Abstract
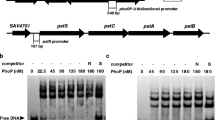
σ25 is an extracytoplasmic function (ECF) σ factor in the bacterium Streptomyces avermitilis that plays a differential regulatory role in avermectin and oligomycin biosynthesis. Gene deletion, complementation, and overexpression experiments showed that σ25 inhibited avermectin production but promoted oligomycin production. σ25 indirectly inhibited avermectin production by affecting the transcription of the pathway-specific activator gene aveR, whereas it directly activated oligomycin production by initiating transcription of the pathway-specific activator gene olmRI. The divergently transcribed genes smrAB are located upstream of sig25 and encode a putative two-component system (TCS). σ25 was found to initiate its own transcription, and its expression was directly activated by SmrA. The precise SmrA-binding sites in the region upstream of sig25 were determined by DNase I footprinting assays and identified two direct repeat sequences CTGTGA-n5-CTGTGA, suggesting that SmrA regulates sig25 transcription by binding to these direct repeats. The deletion of smrAB had the similar effect on avermectin and oligomycin A production to the deletion of sig25, indicating that σ25 and SmrAB function similarly in the regulation of antibiotic production. These findings helpfully clarify the regulation of antibiotic biosynthesis by an ECF σ factor-TCS signal transduction system in S. avermitilis.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bentley SD, Chater KF, Cerdeno-Tarraga AM, Challis GL, Thomson NR, James KD, Harris DE, Quail MA, Kieser H, Harper D (2002) Complete genome sequence of the model actinomycete Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2). Nature 417:141–147
Bierman M, Logan R, O'Brien K, Seno ET, Rao RN, Schoner BE (1992) Plasmid cloning vectors for the conjugal transfer of DNA from Escherichia coli to Streptomyces spp. Gene 116:43–49
Burg RW, Miller BM, Baker EE, Birnbaum J, Currie SA, Hartman R, Kong YL, Monaghan RL, Olson G, Putter I, Tunac JB, Wallick H, Stapley EO, Oiwa R, Omura S (1979) Avermectins, new family of potent anthelmintic agents: producing organism and fermentation. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 15:361–367
Cao M, Wang T, Ye R, Helmann JD (2002) Antibiotics that inhibit cell wall biosynthesis induce expression of the Bacillus subtilis sigma (W) and sigma (M) regulons. Mol Microbiol 45:1267–1276
Chaba R, Alba BM, Guo MS, Sohn J, Ahuja N, Sauer RT, Gross CA (2011) Signal integration by DegS and RseB governs the σE-mediated envelope stress response in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 108:2106–2111
Chen Z, Wen J, Song Y, Wen Y, Li JL (2007) Enhancement and selective production of avermectin B by recombinants of Streptomyces avermitilis via intraspecific protoplast fusion. Chin Sci Bull 52:616–622
Francez-Charlot A, Frunzke J, Reichen C, Ebneter JZ, Gourion B, Vorholt JA (2009) Sigma factor mimicry involved in regulation of general stress response. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 106:3467–3472
Guo J, Zhao JL, Li LL, Chen Z, Wen Y, Li JL (2010) The pathway-specific regulator AveR from Streptomyces avermitilis positively regulates avermectin production while it negatively affects oligomycin biosynthesis. Mol Genet Genomics 283:123–133
Guo J, Zhang X, Luo S, He F, Chen Z, Wen Y, Li JL (2013) A novel TetR family transcriptional regulator, SAV576, negatively controls avermectin biosynthesis in Streptomyces avermitilis. PLoS One 8:e71330
Hong HJ, Paget MS, Buttner MJ (2002) A signal transduction system in Streptomyces coelicolor that activates the expression of a putative cell wall glycan operon in response to vancomycin and other cell wall-specific antibiotics. Mol Microbiol 44:1199–1211
Hutchings MI, Hong HJ, Leibovitz E, Sutcliffe IC, Buttner MJ (2006) The sigma (E) cell envelope stress response of Streptomyces coelicolor is influenced by a novel lipoprotein, CseA. J Bacteriol 188:7222–7229
Ikeda H, Kotaki H, Tanaka H, Omura S (1988) Involvement of glucose catabolism in avermectin production by Streptomyces avermitilis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 32:282–284
Ikeda H, Ishikawa J, Hanamoto A, Shinose M, Kikuchi H, Shiba T, Sakaki Y, Hattori M, Omura S (2003) Complete genome sequence and comparative analysis of the industrial microorganism Streptomyces avermitilis. Nat Biotechnol 21:526–531
Jiang LB, Liu YP, Wang P, Wen Y, Song Y, Chen Z, Li JL (2011) Inactivation of the extracytoplasmic function sigma factor Sig6 stimulates avermectin production in Streptomyces avermitilis. Biotechnol Lett 33:1955–1961
Kieser T, Bibb MJ, Buttner MJ, Chater KF, Hopwood DA (2000) Practical Streptomyces genetics: a laboratory manual. John Innes Foundation, Norwich
Kitani S, Ikeda H, Sakamoto T, Noguchi S, Nihira T (2009) Characterization of a regulatory gene, aveR, for the biosynthesis of avermectin in Streptomyces avermitilis. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 82:1089–1096
Li W, Stevenson CE, Burton N, Jakimowicz P, Paget MS, Buttner MJ, Lawson DM, Kleanthous C (2002) Identification and structure of the anti-sigma factor-binding domain of the disulphide-stress regulated sigma factor σR from Streptomyces coelicolor. J Mol Biol 323:225–236
Li LL, Guo J, Wen Y, Chen Z, Song Y, Li JL (2010) Overexpression of ribosome recycling factor causes increased production of avermectin in Streptomyces avermitilis strains. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 37:673–679
Lin XP, Wen Y, Li M, Chen Z, Guo J, Song Y, Li JL (2009) A new strain of Streptomyces avermitilis produces high yield of oligomycin A with potent anti-tumor activity on human cancer cell lines in vitro. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 81:839–845
Macneil DJ, Klapko LM (1987) Transformation of Streptomyces avermitilis by plasmid DNA. J Ind Microbiol 2:209–218
Mascher T (2013) Signaling diversity and evolution of extracytoplasmic function (ECF) σ factors. Curr Opin Microbiol 16:148–155
Meng XD, Michael HB, Scot AW (2005) A bacterial one-hybrid system for determining the DNA-binding specificity of transcription factors. Nat Biotechnol 23:988–994
Omura S, Ikeda H, Ishikawa J, Hanamoto A, Takahashi C, Shinose M, Takahashi Y, Horikawa H, Nakazawa H, Osonoe T, Kikuchi H, Shiba T, Sakaki Y, Hattori M (2001) Genome sequence of an industrial microorganism Streptomyces avermitilis: deducing the ability of producing secondary metabolites. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 98:12215–12220
Paget MSB, Chamberlin L, Atrih A, Foster SJ, Buttner MJ (1999) Evidence that the extracytoplasmic function sigma factor σE is required for normal cell wall structure in Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2). J Bacteriol 181:204–211
Pinna LA, Lorini M, Moret V, Siliprandi N (1967) Effect of oligomycin and succinate on mitochondrial metabolism of adenine nucleotides. Biochim Biophys Acta 143:18–25
Sambrook J, MacCallum P, and Russell D (2001) Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual, third ed. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press
Shu D, Chen L, Wang W, Yu Z, Ren C, Zhang W, Yang S, Lu Y, Jiang W (2009) afsQ1-Q2-sigQ is a pleiotropic but conditionally required signal transduction system for both secondary metabolism and morphological development in Streptomyces coelicolor. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 81:1149–1160
Staron A, Sofia HJ, Dietrich S, Ulrich LE, Liesegang H, Mascher T (2009) The third pillar of bacterial signal transduction: classification of the extracytoplasmic function (ECF) sigma factor protein family. Mol Microbiol 74:557–581
Tiffert Y, Supra P, Wurm R, Wohlleben W, Wagner R, Reuther J (2008) The Streptomyces coelicolor GlnR regulon: identification of new GlnR targets and evidence for a central role of GlnR in nitrogen metabolism in actinomycetes. Mol Microbiol 67:861–880
Wang R, Mast Y, Wang J, Zhang W, Zhao G, Wohlleben W, Lu Y, Jiang W (2013) Identification of two-component system AfsQ1/Q2 regulon and its cross-regulation with GlnR in Streptomyces coelicolor. Mol Microbiol 87:30–48
Yu Q, Bai LQ, Zhou XF, Deng ZX (2012) Inactivation of the positive LuxR-type oligomycin biosynthesis regulators OlmRI and OlmRII increases avermectin production in Streptomyces avermitilis. Chin Sci Bull 8:869–876
Zhao JL, Wen Y, Chen Z, Song Y, Li JL (2007) An adpA homologue in Streptomyces avermitilis is involved in regulation of morphogenesis and melanogenesis. Chin Sci Bull 52:623–630
Zhuo Y, Zhang W, Chen D, Gao H, Tao J, Liu M, Gou Z, Zhou X, Ye BC, Zhang Q, Zhang S, Zhang LX (2010) Reverse biological engineering of hrdB to enhance the production of avermectins in an industrial strain of Streptomyces avermitilis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 107:11250–11254
Zianni M, Tessanne K, Merighi M, Laguna R, Tabita FR (2006) Identification of the DNA bases of a DNase I footprint by the use of dye primer sequencing on an automated capillary DNA analysis instrument. J Biomol Tech 17:103–113
Zweers JC, Nicolas P, Wiegert T, van Dijl JM, Denham EL (2012) Definition of the σ (W) regulon of Bacillus subtilis in the absence of stress. PLoS One 7:e48471
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant no. 31170045). The authors are grateful to Dr. S. Anderson (Pacific Northwest Diabetes Research Institute, Seattle, WA, USA) for English editing of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(PDF 347 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Luo, S., Sun, D., Zhu, J. et al. An extracytoplasmic function sigma factor, σ25, differentially regulates avermectin and oligomycin biosynthesis in Streptomyces avermitilis . Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 98, 7097–7112 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-014-5759-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-014-5759-7