Abstract
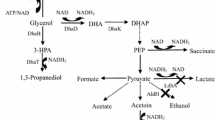
The microbiological production of 2,3-butanediol (2,3-BDO) has attracted considerable attention as an alternative way to produce high-value chemicals from renewable sources. Among the number of 2,3-BDO-producing microorganisms, Klebsiella pneumoniae has been studied most extensively and is known to produce large quantity of 2,3-BDO from a range of substrates. On the other hand, the pathogenic characteristics of the bacteria have limited its industrial applications. In this study, two major virulence traits, outer core LPS and fimbriae, were removed through homologous recombination from 2,3-BDO-producing K. pneumoniae 2242 to expand its uses to the industrial scale. The K. pneumoniae 2242 ∆wabG mutant strain was found to have an impaired capsule, which significantly reduced its ability to bind to the mucous layer and evade the phagocytic activity of macrophage. The association with the human ileocecal epithelial cell, HCT-8, and the bladder epithelial cell, T-24, was also reduced dramatically in the K. pneumoniae 2242 ∆fimA mutant strain that was devoid of fimbriae. However, the growth rate and production yield for 2,3-BDO were unaffected. The K. pneumoniae strains developed in this study, which are devoid of the major virulence factors, have a high potential for the efficient and sustainable production of 2,3-BDO.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Afschar A, Rossell CV, Jonas R, Chanto AQ, Schaller K (1993) Microbial production and downstream processing of 2, 3-butanediol. J Biotechnol 27(3):317–329
Auwerx J (1991) The human leukemia cell line, THP-1: a multifacetted model for the study of monocyte-macrophage differentiation. Experientia 47(1):22–31
Blumenkrantz N, Asboe-Hansen G (1973) New method for quantitative determination of uronic acids. Anal Biochem 54:484–9
Celińska E, Grajek W (2009) Biotechnological production of 2, 3-butanediol—current state and prospects. Biotechnol Adv 27(6):715–725
Cryz S, Pitt T, Fürer E, Germanier R (1984) Role of lipopolysaccharide in virulence of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Infect Immun 44:508–513
De Mas C, Jansen NB, Tsao GT (1988) Production of optically active 2, 3‐butanediol by Bacillus polymyxa. Biotechnol Bioeng 31(4):366–377
Di Martino P, Cafferini N, Joly B, Darfeuille-Michaud A (2003) Klebsiella pneumoniae type 3 pili facilitate adherence and biofilm formation on abiotic surfaces. Res Microbiol 154(1):9–16
Domenico P, Schwartz S, Cunha BA (1989) Reduction of capsular polysaccharide production in Klebsiella pneumoniae by sodium salicylate. Infect Immun 57(12):3778–3782
Fader RC, Duffy L, Davis CP, Kurosky A (1982) Purification and chemical characterization of type 1 pili isolated from Klebsiella pneumoniae. J Biol Chem 257(6):3301–3305
Favre-Bonté S, Licht TR, Forestier C, Krogfelt KA (1999) Klebsiella pneumoniae capsule expression is necessary for colonization of large intestines of streptomycin-treated mice. Infect Immun 67(11):6152–6156
Favre-Bonte S, Joly B, Forestier C (1999) Consequences of reduction of Klebsiella pneumoniae capsule expression on interactions of this bacterium with epithelial cells. Infect Immun 67(2):554–561
Firon N, Ofek I, Sharon N (1984) Carbohydrate-binding sites of the mannose-specific fimbrial lectins of Enterobacteria. Infect Immun 43(3):1088–1090
Fresno S, Jiménez N, Izquierdo L, Merino S, Corsaro MM, De Castro C, Parrilli M, Naldi T, Regué M, Tomás JM (2006) The ionic interaction of Klebsiella pneumoniae K2 capsule and core lipopolysaccharide. Microbiology 152(6):1807–1818
Gasser O, Hess C, Miot S, Deon C, Sanchez J-C (2003) Characterisation and properties of ectosomes released by human polymorphonuclear neutrophils. Exp Cell Res 285(2):243–257
Gerlach G-F, Clegg S, Allen BL (1989) Identification and characterization of the genes encoding the type 3 and type 1 fimbrial adhesins of Klebsiella pneumoniae. J Bacteriol 171(3):1262–1270
Highsmith RC (1985) Floating and algal rafting as potential dispersal mechanisms in brooding invertebrates. Mar Ecol Prog Ser Oldendorf 25(2):169–179
Hornick D, Dayton C, Bedell G, Fick R (1988) Nontuberculous mycobacterial lung disease. Substantiation of a less aggressive approach. CHEST J 93(3):550–555
Jarvis WR, Munn VP, Highsmith AK, Culver DH, Hughes JM (1985) The epidemiology of nosocomial infections caused by Klebsiella pneumoniae. Infect Cont 6(02):68–74
Jung S-G, Jang J-H, Kim A-Y, Lim M-C, Kim B, Lee J, Kim Y-R (2013) Removal of pathogenic factors from 2, 3-butanediol-producing Klebsiella species by inactivating virulence-related wabg gene. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 97(5):1997–2007
Kabha K, Nissimov L, Athamna A, Keisari Y, Parolis H, Parolis L, Grue RM, Schlepper-Schafer J, Ezekowitz A, Ohman DE (1995) Relationships among capsular structure, phagocytosis, and mouse virulence in Klebsiella pneumoniae. Infect Immun 63(3):847–852
Lee H, Maddox I (1986) Continuous production of 2, 3-butanediol from whey permeate using Klebsiella pneumoniae immobilized in calcium alginate. Enz Microbial Technol 8(7):409–411
Link AJ, Phillips D, Church GM (1997) Methods for generating precise deletions and insertions in the genome of wild-type Escherichia coli: application to open reading frame characterization. J Bacteriol 179(20):6228–6237
Maayan MC, Ofek I, Medalia O, Aronson M (1985) Population shift in mannose-specific fimbriated phase of Klebsiella pneumoniae during experimental urinary tract infection in mice. Infect Immun 49(3):785–789
Matatov R, Goldhar J, Skutelsky E, Sechter I, Perry R, Podschun R, Sahly H, Thankavel K, Abraham SN, Ofek I (1999) Inability of encapsulated Klebsiella pneumoniae to assemble functional type 1 fimbriae on their surface. FEMS Microbiol Lett 179(1):123–130
Nan H, Seo S-O, Oh EJ, Seo J-H, Cate JH, Jin Y-S (2014) 2, 3-Butanediol production from cellobiose by engineered Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 98(12):5757–5764
Nelson AL, Roche AM, Gould JM, Chim K, Ratner AJ, Weiser JN (2007) Capsule enhances pneumococcal colonization by limiting mucus-mediated clearance. Infect Immun 75(1):83–90
Ng CY, M-y J, Lee J, Oh M-K (2012) Production of 2, 3-butanediol in Saccharomyces cerevisiae by in silico aided metabolic engineering. Microbial Cell Fact 11:68
Perego P, Converti A, Del Borghi A, Canepa P (2000) 2,3-Butanediol production by Enterobacter aerogenes: selection of the optimal conditions and application to food industry residues. Bioproc Eng 23(6):613–620
Podschun R, Ullmann U (1998) Klebsiella spp. as nosocomial pathogens: epidemiology, taxonomy, typing methods, and pathogenicity factors. Clin Microbiol Rev 11(4):589–603
Raetz CR, Whitfield C (2002) Lipopolysaccharide endotoxins. Ann Rev Biochem 71:635
Rim KB, Park JH, Oh MK, Lee JW (2012) Enhanced 2, 3-butanediol production in recombinant Klebsiella pneumoniae via overexpression of synthesis-related genes. J Microbiol Biotechnol 22(9):1258–1263
Ryan PA, Pancholi V, Fischetti VA (2001) Group A Streptococci bind to mucin and human pharyngeal cells through sialic acid-containing receptors. Infect Immun 69(12):7402–7412
Sahly H, Podschun R, Oelschlaeger TA, Greiwe M, Parolis H, Hasty D, Kekow J, Ullmann U, Ofek I, Sela S (2000) Capsule impedes adhesion to and invasion of epithelial cells by Klebsiella pneumoniae. Infect Immun 68(12):6744–6749
Sawitzke JA, Thomason LC, Costantino N, Bubunenko M, Datta S, Court DL (2007) Recombineering: in vivo genetic engineering in E. coli, S. enterica, and beyond. Methods Enzymol 421:171–199
Schembri MA, Blom J, Krogfelt KA, Klemm P (2005) Capsule and fimbria interaction in Klebsiella pneumoniae. Infect Immun 73(8):4626–4633
Schild S, Lamprecht A-K, Fourestier C, Lauriano CM, Klose KE, Reidl J (2005) Characterizing lipopolysaccharide and core lipid A mutant O1 and O139 Vibrio cholerae strains for adherence properties on mucus-producing cell line HT29-Rev MTX and virulence in mice. Int J Med Microbiol 295(4):243–251
Shi L, Ardehali R, Caldwell KD, Valint P (2000) Mucin coating on polymeric material surfaces to suppress bacterial adhesion. Coll Surf B: Biointerfaces 17(4):229–239
Snyder J, Walker W (1987) Structure and function of intestinal mucin: developmental aspects. Int Arch Allergy Immunol 82(3–4):351–356
Spencer R (1996) Predominant pathogens found in the European prevalence of infection in intensive care study. Europ J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis 15(4):281–285
Strettoti CW, Ristuccia PA, Cunha BA (1984) Topics in clinical microbiology Klebsiella. Infect Cont 5(07):343–348
Struve C, Krogfelt KA (2003) Role of capsule in Klebsiella pneumoniae virulence: lack of correlation between in vitro and in vivo studies. FEMS Microbiol Lett 218(1):149–154
Tarkkanen A-M, Virkola R, Clegg S, Korhonen TK (1997) Binding of the type 3 fimbriae of Klebsiella pneumoniae to human endothelial and urinary bladder cells. Infect Immun 65(4):1546–1549
Tarkkanen A, Allen BL, Williams P, Kauppi M, Haahtela K, Siitonen A, Orskov I, Orskov F, Clegg S, Korhonen T (1992) Fimbriation, capsulation, and iron-scavenging systems of Klebsiella strains associated with human urinary tract infection. Infect Immun 60(3):1187–1192
Vishwanath S, Ramphal R (1984) Adherence of Pseudomonas aeruginosa to human tracheobronchial mucin. Infect Immun 45(1):197–202
Williams P, Tomas J (1990) The pathogenicity of Klebsiella pneumoniae. Rev Med Microbiol 1:196–204
Xiu Z-L, Zeng A-P (2008) Present state and perspective of downstream processing of biologically produced 1,3-propanediol and 2,3-butanediol. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 78(6):917–926
Yinnon A, Butnaru A, Raveh D, Jerassy Z, Rudensky B (1996) Klebsiella bacteraemia: community versus nosocomial infection. QJM 89(12):933–942
Zeng A-P, Biebl H, Deckwer W-D (1990) Effect of pH and acetic acid on growth and 2,3-butanediol production of Enterobacter aerogenes in continuous culture. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 33(5):485–489
Zeng A-P, Sabra W (2011) Microbial production of diols as platform chemicals: recent progresses. Curr Opin Biotechnol 22(6):749–757
Funding
This study was funded by the R&D Program of MKE/KEIT (No. 10035578, development of 2,3-butanediol and derivative production technology for the C-Zero bio-platform industry).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Compliance with ethical standards
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Fig. S1
The correlation between OD and cell mass of K. pneumoniae 2242 and its isogenic mutant strains in LB culture at 37°C for 16 h (PDF 58 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huynh, D.T.N., Kim, AY., Seol, IH. et al. Inactivation of the virulence factors from 2,3-butanediol-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae . Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 99, 9427–9438 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-015-6861-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-015-6861-1