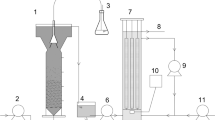
Abstract
A bench scale system consisting of an up-flow packed bed bioreactor (UAPBR) made of polyurethane foam was used for the treatment and regeneration of aqueous solution of ferrous-NTA scrubbed with nitric oxide (NO). The biomass in the UAPBR was sequentially acclimatized under denitrifying and iron reducing conditions using ethanol as electron donor, after which nitric oxide (NO) gas was loaded continuously to the system by absorption. The system was investigated for different parameters viz. pH, removal efficiency of nitric oxide, biological reduction efficiency of FeIINTA-NO and COD utilization. The FeIINTA-NO reduction efficiency reached 87.8 % at a loading rate of 0.24 mmol L−1 h−1, while the scrubber efficiency reached more than 75 % with 250 ppm NO. Stover-Kincannon and a Plug-flow kinetic model based on Michaelis-Menten equation were used to describe the UAPBR performance with respect to FeIINTA-NO and COD removal. The Stover-Kincannon model was found capable of describing the FeIINTA-NO reduction (R m = 8.92 mM h−1 and K NO = 11.46 mM h−1) while plug-flow model provided better fit to the COD utilization (U m = 66.62 mg L−1 h−1, K COD = 7.28 mg L−1). Analyses for pH, FeIIINTA, ammonium, nitrite concentration, and FTIR analysis of the medium samples indicated degradation of NTA, which leads to ammonium and nitrite accumulation in the medium, and affect the regeneration process.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahn JH, Forster CF (2000) Kinetic analyses of the operation of mesophilic and thermophilic anaerobic filters treating a simulated starch wastewater. Process Biochem 36:19–23
American Public Health Association (APHA) (2005) Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater, 19th edn. American Public Health Association, Washington DC
Chandrashekhar B, Pai P, Morone A, Sahu N, Pandey RA (2013) Reduction of NOx in Fe-EDTA and Fe-NTA solutions by an enriched bacterial population. Bioresour Technol 130:644–651
Demmink JF, Beenackers AACM (1998) Gas desulfurization with ferric chelates of EDTA and HEDTA: new model for the oxidative absorption of hydrogen sulfide. Ind Eng Chem Res 37(4):1444–1453
DiChristina TJ (1992) Effects of nitrate and nitrite on dissimilatory iron reduction by Shewanellaputrefaciens 200. J Bacteriol 174:1891–1896
Dilmore R (2005) Evaluation of the kinetics of biologically catalyzed treatment and regeneration of NOx scrubbing process waters. Doctoral Thesis. University of Pittsburgh, 224 p
Dilmore R, Neufeld RD, Hammack RW (2009) Kinetics of chemoheterotrophic microbially mediated reduction of ferric EDTA and the nitrosyl adduct of ferrous EDTA for the treatment and regeneration of spent nitric oxide scrubber liquor. Water Environ Res 79(5):479–487
Dong X, Zhang Y, Zhou J, Chen M, Wang X, Shi Z (2013) Fe(II)EDTA-NO reduction coupled with Fe(II)EDTA oxidation by a nitrate- and Fe(III)-reducing bacterium. Bioresour Technol 138:339–344
Egli T, Weilenmann HU (1986) Biodegradation of NTA in the absence of oxygen. Experientia 42:1061–1062
Enfors SO, Molin N (1973) Biodegradation of nitrilotriacetate (NTA) by bacteria—II. Cultivation of an NTA-degrading bacterium in anaerobic medium. Water Res 7(6):889–893
Gallego AH, Moreira MT, Feijoo G (2009) Quantification of eutrophic aerial compounds in Galicia. Atmosfera 22(2):161–174
Hsieh YHP, Hsieh YP (1997) Valence state of iron in the presence of ascorbic acid and ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid. J Agric Food Chem 45:1126–1129
Kumaraswamy R, Sjollemab K, Kuenena G, Mv L, Muyzer G (2006) Nitrate-dependent [Fe(II)EDTA]2− oxidation by Paracoccusferrooxidans sp. nov., isolated from a denitrifying bioreactor. Syst Appl Microbiol 29:276–286
Li W, Wu C-Z, Zhang S-H, Shao K, Shi Y (2007) Evaluation of microbial reduction Fe(III)EDTA in a chemical absorption–biological reduction integrated NOx removal system. Environ Sci Technol 41:639–644
Lima CAA, Ribeiro R, Foresti E, Zaiat M (2005) Morphological study of biomass during the start-up period of a fixed-bed anaerobic reactor treating domestic sewage. Braz Arch Biol Technol 48(5):841–849
Lovley DR, Blunt-Harris EL (1999) Role of humic bound iron as an electron transfer agent in dissimilatory Fe(III) reduction. Appl Environ Microbiol 65:4252–4254
Luu Y, Ramsay JA (2003) Nitrilotriacetate stimulation of anaerobic Fe(III) respiration by mobilization of humic materials in soil. Appl Environ Microbiol 69:5255–5262
Manconi I, van der Maas P, Lens P (2006) Effect of sulfur compounds on biological reduction of nitric oxide in aqueous Fe(II)EDTA2− solutions. Nitric Oxide-Biol Ch 15(1):40–49
Obuekwe CO, Westlake DWS, Cook FD (1981) Effect of nitrate on reduction of ferric iron by a bacterium isolated from crude oil. Can J Microbiol 27:692–697
Olivieri D, Scoditti E (2005) Impact of environmental factors on lung defenses. Eur Respir Rev 14:51–56
Pandey RA, Chandrashekhar B (2014) Physicochemical and biochemical approaches for treatment of gaseous emissions containing NOx. Crit Rev Environ Sci Technol 44(1):34–96
Park W, Nam YK, Lee MJ, Kim TH (2009) Anaerobic ammonia-oxidation coupled with Fe3+ reduction by an anaerobic culture from a piggery wastewater acclimated to NH4 +/Fe3+ medium. Biotechnol Bioprocess Eng 14(5):680–685
Qureshi N, Annous BA, Ezeji TC, Karcher P, Maddox IS (2005) Biofilm reactors for industrial bioconversion processes: employing potential of enhanced reaction rates. Microb Cell Fact 4:24
Rittmann BE, McCarty PL (2001) Environmental biotechnology: principles and applications. McGraw-Hill, New York
Schneppensieper T, Finkler S, Czap A, van Eldik R, Heus M, Nieuwenhuizen P, Wreesmann C, Abma W (2001) Tuning the reversible binding of NO to iron (II) aminocarboxylate and related complexes in aqueous solution. Eur J Inorg Chem 2:491–501
Shrestha J, Rich JJ, Ehrenfeld JG, Jaffe PR (2009) Oxidation of ammonium to nitrite under iron-reducing conditions in wetland soils: laboratory field demonstrations, and push-pull rate determination. Soil Sci 174(3):156–164
Stover EL, Kincannon DI (1982) Rotating biological contactor scale-up and design, Proc. of the 1st. International Conference on fixed film Biological Processes, 1–21 Kings Island. Ohio.
Van der Maas P, Peng S, Klapwijk B, Lens P (2005) Enzymatic versus non enzymatic conversions during the reduction of EDTA-chelated Fe(III) in BioDeNOx reactors. Environ Sci Technol 39:2616–2623
van der Maas P, Manconi I, Klapwijk B, Lens P (2008) Nitric oxide reduction in BioDeNOx reactors: kinetics and mechanism. Biotechnol Bioeng 100:1099–1107
Viollier E, Inglett PW, Hunter K, Roychoudhury AN, Van Cappellen P (2000) The ferrozine method revisited: Fe(II)/Fe(III) determination in natural waters. Appl Geochem 15(6):785–790
Wang S, Chandrasekhara Rao N, Qiu R, Moletta R (2009) Performance and kinetic evaluation of anaerobic moving bed biofilm reactor for treating milk permeate from dairy industry. Bioresour Technol 100:5641–5647
Wang X, Zhang Y, Dong X, Chen M, Shi Z, Zhou J (2013) FeIIEDTA–NO reduction by sulfide in the anaerobic aqueous phase: stoichiometry and kinetics. Energy Fuels 27(10):6024–6030
Wanner U, Kemmler J, Weilenmann HU, Egli T, EI-Banna T, Auling G (1990) Isolation and growth of a bacterium able to degrade nitrilotriacetic acid under denitrifying conditions. Biodegradation 1:31–41
Wolak M, Eldik R (2002) To be or not to be NO in coordination chemistry? A mechanistic approach. Coord Chem Rev 230:263–282
Yang XJ, Yang L, Dong L, Long XL, YuanW K (2011) Kinetics of the [Fe(III)-EDTA] − reduction by sulfite under the catalysis of activated carbon. Energy Fuels 25(10):4248–4255
Zhang SH, Cai LL, Liu Y, Shi Y, Li W (2009) Effects of NO2 − and NO3 − on the Fe(III)EDTA reduction in a chemical absorption–biological reduction integrated NOx removal system. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology 82(3):557–563
Zhou Y, Gao L, Xia YF, Li W (2012) Enhanced reduction of Fe(II)EDTA-NO/Fe(III)EDTA in NO(x) scrubber solution using a three-dimensional biofilm-electrode reactor. Environ Sci Technol 46(22):12640–12647
Acknowledgments
The authors are thankful to the Director, CSIR-NEERI, for giving kind permission to publish this research work. The financial support extended by Department of Biotechnology (DBT) and Council of Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR), Ministry of Science & Technology, Government of India for the execution of this research work is duly acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(PDF 482 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chandrashekhar, B., Sahu, N., Tabassum, H. et al. Treatment of ferrous-NTA-based NO x scrubber solution by an up-flow anaerobic packed bed bioreactor. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 99, 5281–5293 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-014-6372-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-014-6372-5