockbine NA, Panchalingam S, Tennant SM, Barry EM, Marohn ME, Antonio M, Hossain A, Mandomando I, Ochieng JB, Oundo JO, Qureshi S, Ramamurthy T, Tamboura B, Adegbola RA, Hossain MJ, Saha D, Sen S, Faruque AS, Alonso PL, Breiman RF, Zaidi AK, Sur D, Sow SO, Berkeley LY, O'Reilly CE, Mintz ED, Biswas K, Cohen D, Wu Y, Blackwelder WC, Kotloff KL, Nataro JP, Levine MM (2014) Shigella isolates from the global enteric multicenter study inform vaccine development. Clin Infect Dis 59(7):933–941. https://doi.org/10.1093/cid/ciu468
Miao X, Liu H, Zheng Y, Guo D, Shi C, Xu Y, Xia X (2019) Inhibitory effect of thymoquinone on Listeria monocytogenes ATCC 19115 biofilm formation and virulence attributes critical for human infection. Front Cell Infect Microbiol 9:304. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcimb.2019.00304
Ngome MT, Alves J, de Oliveira ACF, da Silva MP, Mondragon-Bernal OL, Piccoli RH (2018) Linalool, citral, eugenol and thymol: control of planktonic and sessile cells of Shigella flexneri. AMB Express 8(1):105. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13568-018-0634-z
Nickerson KP, Chanin RB, Sistrunk JR, Rasko DA, Fink PJ, Barry EM, Nataro JP, Faherty CS (2017) Analysis of Shigella flexneri resistance, biofilm formation, and transcriptional profile in response to bile salts. Infect Immun 85(6):e01067–e01016. https://doi.org/10.1128/IAI.01067-16
Rahimi E, Shirazi F, Khamesipour F (2017) Isolation and study of the antibiotic resistance properties of Shigella species in meat and meat products. J Food Process Preserv 41(3):e12947. https://doi.org/10.1111/jfpp.12947
Rohinishree YS, Negi PS (2016) Effect of licorice extract on cell viability, biofilm formation and exotoxin production by Staphylococcus aureus. J Food Sci Technol 53(2):1092–1100. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-015-2131-6
Shahin K, Bouzari M, Wang R, Yazdi M (2019) Prevalence and molecular characterization of multidrug-resistant Shigella species of food origins and their inactivation by specific lytic bacteriophages. Int J Food Microbiol 305:108252. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2019.108252
Shi C, Zhao X, Yan H, Meng R, Zhang Y, Li W, Liu Z, Guo N (2016) Effect of tea tree oil on Staphylococcus aureus growth and enterotoxin production. Food Control 62:257–263. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodcont.2015.10.049
Silva-Angulo AB, Zanini SF, Rosenthal A, Rodrigo D, Klein G, Martinez A (2015) Comparative study of the effects of citral on the growth and injury of Listeria innocua and Listeria monocytogenes cells. PLoS One 10(2):e0114026. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0114026
Song Y, Sun M, Feng L, Liang X, Song X, Mu G, Tuo Y, Jiang S, Qian F (2020) Antibiofilm activity of Lactobacillus plantarum 12 exopolysaccharides against Shigella flexneri. Appl Environ Microbiol 86(15). https://doi.org/10.1128/aem.00694-20
Ulasli SS, Celik S, Gunay E, Ozdemir M, Hazman O, Ozyurek A, Koyuncu T, Unlu M (2013) Anticancer effects of thymoquinone, caffeic acid phenethyl ester and resveratrol on A549 non-small cell lung cancer cells exposed to benzo(a)pyrene. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev 14(10):6159–6164. https://doi.org/10.7314/apjcp.2013.14.10.6159
Wang C, Chang T, Yang H, Cui M (2015) Antibacterial mechanism of lactic acid on physiological and morphological properties of Salmonella enteritidis, Escherichia coli and Listeria monocytogenes. Food Control 47:231–236. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodcont.2014.06.034
Zheng X, Guo J, Rao H, Guo D, Huang Y, Xu Y, Liang S, Xia X, Shi C (2020) Antibacterial and antibiofilm activity of coenzyme Q0 against Vibrio parahaemolyticus. Food Control 109:106955. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodcont.2019.106955
Funding
This work was financially supported by the National Key Research and Development Project During the 13th Five-Year Plan (2019YFC1606703).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
YTL conceived the project. YTL and FQX generated the concepts and designed the research. WZL and YYH verified the validity and checked the results. JH and ZXJ assisted in data analysis and data curation. FQX and JH performed the experiments. FQX undertook the original draft writing. GZP and HZQ provided useful suggestions and revised the manuscript. All authors read and approved the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical statement
This study is original and unpublished and has not been submitted elsewhere at the present time. This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Consent for publication
All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fan, Q., Yuan, Y., Jia, H. et al. Antimicrobial and anti-biofilm activity of thymoquinone against Shigella flexneri. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 105, 4709–4718 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-021-11295-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-021-11295-x