Abstract
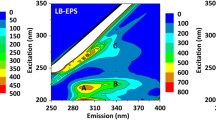
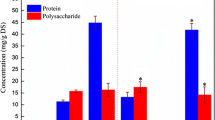
Tightly bound extracellular polymeric substances (TB-EPS) are important components of sludge, playing a crucial role in the behavior of activated sludge. They are located in the innermost layer of EPS which closely combine with the cell surface and are difficult to be extracted. To fully understand the role of TB-EPS, it is extremely important to find an appropriate TB-EPS extraction protocol, which provides maximum yields of TB-EPS under the premise of minimal contribution of cell lysis. Ultrasonic method has been widely applied for TB-EPS extraction due to its unique advantages, but no one has developed a systematic and scientifically optimized method for this protocol. In this study, a novel method based on response surface methodology (RSM) was successfully developed to optimize the conditions of TB-EPS extraction. The optimal conditions were determined at an ultrasound time of 1.00 min, ultrasonic density of 5.59 W/mL and a mixed liquor suspended solid (MLSS) of around 1700–1800 mg/L. Furthermore, combined analysis of microscopy, particle size, and excitation-emission matrix (EEM) was successfully applied to evaluate the optimal conditions. The result indicates that the optimal conditions are efficient, reliable, and reproducible which effectively solves the bottleneck problem of the conflict between cell viability and TB-EPS yield, and little effect on its chemical structure.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adav SS, Lee DJ (2008) Extraction of extracellular polymeric substances from aerobic granule with compact interior structure. J Hazard Mater 154(1–3):1120–1126
Adav SS, Lee DJ, Tay JH (2008) Extracellular polymeric substances and structural stability of aerobic granule. Water Res 42(6–7):1644–1650
APHA (1999) Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater, 19th edn. American Public Health Association, New York
Bala Subramanian S, Yan S, Tyagi RD, Surampalli RY (2010) Extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) producing bacterial strains of municipal wastewater sludge: isolation, molecular identification, EPS characterization and performance for sludge settling and dewatering. Water Res 44(7):2253–2266
Burton K (1956) A study of the conditions and mechanism of the diphenylamine reaction for the colorimetric estimation of deoxyribonucleic acid. Biochem J 2:315–323
Chen W, Westerhoff P, Leenheer JA, Booksh K (2003) Fluorescence excitation-emission matrix regional integration to quantify spectra for dissolved organic matter. Environ Sci Technol 37(24):5701–5710
Coble P (1996) Characterization of marine and terrestrial DOM in seawater using excitation-emission matrix spectroscopy. Environ Microbiol 51(4):325–346(22)
Dominiak DM, Nielsen JL, Nielsen PH (2011) Extracellular DNA is abundant and important for microcolony strength in mixed microbial biofilms. Environ Microbiol 13(3):710–721
Flemming HC, Wingender J (2010) The biofilm matrix. Nat Rev Microbiol 8(9):623–633
Frolund B, Griebe T, Nielsen PH (1995) Enzymatic activity in the activated-sludge floc matrix. Appl Microbiol Biot 43(4):755–761
Han X, Wang Z, Zhu C, Wu Z (2013) Effect of ultrasonic power density on extracting loosely bound and tightly bound extracellular polymeric substances. Desalination 329:35–40
Hou X, Liu S, Zhang Z (2015) Role of extracellular polymeric substance in determining the high aggregation ability of anammox sludge. Water Res 75C:51–62
Huan L, Yiying J, Mahar RB, Zhiyu W, Yongfeng N (2009) Effects of ultrasonic disintegration on sludge microbial activity and dewaterability. J Hazard Mater 161(2–3):1421–1426
Khanal SK, Grewell D, Sung S, Leeuwen J (2007) Ultrasound applications in wastewater sludge pretreatment: a review. Crit Rev Env Sci Tec 37(4):277–313
Korak JA, Dotson AD, Summers RS, Rosario-Ortiz FL (2014) Critical analysis of commonly used fluorescence metrics to characterize dissolved organic matter. Water Res 49:327–338
Li WH, Sheng GP, Liu XW, Yu HQ (2008) Characterizing the extracellular and intracellular fluorescent products of activated sludge in a sequencing batch reactor. Water Res 42(12):3173–3181
Lin H, Zhang M, Wang F, Meng F, Liao B-Q, Hong H, Chen J, Gao W (2014) A critical review of extracellular polymeric substances (EPSs) in membrane bioreactors: characteristics, roles in membrane fouling and control strategies. J Membrane Sci 460:110–125
Loewus FA, Loewus FA (1952) Improvement in anthrone method for determination of carbohydrates. Anal Chem 24(1):219–219
Meng F, Zhou Z, Ni BJ, Zheng X, Huang G, Jia X, Li S, Xiong Y, Kraume M (2011) Characterization of the size-fractionated biomacromolecules: tracking their role and fate in a membrane bioreactor. Water Res 45(15):4661–4671
Ohno T (2002) Fluorescence inner-filtering correction for determining the humification index of dissolved organic matter. Environ Sci Technol 36(4):742–746
Park C, Novak JT (2007) Characterization of activated sludge exocellular polymers using several cation-associated extraction methods. Water Res 41(8):1679–1688
Pellicer-Nacher C, Domingo-Felez C, Mutlu AG, Smets BF (2013) Critical assessment of extracellular polymeric substances extraction methods from mixed culture biomass. Water Res 47(15):5564–5574
Sahinkaya S, Sevimli MF (2013) Effects and modelling of ultrasonic waste-activated sludge disintegration. Water Environ J 27(2):238–246
Sheng GP, Yu HQ (2006) Characterization of extracellular polymeric substances of aerobic and anaerobic sludge using three-dimensional excitation and emission matrix fluorescence spectroscopy. Water Res 40(6):1233–1239
Sheng GP, Yu HQ, Li XY (2010) Extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) of microbial aggregates in biological wastewater treatment systems: a review. Biotechnol Adv 28(6):882–894
Show K-Y, Mao T, Lee D-J (2007) Optimisation of sludge disruption by sonication. Water Res 41(20):4741–4747
Van de Graaf AA, De Bruijn P, Robertson LA, Jetten MSM, Kuenen JG (1996) Autotrophic growth of anaerobic ammonium-oxidizing microorganisms in a fluidized bed reactor. Microbiology-UK 142(3):2187–2196
Wang BB, Chang Q, Peng DC, Hou YP, Li HJ, Pei LY (2014) A new classification paradigm of extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) in activated sludge: separation and characterization of exopolymers between floc level and microcolony level. Water Res 64:53–60
Wang Z, Wu Z, Tang S (2009) Characterization of dissolved organic matter in a submerged membrane bioreactor by using three-dimensional excitation and emission matrix fluorescence spectroscopy. Water Res 43(6):1533–1540
Wilén B-M, Jin B, Lant P (2003) The influence of key chemical constituents in activated sludge on surface and flocculating properties. Water Res 37(9):2127–2139
Wilson HF, Xenopoulos MA (2008) Effects of agricultural land use on the composition of fluvial dissolved organic matter. Nat Geosci 2(1):37–41
Wu Y, Zhou S, Zheng K, Ye X, Qin F (2011) Mathematical model analysis of Fenton oxidation of landfill leachate. Waste Manag 31(3):468–474
Xu J, Sheng GP, Luo HW, Fang F, Li WW, Zeng RJ, Tong ZH, Yu HQ (2011) Evaluating the influence of process parameters on soluble microbial products formation using response surface methodology coupled with grey relational analysis. Water Res 45(2):674–680
Yu GH, He PJ, Shao LM, He PP (2008) Stratification structure of sludge flocs with implications to dewaterability. Environ Sci Technol 42(21):7944–7949
Yu GH, He PJ, Shao LM (2010) Novel insights into sludge dewaterability by fluorescence excitation-emission matrix combined with parallel factor analysis. Water Res 44(3):797–806
Yuan DQ, Wang YL, Feng J (2014) Contribution of stratified extracellular polymeric substances to the gel-like and fractal structures of activated sludge. Water Res 56:56–65
Acknowledgments
This research was financially supported by Nature Science Foundation of China (51478013) and the Funding Projects of Beijing Municipal Commission of Education.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical statement
All of the authors declare that they have no conflict of interest. This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(PDF 391 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jia, F., Yang, Q., Han, J. et al. Modeling optimization and evaluation of tightly bound extracellular polymeric substances extraction by sonication. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 100, 8485–8494 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-016-7748-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-016-7748-5