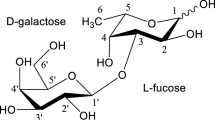
Abstract
Lacto-N-biose (LNB) and galacto-N-biose (GNB) are major building blocks of free oligosaccharides and glycan moieties of glyco-complexes present in human milk and gastrointestinal mucosa. We have previously characterized the phospho-β-galactosidase GnbG from Lactobacillus casei BL23 that is involved in the metabolism of LNB and GNB. GnbG has been used here in transglycosylation reactions, and it showed the production of LNB and GNB with N-acetylglucosamine and N-acetylgalactosamine as acceptors, respectively. The reaction kinetics demonstrated that GnbG can convert 69 ± 4 and 71 ± 1 % of o-nitrophenyl-β-d-galactopyranoside into LNB and GNB, respectively. Those reactions were performed in a semi-preparative scale, and the synthesized disaccharides were purified. The maximum yield obtained for LNB was 10.7 ± 0.2 g/l and for GNB was 10.8 ± 0.3 g/l. NMR spectroscopy confirmed the molecular structures of both carbohydrates and the absence of reaction byproducts, which also supports that GnbG is specific for β1,3-glycosidic linkages. The purified sugars were subsequently tested for their potential prebiotic properties using Lactobacillus species. The results showed that LNB and GNB were fermented by the tested strains of L. casei, Lactobacillus rhamnosus (except L. rhamnosus strain ATCC 53103), Lactobacillus zeae, Lactobacillus gasseri, and Lactobacillus johnsonii. DNA hybridization experiments suggested that the metabolism of those disaccharides in 9 out of 10 L. casei strains, all L. rhamnosus strains and all L. zeae strains tested relies upon a phospho-β-galactosidase homologous to GnbG. The results presented here support the putative role of human milk oligosaccharides for selective enrichment of beneficial intestinal microbiota in breast-fed infants.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Albesharat R, Ehrmann MA, Korakli M, Yazaji S, Vogel RF (2011) Phenotypic and genotypic analyses of lactic acid bacteria in local fermented food, breast milk and faeces of mothers and their babies. Syst Appl Microbiol 34(2):148–155. doi:10.1016/j.syapm.2010.12.001
Ashraf R, Shah NP (2014) Immune system stimulation by probiotic microorganisms. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr 54(7):938–956. doi:10.1080/10408398.2011.619671
Azcarate-Peril MA, Altermann E, Goh YJ, Tallon R, Sanozky-Dawes RB, Pfeiler EA, O'Flaherty S, Buck BL, Dobson A, Duong T, Miller MJ, Barrangou R, Klaenhammer TR (2008) Analysis of the genome sequence of Lactobacillus gasseri ATCC 33323 reveals the molecular basis of an autochthonous intestinal organism. Appl Environ Microbiol 74(15):4610–4625. doi:10.1128/AEM.00054-08
Balogh R, Jankovics P, Beni S (2015) Qualitative and quantitative analysis of N-acetyllactosamine and lacto-N-biose, the two major building blocks of human milk oligosaccharides in human milk samples by high-performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry using a porous graphitic carbon column. J Chromatogr A 1422:140–146. doi:10.1016/j.chroma.2015.10.006
Baugher JL, Durmaz E, Klaenhammer TR (2014) Spontaneously induced prophages in Lactobacillus gasseri contribute to horizontal gene transfer. Appl Environ Microbiol 80(11):3508–3517. doi:10.1128/AEM.04092-13
Becerra JE, Coll-Marques JM, Rodriguez-Diaz J, Monedero V, Yebra MJ (2015) Preparative scale purification of fucosyl-N-acetylglucosamine disaccharides and their evaluation as potential prebiotics and antiadhesins. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 99(17):7165–7176. doi:10.1007/s00253-015-6666-2
Bidart GN, Rodriguez-Diaz J, Monedero V, Yebra MJ (2014) A unique gene cluster for the utilization of the mucosal and human milk-associated glycans galacto-N-biose and lacto-N-biose in Lactobacillus casei. Mol Microbiol 93(3):521–538. doi:10.1111/mmi.12678
Bode L (2012) Human milk oligosaccharides: every baby needs a sugar mama. Glycobiology 22(9):1147–1162. doi:10.1093/glycob/cws074
Denou E, Pridmore RD, Ventura M, Pittet AC, Zwahlen MC, Berger B, Barretto C, Panoff JM, Brussow H (2008) The role of prophage for genome diversification within a clonal lineage of Lactobacillus johnsonii: characterization of the defective prophage LJ771. J Bacteriol 190(17):5806–5813. doi:10.1128/JB.01802-07
Engfer MB, Stahl B, Finke B, Sawatzki G, Daniel H (2000) Human milk oligosaccharides are resistant to enzymatic hydrolysis in the upper gastrointestinal tract. Am J Clin Nutr 71(6):1589–1596
Fujimoto H, Miyasato M, Ito Y, Sasaki T, Ajisaka K (1998) Purification and properties of recombinant beta-galactosidase from Bacillus circulans. Glycoconj J 15(2):155–160
Garrido D, Dallas DC, Mills DA (2013) Consumption of human milk glycoconjugates by infant-associated bifidobacteria: mechanisms and implications. Microbiology 159(Pt 4):649–664. doi:10.1099/mic.0.064113-0
Gasser F, Mandel M (1968) Deoxyribonucleic acid base composition of the genus Lactobacillus. J Bacteriol 96(3):580–588
Hill C, Guarner F, Reid G, Gibson GR, Merenstein DJ, Pot B, Morelli L, Canani RB, Flint HJ, Salminen S, Calder PC, Sanders ME (2014) Expert consensus document. The International Scientific Association for Probiotics and Prebiotics consensus statement on the scope and appropriate use of the term probiotic. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 11(8):506–514. doi:10.1038/nrgastro.2014.66
Honda H, Nagaoka S, Kawai Y, Kemperman R, Kok J, Yamazaki Y, Tateno Y, Kitazawa H, Saito T (2012) Purification and characterization of two phospho-beta-galactosidases, LacG1 and LacG2, from Lactobacillus gasseri ATCC33323(T). J Gen Appl Microbiol 58(1):11–17
Ismail EA, Neve H, Geis A, Heller KJ (2009) Characterization of temperate Lactobacillus gasseri phage LgaI and its impact as prophage on autolysis of its lysogenic host strains. Curr Microbiol 58(6):648–653. doi:10.1007/s00284-009-9384-0
Kalliomaki M, Salminen S, Poussa T, Arvilommi H, Isolauri E (2003) Probiotics and prevention of atopic disease: 4-year follow-up of a randomised placebo-controlled trial. Lancet 361(9372):1869–1871. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(03)13490-3
Lemieux RU, Driguez H (1975) The chemical synthesis of 2-O-(alpha-L-fucopyranosyl)-3-O-(alpha-D-galactopyranosyl)-D-galactose. The terminal structure of the blood-group B antigenic determinant. J Am Chem Soc 97(14):4069–4075
Liu B, Newburg DS (2013) Human milk glycoproteins protect infants against human pathogens. Breastfeed Med 8(4):354–362. doi:10.1089/bfm.2013.0016
Martin R, Heilig GH, Zoetendal EG, Smidt H, Rodriguez JM (2007) Diversity of the Lactobacillus group in breast milk and vagina of healthy women and potential role in the colonization of the infant gut. J Appl Microbiol 103(6):2638–2644. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2672.2007.03497.x
Moran AP, Gupta A, Joshi L (2011) Sweet-talk: role of host glycosylation in bacterial pathogenesis of the gastrointestinal tract. Gut 60(10):1412–1425. doi:10.1136/gut.2010.212704
Moreno-Arribas MV, Polo MC (2008) Occurrence of lactic acid bacteria and biogenic amines in biologically aged wines. Food Microbiol 25(7):875–881. doi:10.1016/j.fm.2008.05.004
Nagaoka S, Honda H, Ohshima S, Kawai Y, Kitazawa H, Tateno Y, Yamazaki Y, Saito T (2008) Identification of five phospho-beta-glycosidases from Lactobacillus gasseri ATCC33323T cultured in lactose medium. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 72(7):1954–1957. doi:10.1271/bbb.80089
Nishimoto M, Kitaoka M (2007a) Identification of N-acetylhexosamine 1-kinase in the complete lacto-N-biose I/galacto-N-biose metabolic pathway in Bifidobacterium longum. Appl Environ Microbiol 73(20):6444–6449. doi:10.1128/AEM.01425-07
Nishimoto M, Kitaoka M (2007b) Practical preparation of lacto-N-biose I, a candidate for the bifidus factor in human milk. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 71(8):2101–2104
Nishimoto M, Kitaoka M (2009) One-pot enzymatic production of beta-D-galactopyranosyl-(1-- > 3)-2-acetamido-2-deoxy-D-galactose (galacto-N-biose) from sucrose and 2-acetamido-2-deoxy-D-galactose (N-acetylgalactosamine). Carbohydr Res 344(18):2573–2576. doi:10.1016/j.carres.2009.09.031
Pedone CA, Arnaud CC, Postaire ER, Bouley CF, Reinert P (2000) Multicentric study of the effect of milk fermented by Lactobacillus casei on the incidence of diarrhoea. Int J Clin Pract 54(9):568–571
Prasad J, Gill H, Smart J, Gopal PK (1998) Selection and characterisation of Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium strains for use as probiotics. Int Dairy J 8(12):993–1002. doi:10.1016/S0958-6946(99)00024-2
Rodriguez-Diaz J, Monedero V (2013) Probiotics against digestive tract viral infections. In: Watson RR, Preedy VR (eds) Bioactive Food as Dietary Interventions for Liver and Gastrointestinal Disease. Academic Press, San Diego, pp. 271–284
Rodriguez-Diaz J, Rubio-del-Campo A, Yebra MJ (2012) Lactobacillus casei ferments the N-Acetylglucosamine moiety of fucosyl-alpha-1,3-N-acetylglucosamine and excretes L-fucose. App Environ Microbiol 78:4613–4619. doi:10.1128/AEM.00474-12
Roy R, Baek MG (2002) Glycodendrimers: novel glycotope isosteres unmasking sugar coding. Case study with T-antigen markers from breast cancer MUC1 glycoprotein. J Biotechnol 90(3–4):291–309
Rubio R, Jofre A, Martin B, Aymerich T, Garriga M (2014) Characterization of lactic acid bacteria isolated from infant faeces as potential probiotic starter cultures for fermented sausages. Food Microbiol 38:303–311. doi:10.1016/j.fm.2013.07.015
Sambrook J, Fritsch EF, Maniatis T (1989) Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual, 2nd edn. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor, NY
Sarmiento-Rubiano LA, Zuniga M, Perez-Martinez G, Yebra MJ (2007) Dietary supplementation with sorbitol results in selective enrichment of lactobacilli in rat intestine. Res Microbiol 158(8–9):694–701. doi:10.1016/j.resmic.2007.07.007
Satoh T, Odamaki T, Namura M, Shimizu T, Iwatsuki K, Nishimoto M, Kitaoka M, Xiao JZ (2013) In vitro comparative evaluation of the impact of lacto-N-biose I, a major building block of human milk oligosaccharides, on the fecal microbiota of infants. Anaerobe 19:50–57. doi:10.1016/j.anaerobe.2012.12.007
Schmaltz RM, Hanson SR, Wong CH (2011) Enzymes in the synthesis of glycoconjugates. Chem Rev 111(7):4259–4307. doi:10.1021/cr200113w
Sun Z, Harris HM, McCann A, Guo C, Argimon S, Zhang W, Yang X, Jeffery IB, Cooney JC, Kagawa TF, Liu W, Song Y, Salvetti E, Wrobel A, Rasinkangas P, Parkhill J, Rea MC, O'Sullivan O, Ritari J, Douillard FP, Paul Ross R, Yang R, Briner AE, Felis GE, de Vos WM, Barrangou R, Klaenhammer TR, Caufield PW, Cui Y, Zhang H, O'Toole PW (2015) Expanding the biotechnology potential of lactobacilli through comparative genomics of 213 strains and associated genera. Nat Commun 6:8322. doi:10.1038/ncomms9322
Szajewska H, Skorka A, Ruszczynski M, Gieruszczak-Bialek D (2013) Meta-analysis: Lactobacillus GG for treating acute gastroenteritis in children--updated analysis of randomised controlled trials. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 38(5):467–476. doi:10.1111/apt.12403
Thurl S, Munzert M, Henker J, Boehm G, Muller-Werner B, Jelinek J, Stahl B (2010) Variation of human milk oligosaccharides in relation to milk groups and lactational periods. Br J Nutr 104(9):1261–1271. doi:10.1017/S0007114510002072
Trincone A (2015) Uncommon Glycosidases for the enzymatic preparation of glycosides. Biomolecules 5(4):2160–2183. doi:10.3390/biom5042160
Turroni F, Ventura M, Butto LF, Duranti S, O'Toole PW, Motherway MO, van Sinderen D (2014) Molecular dialogue between the human gut microbiota and the host: a Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium perspective. Cell Mol Life Sci 71(2):183–203. doi:10.1007/s00018-013-1318-0
Vasquez A, Molin G, Pettersson B, Antonsson M, Ahrne S (2005) DNA-based classification and sequence heterogeneities in the 16S rRNA genes of Lactobacillus casei/paracasei and related species. Syst Appl Microbiol 28(5):430–441. doi:10.1016/j.syapm.2005.02.011
Ventura M, Canchaya C, Pridmore D, Berger B, Brussow H (2003) Integration and distribution of Lactobacillus johnsonii prophages. J Bacteriol 185(15):4603–4608
Vetere A, Miletich M, Bosco M, Paoletti S (2000) Regiospecific glycosidase-assisted synthesis of lacto-N-biose I (Galbeta1-3GlcNAc) and 3'-sialyl-lacto-N-biose I (NeuAcalpha2-3Galbeta1-3GlcNAc). Eur J Biochem 267(4):942–949
Wada J, Ando T, Kiyohara M, Ashida H, Kitaoka M, Yamaguchi M, Kumagai H, Katayama T, Yamamoto K (2008) Bifidobacterium bifidum lacto-N-biosidase, a critical enzyme for the degradation of human milk oligosaccharides with a type 1 structure. Appl Environ Microbiol 74(13):3996–4004. doi:10.1128/AEM.00149-08
Wilstermann M, Magnusson G (1995) Synthesis of disaccharide glycosyl donors suitable for introduction of the beta-D-gal p-(1-- > 3)-alpha-and-beta-D-gal pNAc groups. Carbohydr Res 272(1):1–7
Xiao JZ, Takahashi S, Nishimoto M, Odamaki T, Yaeshima T, Iwatsuki K, Kitaoka M (2010) Distribution of in vitro fermentation ability of lacto-N-biose I, a major building block of human milk oligosaccharides, in bifidobacterial strains. Appl Environ Microbiol 76(1):54–59. doi:10.1128/AEM.01683-09
Yoshida E, Sakurama H, Kiyohara M, Nakajima M, Kitaoka M, Ashida H, Hirose J, Katayama T, Yamamoto K, Kumagai H (2012) Bifidobacterium longum subsp. infantis uses two different beta-galactosidases for selectively degrading type-1 and type-2 human milk oligosaccharides. Glycobiology 22(3):361–368. doi:10.1093/glycob/cwr116
Yu H, Thon V, Lau K, Cai L, Chen Y, Mu S, Li Y, Wang PG, Chen X (2010) Highly efficient chemoenzymatic synthesis of beta1-3-linked galactosides. Chem Commun (Camb) 46(40):7507–7509. doi:10.1039/c0cc02850a
Zhang ZG, Ye ZQ, Yu L, Shi P (2011) Phylogenomic reconstruction of lactic acid bacteria: an update. BMC Evol Biol 11:1. doi:10.1186/1471-2148-11-1
Acknowledgments
This work was financed by funds of the Spanish Ministry for Economy and Competitiveness (MINECO)/FEDER through the Project AGL2014-52996-C2 (1-R and 2-R). G.N.B. was supported by a predoctoral fellowship from the Carolina Foundation and Argentinian Ministry of Education.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Human and animal rights and informed consent
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(PDF 289 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bidart, G.N., Rodríguez-Díaz, J., Palomino-Schätzlein, M. et al. Human milk and mucosal lacto- and galacto-N-biose synthesis by transgalactosylation and their prebiotic potential in Lactobacillus species. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 101, 205–215 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-016-7882-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-016-7882-0