Abstract
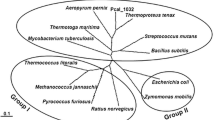
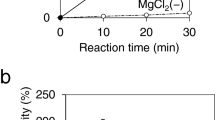
Most of the “repressor, open reading frame, kinase” (ROK) proteins already characterized so far, and exhibiting a kinase activity, take restrictedly d-glucose as substrate. By exploring the sequenced bacterial diversity, 61 ATP-dependent kinases belonging to the ROK family have been identified and experimentally assayed for the phosphorylation of hexoses. These kinases were mainly found to be thermotolerant and highly active toward d-mannose and d-fructose with notable activities toward d-tagatose. Among them, the ATP-dependent kinase from the mesophile Streptococcus mitis (named ScrKmitis) was biochemically characterized and its substrate spectrum further studied. This enzyme possessed impressive catalytic efficiencies toward d-mannose and d-fructose of 1.5 106 s−1 M−1 and 2.7 105 s−1 M−1, respectively, but also significant ones toward d-tagatose (3.5 102 s−1 M−1) and the unnatural monosaccharides d-altrose (1.1 104 s−1 M−1) and d-talose (3.4 102 s−1 M−1). Specific activities measured for all hexoses showed a high stereopreference for d- over l-series. As proof of concept, 8 hexoses were phosphorylated in moderate to good yields, some of them described for the first time like l-sorbose-5-phosphate unusually phosphorylated in position 5. Its thermotolerance, its wide pH tolerance (from 7 to 10), and temperature range (> 85% activity between 40 and 70 °C) open the way to applications in the enzymatic synthesis of monophosphorylated hexoses.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bastard K, Smith AA, Vergne-Vaxelaire C, Perret A, Zaparucha A, De Melo-Minardi R, Mariage A, Boutard M, Debard A, Lechaplais C, Pelle C, Pellouin V, Perchat N, Petit JL, Kreimeyer A, Medigue C, Weissenbach J, Artiguenave F, De Berardinis V, Vallenet D, Salanoubat M (2014) Revealing the hidden functional diversity of an enzyme family. Nat Chem Biol 10(1):42–49. https://doi.org/10.1038/nchembio.1387
Bornscheuer UT (2016) Biocatalysis: successfully crossing boundaries. Angew Chem Int Ed Eng 55(14):4372–4373. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201510042
Charmantray F, Hélaine V, Legeret B, Hecquet L (2009) Preparative scale enzymatic synthesis of d-sedoheptulose-7-phosphate from β-hydroxypyruvate and d-ribose-5-phosphate. J Mol Catal B Enzym 57(1–4):6–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcatb.2008.06.005
Choi JM, Han SS, Kim HS (2015) Industrial applications of enzyme biocatalysis: current status and future aspects. Biotechnol Adv 33:1443–1454. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biotechadv.2015.02.014
Conejo MS, Thompson SM, Miller BG (2010) Evolutionary bases of carbohydrate recognition and substrate discrimination in the ROK protein family. J Mol Evol 70(6):545–556. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00239-010-9351-1
Davids T, Schmidt M, Böttcher D, Bornscheuer UT (2013) Strategies for the discovery and engineering of enzymes for biocatalysis. Curr Opin Chem Biol 17(2):215–220. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbpa.2013.02.022
de Berardinis V, Guérard-Hélaine C, Darii E, Bastard K, Hélaine V, Mariage A, Petit JL, Poupard N, Sánchez-Moreno I, Stam M, Gefflaut T, Salanoubat S, Lemaire M (2017) Expanding the reaction space of aldolases using hydroxypyruvate as a nucleophilic substrate. Green Chem 19:519–526. https://doi.org/10.1039/C6GC02652D
Desvergnes S, Courtiol-Legourd S, Daher R, Dabrowski M, Salmon L, Therisod M (2012) Synthesis and evaluation of malonate-based inhibitors of phosphosugar-metabolizing enzymes: class II fructose-1,6-bis-phosphate aldolases, type I phosphomannose isomerase, and phosphoglucose isomerase. Bioorg Med Chem 20(4):1511–1520. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bmc.2011.12.050
Dorr C, Zaparty M, Tjaden B, Brinkmann H, Siebers B (2003) The hexokinase of the hyperthermophile Thermoproteus tenax. ATP-dependent hexokinases and ADP-dependent glucokinases, two alternatives for glucose phosphorylation in Archaea. J Biol Chem 278(21):18744–18753. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M301914200
Elleuche S, Schröder C, Sahm K, Antranikian G (2014) Extremozymes—biocatalysts with unique properties from extremophilic microorganisms. Curr Opin Biotechnol 29:116–123. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.copbio.2014.04.003
Franke FP, Kapuscinski M, Lyndon P (1985) Synthesis and n.m.r. characterization of intermediates in the l-type pentose phosphate cycle. Carbohydr Res 143:69–76. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0008-6215(00)90696-7
Guérard-Hélaine C, Debacker M, Clapés P, Szekrenyi A, Hélaine V, Lemaire M (2014) Efficient biocatalytic processes for highly valuable terminally phosphorylated C5 to C9 d-ketoses. Green Chem 16(3):1109–1113. https://doi.org/10.1039/c3gc42140f
Guérard-Hélaine C, de Berardinis V, Besnard-Gonnet M, Darii E, Debacker M, Debard A, Fernandes C, Hélaine V, Mariage A, Pellouin V, Perret A, Petit J-L, Sancelme M, Lemaire M, Salanoubat M (2015) Genome mining for innovative biocatalysts: new dihydroxyacetone aldolases for the chemist’s toolbox. ChemCatChem 7(12):1871–1879. https://doi.org/10.1002/cctc.201500014
Hansen T, Reichstein B, Schmid R, Schönheit P (2002) The first Archaeal ATP-dependent glucokinase, from the hyperthermophilic crenarchaeon Aeropyrum pernix, represents a monomeric, extremely thermophilic ROK glucokinase with broad hexose specificity. J Bacteriol 184(21):5955–5965. https://doi.org/10.1128/jb.184.21.5955-5965.2002
Heinonen JK, Lahti RJ (1981) A new and convenient colorimetric determination of inorganic orthophosphate and its application to the assay of inorganic pyrophosphatase. Anal Biochem 113(2):313–317. https://doi.org/10.1016/0003-2697(81)90082-8
Hélaine V, Mahdi R, Sudhir Babu GV, de Berardinis V, Wohlgemuth R, Lemaire M, Guérard-Hélaine C (2015) Straightforward synthesis of terminally phosphorylated L-sugars via multienzymatic cascade reactions. Adv Synth Catal 357(8):1703–1708. https://doi.org/10.1002/adsc.201500190
Holmes KC, Sander C, Valencia A (1993) A new ATP-binding fold in actin, hexokinase and Hsc70. Trends Cell Biol 3(2):53–59. https://doi.org/10.1016/0962-8924(93)90161-S
Howe K, Bateman A, Durbin R (2002) QuickTree: building huge neighbour-joining trees of protein sequences. Bioinformatics 18(11):1546–1547. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/18.11.1546
Jaworek D, Welsch J (1985) Adenosine 5-diphosphate and adenosine 5-monophosphate. In: Bergmeyer HU, Bergmeyer J, Graßl M (eds) Methods Enz Anal, vol 7, pp 365–370
Katoh K, Misawa K, Kuma K, Miyata T (2002) MAFFT: a novel method for rapid multiple sequence alignment based on fast Fourier transform. Nucleic Acids Res 30(14):3059–3066
Koerner Jr TA, Voll RJ, Cary LW, Younathan ES (1980) Carbon-13 nuclear magnetic resonance studies and anomeric composition of ketohexose phosphates in solution. Biochemistry 19(12):2795–2801. https://doi.org/10.1021/bi00553a040
Kreimeyer A, Perret A, Lechaplais C, Vallenet D, Medigue C, Salanoubat M, Weissenbach J (2007) Identification of the last unknown genes in the fermentation pathway of lysine. J Biol Chem 282(10):7191–7197. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M609829200
Kreuzer P, Gartner D, Allmansberger R, Hillen W (1989) Identification and sequence analysis of the Bacillus subtilis W23 xylR gene and xyl operator. J Bacteriol 7(171):3840–3845. https://doi.org/10.1021/bi00553a040
Larion M, Moore LB, Thompson SM, Miller BG (2007) Divergent evolution of function in the ROK sugar kinase superfamily: role of enzyme loops in substrate specificity. Biochemistry 46(47):13564–13572. https://doi.org/10.1021/bi700924d
Letunic I, Bork P (2016) Interactive tree of life (iTOL) v3: an online tool for the display and annotation of phylogenetic and other trees. Nucleic Acids Res 44(W1):W242–W245. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkw290
Littlechild JA (2015) Enzymes from extreme environments and their industrial applications. Front Bioeng Biotechnol 3:161. https://doi.org/10.3389/fbioe.2015.00161
Miller BG, Raines RT (2004) Identifying latent enzyme activities: substrate ambiguity within modern bacterial sugar kinases. Biochemistry 43(21):6387–6392. https://doi.org/10.1021/bi049424m
Mukai T, Kawai S, Matsukawa H, Matuo Y, Murata K (2003) Characterization and molecular cloning of a novel enzyme, inorganic polyphosphate/ATP-glucomannokinase, of Arthrobacter sp. strain KM. Appl Environ Microbiol 69(7):3849–3857. https://doi.org/10.1128/aem.69.7.3849-3857.2003
Nishimasu H, Fushinobu S, Shoun H, Wakagi T (2007) Crystal structures of an ATP-dependent hexokinase with broad substrate specificity from the hyperthermophilic archaeon Sulfolobus tokodaii. J Biol Chem 282(13):9923–9931. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M610678200
Nocek B, Stein AJ, Jedrzejczak R, Cuff ME, Li H, Volkart L, Joachimiak A (2011) Structural studies of ROK fructokinase YdhR from Bacillus subtilis: insights into substrate binding and fructose specificity. J Mol Biol 406(2):325–342. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmb.2010.12.021
Plumbridge J (2001) DNA binding sites for the Mlc and NagC proteins: regulation of nagE, encoding the N-acetylglucosamine-specific transporter in Escherichia coli. Nucleic Acids Res 29(2):506–514. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/29.2.506
Postma PW, Lengeler JW, Jacobson GR (1993) Phosphoenolpyruvate:carbohydrate phosphotransferase systems of bacteria. Microbiol Rev 3(57):543–594
Qian Z, Zhao J, Bai X, Tong W, Chen Z, Wei H, Wang Q, Liu S (2013) Thermal stability of glucokinases in Thermoanaerobacter tengcongensis. Biomed Res Int 2013:646539. https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/646539
Ramos I, Guzman S, Escalante L, Imriskova I, Rodriguez-Sanoja R, Sanchez S, Langley E (2004) Glucose kinase alone cannot be responsible for carbon source regulation in Streptomyces peucetius var. caesius. Res Microbiol 155(4):267–274. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resmic.2004.01.004
Rother C, Gutmann A, Gudiminchi R, Weber H, Lepak A, Nidetzky B (2017) Biochemical characterization and mechanistic analysis of the levoglucosan kinase from Lipomyces starkeyi. Chembiochem 19:596–603. https://doi.org/10.1002/cbic.201700587
Rudolph FB, Fromm HJ (1971) A study on the kinetics and mechanism of D-lyxose and D-xylose activation of the adenosine triphosphatase activity associated with yeast hexokinase. J Biol Chem 7(246):2104–2110
Sánchez-Moreno I, Hélaine V, Poupard N, Charmantray F, Légeret B, Hecquet L, García-Junceda E, Wohlgemuth R, Guérard-Hélaine C, Lemaire M (2012) One-pot cascade reactions using fructose-6-phosphate aldolase: efficient synthesis of D-arabinose 5-phosphate, D-fructose 6-phosphate and analogues. Adv Synth Catal 354(9):1725–1730. https://doi.org/10.1002/adsc.201200150
Sato Y, Poy F, Jacobson GR, Kuramitsu HK (1989) Characterization and sequence analysis of the scrA gene encoding enzyme IIScr of the Streptococcus mutans phosphoenolpyruvate-dependent sucrose phosphotransferase system. J Bacteriol 1(171):263–271. https://doi.org/10.1128/JB.171.1.263-271
Sato Y, Yamamoto Y, Kizaki H, Kuramitsu HK (1993) Isolation, characterization and sequence analysis of the scrK gene encoding fructokinase of Streptococcus mutans. J Gen Microbiol 139(5):921–927. https://doi.org/10.1099/00221287-139-5-921
Schorken U (1998) Thiamin-dependent enzymes as catalysts in chemoenzymatic syntheses. Biochim Biophys Acta 1385(E 2):229–243
Scopes RK, Testolin V, Stoter A, Griffiths-Smith K, Algar EM (1985) Simultaneous purification and characterization of glucokinase, fructokinase and glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase from Zymomonas mobilis. Biochem J 228(3):627–634
Shaeri J, Wright I, Rathbone EB, Wohlgemuth R, Woodley JM (2008) Characterization of enzymatic D-xylulose 5-phosphate synthesis. Biotechnol Bioeng 101(4):761–767. https://doi.org/10.1002/bit.21949
Sizemore C, Buchner E, Rygus T, Witke C, Gotz F, Hillen W (1991) Organization, promoter analysis and transcriptional regulation of the Staphylococcus xylosus xylose utilization operon. Mol Gen Genet 227(3):377–384. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00273926
Solovjeva ON, Kochetov GA (2008) Enzymatic synthesis of d-xylulose 5-phosphate from hydroxypyruvate and d-glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate. J Mol Catal B Enzym 54(3–4):90–92. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcatb.2007.12.016
Sproul AA, Lambourne LT, Jean-Jacques DJ, Kornberg HL (2001) Genetic control of manno(fructo)kinase activity in Escherichia coli. PNAS 98(26):15257–15259. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.211569798
Thompson J, Sackett DL, Donkersloot JA (1991) Purification and properties of fructokinase I from Lactococcus lactis. Localization of scrK on the sucrose-nisin transposon Tn5306. J Biol Chem 33(266):22626–22633
Thompson J, Nguyen NY, Robrish SA (1992) Sucrose fermentation by Fusobacterium mortiferum ATCC 25557: transport, catabolism, and products. J Bacteriol 10(174):3227–3235
Titgemeyer F, Reizer J, Reizer A, Saier MH Jr (1994) Evolutionary relationships between sugar kinases and transcriptional repressors in bacteria. Microbiology 140(Pt 9):2349–2354. https://doi.org/10.1099/13500872-140-9-2349
Uehara T, Park JT (2004) The N-acetyl-D-glucosamine kinase of Escherichia coli and its role in murein recycling. J Bacteriol 186(21):7273–7279. https://doi.org/10.1128/JB.186.21.7273-7279.2004
Vergne-Vaxelaire C, Bordier F, Fossey A, Besnard-Gonnet M, Debard A, Mariage A, Pellouin V, Perret A, Petit J-L, Stam M, Salanoubat M, Weissenbach J, De Berardinis V, Zaparucha A (2013) Nitrilase activity screening on structurally diverse substrates: providing biocatalytic tools for organic synthesis. Adv Synth Catal 355(9):1763–1779. https://doi.org/10.1002/adsc.201201098
Weisser P, Kramer R, Sprenger GA (1996) Expression of the Escherichia coli pmi gene, encoding phosphomannose-isomerase in Zymomonas mobilis, leads to utilization of mannose as a novel growth substrate, which can be used as a selective marker. Appl Environ Microbiol 11(62):4155–4161
Wohlgemuth R (2009) C2-Ketol elongation by transketolase-catalyzed asymmetric synthesis. J Mol Catal B Enzym 61(1–2):23–29. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcatb.2009.04.001
Wohlgemuth R, Liese A, Streit W (2017) Biocatalytic phosphorylations of metabolites: past, present, and future. Trends Biotechnol 35(5):452–465. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tibtech.2017.01.005
Zebiri I, Balieu S, Guilleret A, Reynaud R, Haudrechy A (2011) The chemistry of l-Sorbose. Eur J Org Chem 2011(16):2905–2910. https://doi.org/10.1002/ejoc.201001578
Zembrzuski B, Chilco P, Liu XL, Liu J, Conway T, Scopes R (1992) Cloning, sequencing, and expression of the Zymomonas mobilis fructokinase gene and structural comparison of the enzyme with other hexose kinases. J Bacteriol 11(174):3455–3460
Zhao S, Kumar R, Sakai A, Vetting MW, Wood BM, Brown S, Bonanno JB, Hillerich BS, Seidel RD, Babbitt PC, Almo SC, Sweedler JV, Gerlt JA, Cronan JE, Jacobson MP (2013) Discovery of new enzymes and metabolic pathways using structure and genome context. Nature 502(7473):698–702. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature12576
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Jean-François Gallard (ICSN, France) for 1H-31P NMR experiments, Olek Maciejak and Marie-Jeanne Clément (SABNP, INSERM U 1204—Université d’Evry Val-d’Essonne, Université Paris-Saclay, France) for assistance in 1H and 13C NMR experiments, the Region Ile de France for financial support of the 600 MHz NMR spectrometer, Alain Perret for fruitful discussions and proofreading of the manuscript, and Christine Pelle and Peggy Sirvain for nickel affinity chromatography purification of ScrKmitis. We thank C. Rivoire (the Swiss-Prot Group at the SIB Swiss Institute of Bioinformatics) for earlier Uniprot identifier assignments.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(PDF 2580 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vergne-Vaxelaire, C., Mariage, A., Petit, JL. et al. Characterization of a thermotolerant ROK-type mannofructokinase from Streptococcus mitis: application to the synthesis of phosphorylated sugars. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 102, 5569–5583 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-018-9018-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-018-9018-1