Abstract
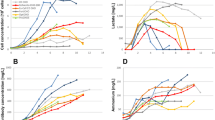
Tyrosine (Tyr) is crucial to the maintenance of the monoclonal antibody (mAb) titers and quality attributes in fed-batch cultures of recombinant Chinese hamster ovary (rCHO) cells. However, the relation between tyrosine and these aspects is not yet fully defined. In order to further elucidate such a relation, two groups of fed-batch experiments with high tyrosine (H-T) or low tyrosine (L-T) additions producing an IgG1 monoclonal antibody against CD20 were implemented to investigate the intracellular and extracellular effects of tyrosine on the culture performance. It was found that the scarcity of tyrosine led to the distinctive reduction in both viable cell density and antibody specific production rate, hence the sharply reduced titer, possibly related to the impaired translation efficiency caused by the substrate limitation of tyrosine. In addition, alterations to the critical quality attributes were detected in the L-T group, compared to those in the H-T condition. Notable decrease in the contents of intact antibody was found under the L-T condition because of the elevated reductive level in the supernatant. Moreover, the aggregate content in the L-T condition was also reduced, probably resulting from the accumulation of extracellular cystine. In particular, the lysine variant content noticeably increased with tyrosine limitation owing to the downregulation of two carboxypeptidases, i.e., CpB and CpH. Overall, understanding the role of tyrosine in these aspects is fundamental to the increase of product titers and control of critical quality attributes in the monoclonal antibody production of rCHO cell fed-batch cultures.
Key points
• Tyrosine is essential in the maintenance of product titers and the control of product qualities in high cell density cultivations in rCHO cell.
• This study revealed the bottleneck of decreased q mAb upon the deficiency of tyrosine.
• The impact of tyrosine on the critical product qualities and the underlying mechanisms were also thoroughly assessed.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
All processed data are available without restriction upon inquiry.
References
Bar-Peled L, Sabatini DM (2014) Regulation of mTORC1 by amino acids. Trends Cell Biol 24(7):400–406. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tcb.2014.03.003
Banks DD, Gadgil HS, Pipes GD, Bondarenko PV, Hobbs V, Scavezze JL, Kim J, Jiang XR, Mukku V, Dillon TM (2008) Removal of cysteinylation from an unpaired sulfhydryl in the variable region of a recombinant monoclonal IgG1 antibody improves homogeneity, stability, and biological activity. J Pharm Sci 97(2):775–790. https://doi.org/10.1002/jps.21014
Brych SR, Gokarn Y, Hultgen H, Stevenson R, Rajan R, Matsumura M (2010) Characterization of antibody aggregation: role of buried, unpaired cysteines in particle formation. J Pharm Sci 99(2):764–781. https://doi.org/10.1002/jps.21868
Chakrabarti A, Chen AW, Varner JD (2011) A review of the mammalian unfolded protein response. Biotechnol Bioeng 108(12):2777–2793. https://doi.org/10.1002/bit.23282
Chen CC, Zhu Y, Evans LB (1989) Phase partitioning of biomolecules: solubilities of amino acids. Biotechnol Prog 5(3):111–118. https://doi.org/10.1002/btpr.5420050309
Clincke ME, Mölleryd C, Zhang Y, Lindskog E, Walsh K, Chotteau V (2013) Very high density of CHO cells in perfusion by ATF or TFF in wave bioreactor™. Part i. effect of the cell density on the process. Biotechnol Progr 29. doi: https://doi.org/10.1002/btpr.1704
Cromwell MEM, Hilario E, Jacobson F (2006) Protein aggregation and bioprocessing. AAPS J 8(3):E572–E579. https://doi.org/10.1208/aapsj080366
Cruz HJ, Freitas CM, Alves PM, Moreira JL, Carrondo MJT (2000) Effects of ammonia and lactate on growth, metabolism, and productivity of BHK cells. Enzym Microb Technol 27(1–2):43–52. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0141-0229(00)00151-4
Dinnis DM, James DC (2005) Engineering mammalian cell factories for improved recombinant monoclonal antibody production: lessons from nature? Biotechnol Bioeng 91(2):180–189. https://doi.org/10.1002/bit.20499
Drew R, Miners JO (1984) The effects of buthionine sulphoximine (BSO) on glutathione depletion and xenobiotic biotransformation. Biochem Pharmacol 33(19):2989–2994. https://doi.org/10.1016/0006-2952(84)90598-7
Du Y, Walsh A, Ehrick R, Xu W, May K, Liu H (2012) Chromatographic analysis of the acidic and basic species of recombinant monoclonal antibodies. mAbs 4(5): 578-585. doi: https://doi.org/10.4161/mabs.21328
Efeyan A, Zoncu R, Sabatini DM (2012) Amino acids and mTORC1: from lysosomes to disease. Trends Mol Med 18(9):524–533. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molmed.2012.05.007
Feeney L, Carvalhal V, Yu XC, Chan B, Michels DA, Wang YJ (2013) Eliminating tyrosine sequence variants in CHO cell lines producing recombinant monoclonal antibodies. Biotechnol Bioeng 110(4):1087–1097. https://doi.org/10.1002/bit.24759
Flydal MI, Martinez A (2013) Phenylalanine hydroxylase: function, structure, and regulation. IUBMB Life 65(4):341–349. https://doi.org/10.1002/iub.1150
Fomina-Yadlin D, Gosink JJ, McCoy R, Follstad B, Morris A, Russell CB, McGrew JT (2013) Cellular responses to individual amino-acid depletion in antibody-expressing and parental CHO cell lines. Biotechnol Bioeng 111(5):965–979. https://doi.org/10.1002/bit.25155
Gramer MJ, Eckblad JJ, Donahue R, Brown J, Shultz C, Vickerman K (2011) Modulation of antibody galactosylation through feeding of uridine, manganese chloride, and galactose. Biotechnol Bioeng 108(7):1591–1602. https://doi.org/10.1002/bit.23075
Grubb S, Guo L, Fisher AE, Brodsky JL (2012) Protein disulfide isomerases contribute differentially to the endoplasmic reticulum–associated degradation of apolipoprotein B and other substrates. Mol Biol Cell 23(4):520–532. https://doi.org/10.1091/mbc.E11-08-0704
Handlogten MM, Zhu M, Ahuja S (2017) Glutathione and thioredoxin systems contribute to recombinant monoclonal antibody interchain disulfide bond reduction during bioprocessing. Biotechnol Bioeng 114(7):1469–1477. https://doi.org/10.1002/bit.26278
Hatahet F, Ruddock LW (2009) Protein disulfide isomerase: a critical evaluation of its function in disulfide bond formation. Antioxid Redox Sign 11(11):2807–2850. https://doi.org/10.1089/ars.2009.2466
Hara K, Yonezawa K, Weng QP, Kozlowski MT, Belham C, Avruch J (1998) Amino acid sufficiency and mTOR regulate p70 S6 kinase and eiF-4E BP1 through a common effector mechanism. J Biol Chem 273(23):14484–14494. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.273.23.14484
Hetz C (2012) The unfolded protein response: controlling cell fate decisions under ER stress and beyond. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 13(2):89–102. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrm3270
Huang YM, Hu WW, Rustandi E, Chang K, Yusuf-Makagiansar H, Ryll T (2010) Maximizing productivity of CHO cell-based fed-batch culture using chemically defined media conditions and typical manufacturing equipment. Biotechnol Prog 26(5):1400–1410. https://doi.org/10.1002/btpr.436
Jing Y, Borys M, Nayak S, Egan S, Qian Y, Pan SH (2012) Identification of cell culture conditions to control protein aggregation of IgG fusion proteins expressed in Chinese hamster ovary cells. Process Biochem 47(1):69–75. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procbio.2011.10.009
Jardon MA, Sattha B, Braasch K, Leung AO, Côté HCF, Butler M, Piret JM (2011) Inhibition of glutamine-dependent autophagy increases t-PA production in CHO cell fed-batch processes. Biotechnol Bioeng 109(5):1228–1238. https://doi.org/10.1002/bit.24393
Ju HK, Hwang SJ, Jeon CJ, Lee GM, Yoon SK (2009) Use of NaCl prevents aggregation of recombinant COMP–angiopoietin-1 in Chinese hamster ovary cells. J Biotechnol 143(2):145–150. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbiotec.2009.06.017
Kang S, Mullen J, Miranda LP, Deshpande R (2012) Utilization of tyrosine- and histidine-containing dipeptides to enhance productivity and culture viability. Biotechnol Bioeng 109(9):2286–2294. https://doi.org/10.1002/bit.24507
Kao YH, Hewitt DP, Trexler-Schmidt M, Laird MW (2010) Mechanism of antibody reduction in cell culture production processes. Biotechnol Bioeng 107(4):622–632. https://doi.org/10.1002/bit.22848
Kilberg MS, Pan YX, Chen H, Leung-Pineda V (2005) Nutritional control of gene expression: how mammalian cells respond to amino acid limitation. Annu Rev Nutr 25(1):59–85. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.nutr.24.012003.132145
Kilberg MS, Shan J, Su N (2009) ATF4-dependent transcription mediates signaling of amino acid limitation. Trends Endocrinol Metab 20(9):436–443. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tem.2009.05.008
Kim NS, Lee GM (2002) Response of recombinant Chinese hamster ovary cells to hyperosmotic pressure: effect of Bcl-2 overexpression. J Biotechnol 95(3):237–248. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0168-1656(02)00011-1
Kimura R, Miller WM (1996) Effects of elevated pCO2 and/or osmolality on the growth and recombinant tPA production of CHO cells. Biotechnol Bioeng 52(1):152–160. https://doi.org/10.1002/(sici)1097-0290(19961005)52:1<152::aid-bit15>3.0.co;2-q
Lacy ER, Baker M, Brigham-Burke M (2008) Free sulfhydryl measurement as an indicator of antibody stability. Anal Biochem 382(1):66–68. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ab.2008.07.016
Lai T, Yang Y, Ng SK (2013) Advances in mammalian cell line development technologies for recombinant protein production. Pharmaceuticals 6(5):579–603. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph6050579
Lichter-Konecki U, Hipke CM, Konecki DS (1999) Human phenylalanine hydroxylase gene expression in kidney and other nonhepatic tissues. Mol Genet Metab 67(4):308–316. https://doi.org/10.1006/mgme.1999.2880
Lin J, Takagi M, Qu Y, Gao P, Yoshida T (1999) Enhanced monoclonal antibody production by gradual increase of osmotic pressure. Cytotechnology 29(1):27–33. https://doi.org/10.1023/a:1008016806599
Liu H, Gaza-Bulseco G, Faldu D, Chumsae C, Sun J (2008) Heterogeneity of monoclonal antibodies. J Pharm Sci 97(7):2426–2447. https://doi.org/10.1002/jps.21180
Luo J, Zhang J, Ren D, Tsai WL, Li F, Amanullah A (2012) Probing of C-terminal lysine variation in a recombinant monoclonal antibody production using Chinese hamster ovary cells with chemically defined media. Biotechnol Bioeng 109(9):2306–2315. https://doi.org/10.1002/bit.24510
Ma XM, Blenis J (2009) Molecular mechanisms of mTOR-mediated translational control. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 10(5):307–318. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrm2672
Mcqueen A, Bailey JE (1990) Effect of ammonium ion and extracellular pH on hybridoma cell metabolism and antibody production. Biotechnol Bioeng 35(11):1067–1077. https://doi.org/10.1002/bit.260351102
Mosser M, Chevalot I, Olmos E, Blanchard F, Kapel R, Oriol E (2013) Combination of yeast hydrolysates to improve CHO cell growth and igG production. Cytotechnology 65(4):629–641. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10616-012-9519-1
Mulukutla BC, Kale J, Kalomeris T, Jacobs M, Hiller GW (2017) Identification and control of novel growth inhibitors in fed-batch cultures of Chinese hamster ovary cells. Biotechnol Bioeng 114:1779–1790. https://doi.org/10.1002/bit.26313
Nishiuch Y, Sasaki M, Nakayasu M, Oikawa A (1976) Cytotoxicity of cysteine in culture media. In Vitro Cell Dev-Pl 12(9): 635–638. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02797462
Nyberg GB, Balcarcel RR, Follstad BD, Stephanopoulos G, Wang DIC (1999) Metabolism of peptide amino acids by Chinese hamster ovary cells grown in a complex medium. Biotechnol Bioeng 62(3):324–335. https://doi.org/10.1002/(sici)1097-0290(19990205)62:3<324::aid-bit9>3.0.co;2-c
Ozturk SS, Palsson BO (1991) Growth, metabolic, and antibody production kinetics of hybridoma cell culture: 1. Analysis of data from controlled batch reactors. Biotechnol Prog 7:471–480. https://doi.org/10.1021/bp00012a001
Ozturk SS, Riley MR, Palsson BO (1992) Effects of ammonia and lactate on hybridoma growth, metabolism, and antibody production. Biotechnol Bioeng 39(4):418–431. https://doi.org/10.1002/bit.260390408
Siu F, Bain PJ, Leblanc-Chaffin R, Chen H, Kilberg MS (2002) ATF4 is a mediator of the nutrient-sensing response pathway that activates the human asparagine synthetase gene. J Bio Chem 277(27):24120–24127. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M201959200
Steve KW, Vig P, Chua F, Teo WK, Yap MGS (1993) Substantial overproduction of antibodies by applying osmotic pressure and sodium butyrate. Biotechnol Bioeng 42:601–610. https://doi.org/10.1002/bit.260420508
Stokes AH, Lewis DY, Lash LH, Jerome WG, Vrana KE (2000) Dopamine toxicity in neuroblastoma cells: role of glutathione depletion by L-BSO and apoptosis. Brain Res 858(1):1–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0006-8993(99)02329-X
Tang H, Zhang X, Zhang W, Fan L, Wang H, Tan WS, Zhao L (2019) Insight into the roles of tyrosine on rCHO cell performance in fed-batch cultures. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 103:6483–6494. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-019-09921-w
Van den Bremer ET, Beurskens FJ, Voorhorst M, Engelberts PJ, De Jong RN, Van der Boom BG, Parren PW (2015) Human IgG is produced in a pro-form that requires clipping of C-terminal lysines for maximal complement activation. MAbs 7(4):672–680. https://doi.org/10.1080/19420862.2015.1046665
Vázquez-Rey M, Lang DA (2011) Aggregates in monoclonal antibody manufacturing processes. Biotechnol Bioeng 108(7):1494–1508. https://doi.org/10.1002/bit.23155
Vlasak J, Ionescu R (2011) Fragmentation of monoclonal antibodies. MAbs 3(3):253–263. https://doi.org/10.4161/mabs.3.3.15608
Vogel C, Marcotte EM (2012) Insights into the regulation of protein abundance from proteomic and transcriptomic analyses. Nat Rev Genet 13:679–232. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrg3185
Wurm F (2004) Production of recombinant protein therapeutics in cultivated mammalian cells. Nat Biotechnol 22:1393–1398. https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt1026
Xiang T, Chumsae C, Liu H (2009) Localization and quantitation of free sulfhydryl in recombinant monoclonal antibodies by differential labeling with 12C and 13C iodoacetic acid and LC−MS analysis. Anal Chem 81(19):8101–8108. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac901311y
Yang M, Butler M (2000) Effects of ammonia on CHO cell growth, erythropoietin production, and glycosylation. Biotechnol Bioeng 68(4):370–380. https://doi.org/10.1002/(SICI)1097-0290(20000520)68:4<370::AID-BIT2>3.0.CO;2-K
Yang WC, Minkler DF, Kshirsagar R, Ryll T, Huang YM (2016) Concentrated fed-batch cell culture increases manufacturing capacity without additional volumetric capacity. J Biotechnol 217:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbiotec.2015.10.009
Yu M, Hu Z, Pacis E, Vijayasankaran N, Shen A, Li F (2011) Understanding the intracellular effect of enhanced nutrient feeding toward high titer antibody production process. Biotechnol Bioeng 108(5):1078–1088. https://doi.org/10.1002/bit.23031
Zhang W, Czupryn MJ (2002) Free sulfhydryl in recombinant monoclonal antibodies. Biotechnol Progr 18(3): 509–513. doi: https://doi.org/10.1021/bp025511z
Zhang X, Tang H, Sun YT, Liu X, Fan L, Tang WS (2015) Elucidating the effects of arginine and lysine on a monoclonal antibody C-terminal lysine variation in CHO cell cultures. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 99(16):6643–6652. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-015-6617-y
Zhang YB, Howitt J, Mccorkle S, Lawrence P, Springer K, Freimuth P (2004) Protein aggregation during overexpression limited by peptide extensions with large net negative charge. Protein Expr Purif 36(2):207–216. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pep.2004.04.020
Zhu MM, Goyal A, Rank DL, Gupta SK, Boom TV, Lee SS (2008) Effects of elevated pCO2 and osmolality on growth of CHO cells and production of antibody-fusion protein B1: a case study. Biotechnol Prog 21:70–77. https://doi.org/10.1021/bp049815s
Zimmer A, Mueller R, Wehsling M, Schnellbaecher A, Hagen JV (2014) Improvement and simplification of fed-batch bioprocesses with a highly soluble phosphotyrosine sodium salt. J Biotechnol 186:110–118. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbiotec.2014.06.026
Funding
This work was supported by the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (No. 22221818014).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
This work does not involve any human participation nor live animals performed by any of the listed authors.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(PDF 251 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, W., Liu, X., Tang, H. et al. Investigation into the impact of tyrosine on the product formation and quality attributes of mAbs in rCHO cell cultures. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 104, 6953–6966 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-020-10744-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-020-10744-3