Abstract
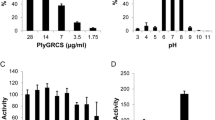
Endolysin from Staphylococcus aureus phage SA97 (LysSA97) was cloned and investigated. LysSA97 specifically lyse the staphylococcal strains and effectively disrupted staphylococcal biofilms. Bioinformatic analysis of LysSA97 revealed a novel putative cell wall binding domain (CBD) as well as two enzymatically active domains (EADs) containing cysteine, histidine-dependent amidohydrolases/peptidases (CHAP, PF05257) and N-acetylmuramoyl-L-alanine amidase (Amidase-3, PF01520) domains. Comparison of 98 endolysin genes of S. aureus phages deposited in GenBank showed that they can be classified into six groups based on their domain composition. Interestingly, approximately 80.61 % of the staphylococcal endolysins have a src-homology 3 (SH3, PF08460) domain as CBD, but the remaining 19.39 %, including LysSA97, has a putative C-terminal CBD with no homology to the known CBD. The fusion protein containing green fluorescent protein and the putative CBD of LysSA97 showed a specific binding spectrum against staphylococcal cells comparable to SH3 domain (PF08460), suggesting that the C-terminal domain of LysSA97 is a novel CBD of staphylococcal endolysins.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altschul SF, Madden TL, Schaffer AA, Zhang J, Zhang Z, Miller W, Lipman DJ (1997) Gapped BLAST and PSI-BLAST: a new generation of protein database search programs. Nucleic Acids Res 25:3389–3402. doi:10.1093/nar/25.17.3389
Archer NK, Mazaitis MJ, Costerton JW, Leid JG, Powers ME, Shirtliff ME (2011) Staphylococcus aureus biofilms properties, regulation and roles in human disease. Virulence 2:445–459. doi:10.4161/viru.2.5.17724
Arciola CR, Montanaro L, Baldassarri L, Borsetti E, Cavedagna D, Donati E (1999) Slime production by staphylococci isolated from prosthesis-associated infections. New Microbiol 22:337–341. doi:10.1007/978-1-4471-3454-1_55
Baba T, Bae T, Schneewind O, Takeuchi F, Hiramatsu K (2008) Genome sequence of Staphylococcus aureus strain Newman and comparative analysis of staphylococcal genomes: polymorphism and evolution of two major pathogenicity islands. J Bacteriol 190:300–310. doi:10.1128/JB.01000-07
Becker SC, Foster-Frey J, Stodola AJ, Anacker D, Donovan DM (2009) Differentially conserved staphylococcal SH3b_5 cell wall binding domains confer increased staphylolytic and streptolytic activity to a streptococcal prophage endolysin domain. Gene 443:32–41. doi:10.1016/j.gene.2009.04.023
Chang Y, Lee JH, Shin H, Heu S, Ryu S (2013) Characterization and complete genome sequence analysis of Staphylococcus aureus bacteriophage SA12. Virus Genes 47:389–393. doi:10.1007/s11262-013-0938-7
Chang Y, Shin H, Lee JH, Park C, Paik S, Ryu S (2015) Isolation and genome characterization of the virulent Staphylococcus aureus bacteriophage SA97. Viruses 7:5225–5242. doi:10.3390/v7102870
Cone LA, Sontz EM, Wilson JW, Mitruka SN (2005) Staphylococcus capitis endocarditis due to a transvenous endocardial pacemaker infection: case report and review of Staphylococcus capitis endocarditis. Int J Infect Dis 9:335–339. doi:10.1016/j.ijid.2004.08.004
Cuong Vuong MO (2002) Staphylococcus epidermidis infections. Microbes Infec 4:481–489. doi:10.1016/S1286-4579(02)01563-0
Daniel B, Saleem M, Naseer G, Fida A (2014) Significance of Staphylococcus haemolyticus in hospital acquired infections. J Pioneer Med Sci 4:119–125
Eugster MR, Haug MC, Huwiler SG, Loessner MJ (2011) The cell wall binding domain of Listeria bacteriophage endolysin PlyP35 recognizes terminal GlcNAc residues in cell wall teichoic acid. Mol Microbiol 81:1419–1432. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2958.2011.07774.x
Fein JE, Rogers HJ (1976) Autolytic enzyme-deficient mutants of Bacillus subtilis 168. J Bacteriol 127:1427–1442
Fenton M, Keary R, McAuliffe O, Ross RP, O’Mahony J, Coffey A (2013) Bacteriophage-derived peptidase CHAPk eliminates and prevents staphylococcal biofilms. Int J Microbiol 2013:625341. doi:10.1155/2013/625341
Fernandes S, Proenca D, Cantante C, Silva FA, Leandro C, Lourenco S, Milheirico C, de Lencastre H, Cavaco-Silva P, Pimentel M, Sao-Jose C (2012) Novel chimerical endolysins with broad antimicrobial activity against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Microb Drug Resist 18:333–343. doi:10.1089/mdr.2012.0025
Finn RD, Bateman A, Clements J, Coggill P, Eberhardt RY, Eddy SR, Heger A, Hetherington K, Holm L, Mistry J, Sonnhammer EL, Tate J, Punta M (2014) Pfam: the protein families database. Nucleic Acids Res 42:D222–D230. doi:10.1093/nar/gkt1223
Fischetti VA (2008) Bacteriophage lysins as effective antibacterials. Curr Opin Microbiol 11:393–400. doi:10.1016/j.mib.2008.09.012
Fox LK, Zadoks RN, Gaskins CT (2005) Biofilm production by Staphylococcus aureus associated with intramammary infection. Vet Microbiol 107:295–299. doi:10.1016/j.vetmic.2005.02.005
Gaeng S, Scherer S, Neve H, Loessner MJ (2000) Gene cloning and expression and secretion of Listeria monocytogenes bacteriophage-lytic enzymes in Lactococcus lactis. Appl Environ Microbiol 66:2951–2958. doi:10.1128/aem.66.7.2951-2958.2000
Grundling A, Schneewind O (2006) Cross-linked peptidoglycan mediates lysostaphin binding to the cell wall envelope of Staphylococcus aureus. J Bacteriol 188:2463–2472. doi:10.1128/JB.188.7.2463-2472.2006
Gu J, Lu R, Liu X, Han W, Lei L, Gao Y, Zhao H, Li Y, Diao Y (2011a) LysGH15B, the SH3b domain of staphylococcal phage endolysin LysGH15, retains high affinity to staphylococci. Curr Microbiol 63:538–542. doi:10.1007/s00284-011-0018-y
Gu J, Xu W, Lei L, Huang J, Feng X, Sun C, Du C, Zuo J, Li Y, Du T, Li L, Han W (2011b) LysGH15, a novel bacteriophage lysin, protects a murine bacteremia model efficiently against lethal methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus infection. J Clin Microbiol 49:111–117. doi:10.1128/JCM.01144-10
Hadzija O (1974) A simple method for the quantitative determination of muramic acid. Anal Biochem 60:512–517. doi:10.1016/0003-2697(74)90261-9
Hazenberg MP, de Visser H (1992) Assay for N-acetylmuramyl-L-alanine amidase in serum by determination of muramic acid released from the peptidoglycan of Brevibacterium divaricatum. Eur J Clin Chem Clin Biochem 30:141–144
Hendrickx AP, van Schaik W, Willems RJ (2013) The cell wall architecture of Enterococcus faecium: from resistance to pathogenesis. Future Microbiol 8:993–1010. doi:10.2217/Fmb.13.66
Hovelius B, Mardh PA (1984) Staphylococcus saprophyticus as a common cause of urinary-tract infections. Rev Infect Dis 6:328–337. doi:10.1093/clinids/6.3.328
Jin JW, Zhang L, Zha XL, Li HL, Qu D (2005) Effect of glucose on biofilm and the gene ica expression in Staphylococcus epidermidis with different biofilm-forming capability. Acta Microbiol Sin 45:431–436
Jones P, Binns D, Chang HY, Fraser M, Li W, McAnulla C, McWilliam H, Maslen J, Mitchell A, Nuka G, Pesseat S, Quinn AF, Sangrador-Vegas A, Scheremetjew M, Yong SY, Lopez R, Hunter S (2014) InterProScan 5: genome-scale protein function classification. Bioinformatics 30:1236–1240. doi:10.1093/bioinformatics/btu031
Kamisango K, Saiki I, Tanio Y, Okumura H, Araki Y, Sekikawa I, Azuma I, Yamamura Y (1982) Structures and biological-activities of peptidoglycans of Listeria monocytogenes and Propionibacterium acnes. J Biochem 92:23–33
Kumar S, Nei M, Dudley J, Tamura K (2008) MEGA: a biologist-centric software for evolutionary analysis of DNA and protein sequences. Brief Bioinform 9:299–306. doi:10.1093/bib/bbn017
Kuroda A, Sekiguchi J (1990) Cloning, sequencing and genetic mapping of a Bacillus subtilis cell wall hydrolase gene. J Gen Microbiol 136:2209–2216. doi:10.1099/00221287-136-11-2209
Larkin MA, Blackshields G, Brown NP, Chenna R, McGettigan PA, McWilliam H, Valentin F, Wallace IM, Wilm A, Lopez R, Thompson JD, Gibson TJ, Higgins DG (2007) Clustal W and Clustal X version 2.0. Bioinformatics 23:2947–2948. doi:10.1093/bioinformatics/btm404
Leive L (1968) Studies on the permeability change produced in coliform bacteria by ethylenediaminetetraacetate. J Biol Chem 243:2373–2380
Loeffler JM, Nelson D, Fischetti VA (2001) Rapid killing of Streptococcus pneumoniae with a bacteriophage cell wall hydrolase. Science 294:2170–2172. doi:10.1126/science.1066869
Loessner MJ (2005) Bacteriophage endolysins-current state of research and applications. Curr Opin Microbiol 8:480–487. doi:10.1016/j.mib.2005.06.002
Loessner MJ, Kramer K, Ebel F, Scherer S (2002) C-terminal domains of Listeria monocytogenes bacteriophage murein hydrolases determine specific recognition and high-affinity binding to bacterial cell wall carbohydrates. Mol Microbiol 44:335–349. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2958.2002.02889.x
Melchior MB, Vaarkamp H, Fink-Gremmels J (2006) Biofilms: a role in recurrent mastitis infections? Vet J 171:398–407. doi:10.1016/j.tvjl.2005.01.006
Moreira JMR, Gomes LC, Araujo JDP, Miranda JM, Simoes M, Melo LF, Mergulhao FJ (2013) The effect of glucose concentration and shaking conditions on Escherichia coli biofilm formation in microtiter plates. Chem Eng Sci 94:192–199. doi:10.1016/j.ces.2013.02.045
Obeso JM, Martinez B, Rodriguez A, Garcia P (2008) Lytic activity of the recombinant staphylococcal bacteriophage phiH5 endolysin active against Staphylococcus aureus in milk. Int J Food Microbiol 128:212–218. doi:10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2008.08.010
Oliveira H, Azeredo J, Lavigne R, Kluskens LD (2012) Bacteriophage endolysins as a response to emerging foodborne pathogens. Trends Food Sci Tech 28:103–115. doi:10.1016/j.tifs.2012.06.016
Oliveira H, Melo LD, Santos SB, Nobrega FL, Ferreira EC, Cerca N, Azeredo J, Kluskens LD (2013) Molecular aspects and comparative genomics of bacteriophage endolysins. J Virol 87:4558–4570. doi:10.1128/JVI.03277-12
Park KH, Kurokawa K, Zheng L, Jung DJ, Tateishi K, Jin JO, Ha NC, Kang HJ, Matsushita M, Kwak JY, Takahashi K, Lee BL (2010) Human serum mannose-binding lectin senses wall teichoic acid Glycopolymer of Staphylococcus aureus, which is restricted in infancy. J Biol Chem 285:27167–27175. doi:10.1074/jbc.M110.141309
Park J, Yun J, Lim JA, Kang DH, Ryu S (2012) Characterization of an endolysin, LysBPS13, from a Bacillus cereus bacteriophage. FEMS Microbiol Lett 332:76–83. doi:10.1111/j.1574-6968.2012.02578.x
Regulski K, Courtin P, Kulakauskas S, Chapot-Chartier MP (2013) A novel type of peptidoglycan-binding domain highly specific for amidated D-asp cross-bridge, identified in Lactobacillus casei bacteriophage endolysins. J Biol Chem 288:20416–20426. doi:10.1074/jbc.M112.446344
Salazar JK, Wu ZC, Yang WX, Freitag NE, Tortorello ML, Wang H, Zhang W (2013) Roles of a novel Crp/Fnr family transcription factor Lmo0753 in soil survival, biofilm production and surface attachment to fresh produce of Listeria monocytogenes. PLoS One 8:e75736. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0075736
Schleifer KH, Kandler O (1972) Peptidoglycan types of bacterial cell walls and their taxonomic implications. Bacteriol Rev 36:407–477
Schmelcher M, Shen Y, Nelson DC, Eugster MR, Eichenseher F, Hanke DC, Loessner MJ, Dong S, Pritchard DG, Lee JC, Becker SC, Foster-Frey J, Donovan DM (2015) Evolutionarily distinct bacteriophage endolysins featuring conserved peptidoglycan cleavage sites protect mice from MRSA infection. J Antimicrob Chemoth 70:1453–1465. doi:10.1093/jac/dku552
Shen Y, Koller T, Kreikemeyer B, Nelson DC (2013) Rapid degradation of Streptococcus pyogenes biofilms by PlyC, a bacteriophage-encoded endolysin. J Antimicrob Chemother 68:1818–1824. doi:10.1093/jac/dkt104
Simoes LC, Simoes M, Vieira MJ (2007) Biofilm interactions between distinct bacterial genera isolated from drinking water. Appl Environ Microbiol 73:6192–6200. doi:10.1128/Aem.00837-07
Son JS, Lee SJ, Jun SY, Yoon SJ, Kang SH, Paik HR, Kang JO, Choi YJ (2010) Antibacterial and biofilm removal activity of a podoviridae Staphylococcus aureus bacteriophage SAP-2 and a derived recombinant cell-wall-degrading enzyme. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 86:1439–1449. doi:10.1007/s00253-009-2386-9
Son B, Yun J, Lim JA, Shin H, Heu S, Ryu S (2012) Characterization of LysB4, an endolysin from the Bacillus cereus-infecting bacteriophage B4. BMC Microb 12:33. doi:10.1186/1471-2180-12-33
Szweda P, Schielmann M, Kotlowski R, Gorczyca G, Zalewska M, Milewski S (2012) Peptidoglycan hydrolases-potential weapons against Staphylococcus aureus. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 96:1157–1174. doi:10.1007/s00253-012-4484-3
Theodoros Kelesidis ST (2010) Staphylococcus intermedius is not only a zoonotic pathogen, but may also cause skin abscesses in humans after exposure to saliva. Int J Infect Dis 14:e838–e841. doi:10.1016/j.ijid.2010.02.2249
Voineagu L, Braga V, Botnarciuc M, Barbu A, Tataru M (2012) Emergence of Staphylococcus hominis strains in general infections. ARS Medica Tomitana 18:80–82. doi:10.2478/v10307-012-0016-8
Won YS, Kwon HJ, Oh GT, Kim BH, Lee CH, Park YH, Hyun BH, Choi YK (2002) Identification of Staphylococcus xylosus isolated from C57BL/6 J-Nos2 tm1Lau mice with dermatitis. Microbiol Immunol 46:629–632
Wu JA, Kusuma C, Mond JJ, Kokai-Kun JF (2003) Lysostaphin disrupts Staphylococcus aureus and Staphylococcus epidermidis biofilms on artificial surfaces. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 47:3407–3414. doi:10.1128/aac.47.11.3407-3414.2003
Yang H, Zhang Y, Huang Y, Yu J, Wei H (2014a) Degradation of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus biofilms using a chimeric lysin. Biofouling 30:667–674. doi:10.1080/08927014.2014.905927
Yang H, Zhang Y, Yu J, Huang Y, Zhang XE, Wei H (2014b) Novel chimeric lysin with high-level antimicrobial activity against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in vitro and in vivo. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 58:536–542. doi:10.1128/AAC.01793-13
Acknowledgments
We thank Dr. Bok Luel Lee at Pusan National University for sharing S. aureus strains (Newman and RN4220 wild-type strains). This work was supported by Agriculture, Food and Rural Affairs Research Center Support Program, Ministry of Agriculture, Food and Rural Affairs, and the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grant funded by the MSIP (NRF-2014R1A2A1A10051563), Republic of Korea.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(PDF 331 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chang, Y., Ryu, S. Characterization of a novel cell wall binding domain-containing Staphylococcus aureus endolysin LysSA97. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 101, 147–158 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-016-7747-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-016-7747-6