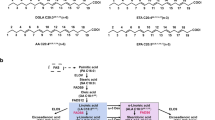
Abstract
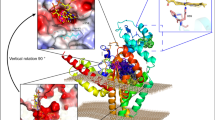
The ω-3 fatty acid desaturase (ω3Des) is a key enzyme in the biosynthesis of polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs). However, the enzyme exhibits a significant preference towards different fatty acid substrates. To examine the molecular mechanism of its substrate specificity, a series of site-directed mutants were constructed based on the membrane topology model and functionally characterised by heterologous expression in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Our results revealed that the W106F and V137T mutations markedly decreased the enzyme activity which indicated that these two residues were associated with substrate recognition. In contrast, the A44S, M156I and W291M mutations showed significant increments (30 to 40%) of the conversion rate for AA substrate desaturation, which suggests that these residues play a pivotal role in desaturation of longer chain-length substrates. Through homology modelling of 3-dimensional structures and molecular docking of FADS15, we propose that the critical residues that bind to the CoA groups may affect substrate localisation and govern substrate preference and chain-length specificity. Our work increases the understanding of the structure-function relationships of the microbial membrane-bound desaturases. The growing knowledge of the molecular mechanism will also aid in the efficient production of value-added fatty acids.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
An L, Pang YW, Gao HM, Tao L, Miao K, Wu ZH, Tian JH (2012) Heterologous expression of C. elegans fat-1 decreases the n-6/n-3 fatty acid ratio and inhibits adipogenesis in 3T3-L1 cells. Biochem Bioph Res Co 428(3):405–410. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2012.10.068
Bai Y, Mccoy JG, Levin EJ, Sobrado P, Rajashankar KR, Fox BG, Zhou M (2015) X-ray structure of a mammalian stearoyl-CoA desaturase. Nature 524(7564):252–256. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature14549
Chandler AM (2005) Treatment for asthma and arthritis and other inflammatory diseases. WO 83:391–395
Chen H, Gu Z, Zhang H, Wang M, Chen W, Lowther WT, Chen YQ (2013) Expression and purification of integral membrane fatty acid desaturases. PLoS One 8(3):e58139. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0058139
Chen Y, Zhang M, Gou K (2010) SDD17 desaturase can convert arachidonic acid to eicosapentaenoic acid in mammalian cells. Biochem Bioph Res Co 394(1):158–162. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2010.02.134
Damude HG, Zhang H, Farrall L, Ripp KG, Tomb JF, Hollerbach D, Yadav NS (2006) Identification of bifunctional delta12/omega3 fatty acid desaturases for improving the ratio of omega3 to omega6 fatty acids in microbes and plants. P Natl Acad Sci USA 103(25):9446–9451. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0511079103
Fu Y, Fan X, Li X, Wang H, Chen H (2013) The desaturase OPIN17 from Phytophthora infestans converts arachidonic acid to eicosapentaenoic acid in CHO cells. Appl Biochem Biotechy 171(4):975–988. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-013-0332-x
Gómez CC, Bermejo López LM, Loria KV (2011) Importance of a balanced omega 6/omega 3 ratio for the maintenance of health: nutritional recommendations. Nutr Hosp 26(2):323. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0212-16112011000200013
Gagne SJ, Reed DW, Gray GR, Covello PS (2009) Structural control of chemoselectivity, stereoselectivity, and substrate specificity in membrane-bound fatty acid acetylenases and desaturases. Biochemistry 48(51):12298–12304. https://doi.org/10.1021/bi901605d
Hoffmann M, Hornung E, Busch S, Kassner N, Ternes P, Braus GH, Feussner I (2007) A small membrane-peripheral region close to the active center determines regioselectivity of membrane-bound fatty acid desaturases from Aspergillus nidulans. J Biol Chem 282(37):26666–26674. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M705068200
Hongsthong A, Subudhi S, Sirijuntarat M, Cheevadhanarak S (2004) Mutation study of conserved amino acid residues of Spirulina Δ6-acyl-lipid desaturase showing involvement of histidine 313 in the regioselectivity of the enzyme. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 66(1):74–84. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-004-1655-x
Hui W, Klein MG, Hua Z, Lane W, Snell G, Levin I, Ke L, Sang BC (2015) Crystal structure of human stearoyl-coenzyme A desaturase in complex with substrate. Nat Struct Mol Biol 22(7):581–585. https://doi.org/10.1038/nsmb.3049
Kikukawa H, Sakuradani E, Kishino S, Park SB, Ando A, Shima J, Ochiai M, Shimizu S, Ogawa J (2013) Characterization of a trifunctional fatty acid desaturase from oleaginous filamentous fungus Mortierella alpina 1S-4 using a yeast expression system. J Biosci Bioeng 116(6):672–676. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbiosc.2013.05.023
Krogh A, Larsson BHG, Ell S (2001) Predicting transmembrane protein topology with a hidden Markov model: application to complete genomes. J Mol Biol 305(3):567–580. https://doi.org/10.1006/jmbi.2000.4315
Li S, Song L, Zhang G, Yin WB, Chen YH, Wang RC, Hu ZM (2011) Newly identified essential amino acid residues affecting Δ8-sphingolipid desaturase activity revealed by site-directed mutagenesis. Biochem Bioph Res Co 416(1–2):165–171. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2011.11.017
Lim ZL, Senger T, Vrinten P (2014) Four amino acid residues influence the substrate chain-length and regioselectivity of Siganus canaliculatus Δ4 and Δ5/6 desaturases. Lipids 49(4):357–367. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11745-014-3880-0
Meesapyodsuk D, Qiu X (2014) Structure determinants for the substrate specificity of acyl-CoA Delta9 desaturases from a marine copepod. ACS Chem Biol 9(4):922–934. https://doi.org/10.1021/cb400675d
Naranong S, Laoteng K, Kittakoop P, Tanticharoen M, Cheevadhanarak S (2006) Targeted mutagenesis of a fatty acid Delta6-desaturase from Mucor rouxii: role of amino acid residues adjacent to histidine-rich motif II. Biochem Bioph Res Co 339(4):1029–1034. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2005.11.115
Oura T, Kajiwara S (2004) Saccharomyces kluyveri FAD3 encodes an omega3 fatty acid desaturase. Microbiology 150(Pt 6):1983–1990. https://doi.org/10.1099/mic.0.27049-0
Oura T, Kajiwara S (2008) Substrate specificity and regioselectivity of delta12 and omega3 fatty acid desaturases from Saccharomyces kluyveri. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 72(12):3174–3179. https://doi.org/10.1271/bbb.80361
Peng J, Schwartz D, Elias JE, Thoreen CC, Cheng D, Marsischky G, Roelofs J, Finley D, Gygi SP (2003) A proteomics approach to understanding protein ubiquitination. Nat Biotechnol 21(8):921–926. https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt849
Pereira SL, Huang YS, Bobik EG, Kinney AJ, Stecca KL, Packer JC, Mukerji P (2004) A novel omega3-fatty acid desaturase involved in the biosynthesis of eicosapentaenoic acid. Biochem J 378(2):665–671. https://doi.org/10.1042/BJ20031319
Roy A, Kucukural A, Zhang Y (2010) I-TASSER: a unified platform for automated protein structure and function prediction. Nat Protoc 5(4):725–738. https://doi.org/10.1038/nprot.2010.5
Sakuradani E, Abe T, Iguchi K, Shimizu S (2005) A novel fungal ω3-desaturase with wide substrate specificity from arachidonic acid-producing Mortierella alpina 1S-4. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 66(6):648–654. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-004-1760-x
Sakuradani E, Abe T, Shimizu S (2009) Identification of mutation sites on omega3 desaturase genes from Mortierella alpina 1S-4 mutants. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 107(1):7–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbiosc.2008.08.001
Sasata RJ, Reed DW, Loewen MC, Covello PS (2004) Domain swapping localizes the structural determinants of regioselectivity in membrane-bound fatty acid desaturases of Caenorhabditis elegans. J Biol Chem 279(38):39296–39302. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M405712200
Sayanova O, Beaudoin F, Libisch B, Castel A, Shewry PR, Napier JA (2001) Mutagenesis and heterologous expression in yeast of a plant D6-fatty acid desaturase. J Exp Bot 52(360):1581–1585. https://doi.org/10.1093/jexbot/52.360.1581
Shi H, Chen H, Gu Z, Song Y, Zhang H, Chen W, Chen YQ (2015) Molecular mechanism of substrate specificity for delta 6 desaturase from Mortierella alpina and Micromonas pusilla. J Lipid Res 56(12):2309–2321. https://doi.org/10.1194/jlr.M062158
Sierecki E, Sinko W, Mccammon JA, Newton AC (2010) Discovery of small molecule inhibitors of the PH domain leucine-rich repeat protein phosphatase (PHLPP) by chemical and virtual screening. J Med Chem 53(19):6899–6911. https://doi.org/10.1021/jm100331d
Song L, Lu W, Hu J, Yin WB, Chen YH, Wang BL, Wang RC, Hu ZM (2013) The role of C-terminal amino acid residues of a Δ6-fatty acid desaturase from blackcurrant. Biochem Bioph Res Co 431(4):675–679. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2013.01.062
Song L, Zhang Y, Li S, Hu J, Yin WB, Chen YH, Hao ST, Wang BL, Wang RR, Hu ZM (2014) Identification of the substrate recognition region in the Δ6-fatty acid and Δ8-sphingolipid desaturase by fusion mutagenesis. Planta 239(4):753–763. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-013-2006-x
Vanden Heuvel JP (2012) Nutrigenomics and nutrigenetics of ω3 polyunsaturated fatty acids. Prog Mol Biol Transl Sci 108:75–112. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-398397-8.00004-6
Wang L, Chen W, Feng Y, Ren Y, Gu Z, Chen H, Wang H, Thomas MJ, Zhang B, Berquin IM (2011) Genome characterization of the oleaginous fungus Mortierella alpina. PLoS One 6(12):e28319. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0028319
Wang M, Chen H, Ailati A, Chen W, Chilton FH, Lowther WT, Chen YQ (2017) Substrate specificity and membrane topologies of the iron-containing ω3 and ω6 desaturases from Mortierella alpina. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 102:211–223. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-017-8585-x
Wang M, Gu Z, Zhang H, Chen W, Chen YQ (2013) Omega 3 fatty acid desaturases from microorganisms: structure, function, evolution, and biotechnological use. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 97(24):10255–10262. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-013-5336-5
Xue Z, He H, Dieter H, Macool DJ, Yadav NS, Zhang H, Bogdan S, Zhu Q (2013) Identification and characterization of new Δ-17 fatty acid desaturases. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 97(5):1973–1985. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-012-4068-2
Zhang P, Liu S, Cong B, Wu G, Liu C, Lin X, Shen J, Huang X (2011) A novel omega-3 fatty acid desaturase involved in acclimation processes of polar condition from Antarctic ice algae Chlamydomonas sp. ICE-L. Mar Biotechnol 13(3):393–401. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10126-010-9309-8
Zhang X, Li M, Wei D, Xing L (2008) Identification and characterization of a novel yeast omega3-fatty acid desaturase acting on long-chain n-6 fatty acid substrates from Pichia pastoris. Yeast 25(1):21–27. https://doi.org/10.1002/yea.1546
Zhang X, Wei D, Li M, Qi Y, Xing L (2009) Evolution-related amino acids play important role in determining regioselectivity of fatty acid desaturase from Pichia pastoris. Mol Biol Rep 36(3):567–573. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-008-9215-6
Funding
This research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 31722041, 31530056), the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (No. JUSRP51702A) and the Jiangsu Province “Collaborative Innovation Center for Food Safety and Quality Control”.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(PDF 143 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rong, C., Chen, H., Wang, M. et al. Molecular mechanism of substrate preference for ω-3 fatty acid desaturase from Mortierella alpina by mutational analysis and molecular docking. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 102, 9679–9689 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-018-9321-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-018-9321-x