Abstract
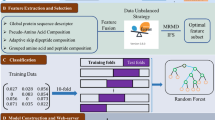
Cancer is a terrible disease, recent studies reported that tumor T cell antigens (TTCAs) may play a promising role in cancer treatment. Since experimental methods are still expensive and time-consuming, it is highly desirable to develop automatic computational methods to identify tumor T cell antigens from the huge amount of natural and synthetic peptides. Hence, in this study, a novel computational model called iTTCA-MFF was proposed to identify TTCAs. In order to describe the sequence effectively, the physicochemical (PC) properties of amino acid and residue pairwise energy content matrix (RECM) were firstly employed to encode peptide sequences. Then, two different approaches including covariance and Pearson’s correlation coefficient (PCC) were used to collect discriminative information from PC and RECM matrixes. Next, an effective feature selection approach called the least absolute shrinkage and selection operator (LAASO) was adopted to select the optimal features. These selected optimal features were fed into support vector machine (SVM) for identifying TTCAs. We performed experiments on two different datasets, experimental results indicated that the proposed method is promising and may play a complementary role to the existing methods for identifying TTCAs. The datasets and codes can be available at https://figshare.com/articles/online_resource/iTTCA-MFF/17636120.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets and source code of this study can be downloaded via https://figshare.com/articles/online_resource/iTTCA-MFF/17636120.
References
Akbar S, Rahman AU, Hayat M, Sohail M (2020) cACP: Classifying anticancer peptides using discriminative intelligent model via Chou’s 5-step rules and general pseudo components. Chemomet Intel Lab Syst 196:103912
Beheshti I, Demirel H (2016) Initiative AsDN. Feature-ranking-based Alzheimer’s disease classification from structural MRI. Magnet Resonance Imaging 34(3):252–63.
Bin Y, Zhang W, Tang W, Dai R, Li M, Zhu Q et al (2020) Prediction of neuropeptides from sequence information using ensemble classifier and hybrid features. J Proteome Res 19(9):3732–3740
Bobisse S, Foukas PG, Coukos G, Harari A (2016) Neoantigen-based cancer immunotherapy. Annals Translation Med 4(14):262
Bray FI, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel RL, Torre LA, Jemal A (2018) Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA: A Cancer J Clinic 68(6):394–424
Charoenkwan P, Nantasenamat C, Hasan MM, Shoombuatong W (2020) iTTCA-Hybrid: improved and robust identification of tumor T cell antigens by utilizing hybrid feature representation. Analytic Biochem 113747
Chen H, Duan X, Liu F, Lu F, Ma X, Zhang Y et al (2016) Multivariate classification of autism spectrum disorder using frequency-specific resting-state functional connectivity—a multi-center study. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 64:1–9
Cortes C, Vapnik V (1995) Support-vector networks. Mach Learn 20(3):273–297
Couzin-Frankel J (2013) Cancer immunotherapy. Am Assoc Adv Sci
Dai R, Zhang W, Tang W, Wynendaele E, Zhu Q, Bin Y et al (2021) BBPpred: sequence-based prediction of blood-brain barrier peptides with feature representation learning and logistic regression. J Chem Inf Model 61(1):525–534
Ding C, Yuan L, Guo S, Lin H, Chen W (2012) Identification of mycobacterial membrane proteins and their types using over-represented tripeptide compositions. J Proteomics 77:321–328
Dosztanyi Z, Csizmok V, Tompa P, Simon I (2005) The pairwise energy content estimated from amino acid composition discriminates between folded and intrinsically unstructured proteins. J Mol Biol 347(4):827–839
Fu X, Cai L, Zeng X, Zou Q (2020) StackCPPred: a stacking and pairwise energy content-based prediction of cell-penetrating peptides and their uptake efficiency. Bioinformatics 36(10):3028–3034
Harris F, Dennison SR, Singh J, Phoenix DA (2013) On the selectivity and efficacy of defense peptides with respect to cancer cells. Med Res Rev 33(1):190–234
Jones DT, Cozzetto D (2015) DISOPRED3: precise disordered region predictions with annotated protein-binding activity. Bioinformatics 31(6):857–863
Khazaee A, Ebrahimzadeh A, Babajani-Feremi A (2016) Application of advanced machine learning methods on resting-state fMRI network for identification of mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer’s disease. Brain Imaging Behav 10(3):799–817
Li B, Feng K, Ding J, Cai Y (2014) Predicting DNA-binding sites of proteins based on sequential and 3D structural information. Mol Genet Genomics 289(3):489–499
Lin J, Chen H, Li S, Liu Y, Li X, Yu B (2019) Accurate prediction of potential druggable proteins based on genetic algorithm and Bagging-SVM ensemble classifier. Artif Intell Med 98:35–47
Lin H, Ding H (2011) Predicting ion channels and their types by the dipeptide mode of pseudo amino acid composition. J Theor Biol 269(1):64–69
Lissabet JFB, Belen LH, Farias JG (2019) TTAgP 1.0: a computational tool for the specific prediction of tumor T cell antigens. Comput Biol Chem 83:107103
Liu J, Ji S, Ye J (2009) SLEP: sparse learning with efficient projections. Arizona State University 6(491):7
Liu Z, Xiao X, Yu D-J, Jia J, Qiu W-R, Chou K-C (2016) pRNAm-PC: predicting N6-methyladenosine sites in RNA sequences via physical–chemical properties. Anal Biochem 497:60–67
Manavalan B, Basith S, Shin TH, Wei L, Lee G (2019) AtbPpred: a robust sequence-based prediction of anti-tubercular peptides using extremely randomized trees. Comput Struct Biotechnol J 17:972–981
Mészáros B, Erdős G, Dosztányi Z (2018) IUPred2A: context-dependent prediction of protein disorder as a function of redox state and protein binding. Nucleic Acids Res 46(W1):W329–W337
Mishra A, Pokhrel P, Hoque MT (2019) StackDPPred: a stacking based prediction of DNA-binding protein from sequence. Bioinformatics 35(3):433–441
Mizukoshi E, Nakamoto Y, Arai K, Yamashita T, Sakai A, Sakai Y et al (2011) Comparative analysis of various tumor-associated antigen-specific t-cell responses in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 53(4):1206–1216
Olsen LR, Tongchusak S, Lin H, Reinherz EL, Brusic V, Zhang GL (2017) TANTIGEN: a comprehensive database of tumor T cell antigens. Cancer Immunol Immunother 66(6):731–735
Saini SK, Rekers N, Hadrup SR (2017) Novel tools to assist neoepitope targeting in personalized cancer immunotherapy. Ann Oncol 28:3–10
Schumacher TNM, Schreiber RD (2015) Neoantigens in cancer immunotherapy. Science 348(6230):69–74
Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A (2016) Cancer statistics, 2016. CA: A Cancer J Clinic 66(1):7–30
Shoombuatong W, Schaduangrat N, Pratiwi R, Nantasenamat C (2019) THPep: a machine learning-based approach for predicting tumor homing peptides. Comput Biol Chem 80:441–451
Tang H, Su Z-D, Wei H-H, Chen W, Lin H (2016) Prediction of cell-penetrating peptides with feature selection techniques. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 477(1):150–154
Thundimadathil J (2012) Cancer treatment using peptides: current therapies and future prospects. J Amino Acids 967347
Ueki K, Sato K, Nakamura S, Terada T, Sumikoshi K, Shimizu K (2016) Development of a computational method for lipid-binding protein prediction
Verma R, Tiwari A, Kaur S, Varshney GC, Raghava GP (2008) Identification of proteins secreted by malaria parasite into erythrocyte using SVM and PSSM profiles. BMC Bioinformatics 9(1):201
Vita R, Mahajan S, Overton JA, Dhanda SK, Martini S, Cantrell JR et al (2019) The Immune Epitope Database (IEDB): 2018 update. Nucleic Acids Res 47
Vijayakumar S, Ptv L (2015) ACPP: a web server for prediction and design of anti-cancer peptides. Int J Pept Res Ther 21(1):99–106
Wang K, Li S, Wang Q, Hou C (2019) Identification of hormone-binding proteins using a novel ensemble classifier. Computing 101(6):693–703
Wang X, Zhang W, Zhang Q, Li G (2015) MultiP-SChlo: multi-label protein subchloroplast localization prediction with Chou’s pseudo amino acid composition and a novel multi-label classifier. Bioinformatics 31(16):2639–2645
Xiao X, Wang P, Chou K (2012) iNR-PhysChem: a sequence-based predictor for identifying nuclear receptors and their subfamilies via physical-chemical property matrix. PLoS One 7(2)
Xiao X, Wang P, Lin WZ, Jia JH, Chou KC (2013) iAMP-2L: A two-level multi-label classifier for identifying antimicrobial peptides and their functional types. Anal Biochem 436(2):168–177
Xiao X, Zou H, Lin W (2015) iMem-Seq: A multi-label learning classifier for predicting membrane proteins types. J Membr Biol 248(4):745–752
Xiao X, Xu Z, Qiu W, Wang P, Ge H, Chou K (2019) iPSW(2L)-PseKNC: a two-layer predictor for identifying promoters and their strength by hybrid features via pseudo K-tuple nucleotide composition. Genomics 111(6):1785–1793
Zhang GL, Chitkushev L, Keskin DB, Brusic V (eds.) (2019) TANTIGEN 2.0: an online database and analysis platform for tumor T cell antigens. Bioinformat Biomed
Zuo Y, Li Q (2010) Using K-minimum increment of diversity to predict secretory proteins of malaria parasite based on groupings of amino acids. Amino Acids 38(3):859–867
Zou H-L (2016) A new multi-label classifier for identifying the functional types of singleplex and multiplex antimicrobial peptides. Int J Pept Res Ther 22(2):281–287
Zou H-L, Xiao X (2016) Classifying multifunctional enzymes by incorporating three different models into Chou’s general pseudo amino acid composition. J Membr Biol 249(4):551–557
Zou H, Yang J (2019a) Dynamic thresholding networks for schizophrenia diagnosis. Artif Intell Med 96:25–32
Zou H, Yang J (2019b) Multi-frequency dynamic weighted functional connectivity networks for schizophrenia diagnosis. Appl Magn Reson 50(7):847–859
Zou H, Yin Z (2021) Identifying dipeptidyl peptidase-IV inhibitory peptides based on correlation information of physicochemical properties. Internatl J Peptide Res Therapeut 1–9
Funding
This work was supported by the National Nature Scientific Foundation of China (No. 62061019), the General Project of Jiangxi Natural Science Foundation (20202BABL202014), and the General Project of Jiangxi Education Department (GJJ190587).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Hongliang Zou: conceptualization, methodology, data curation, writing-original draft, preparation, visualization, investigation, validation, writing-review and editing. Fan Yang: supervision. Zhijian Yin: supervision, funding acquisition.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zou, H., Yang, F. & Yin, Z. iTTCA-MFF: identifying tumor T cell antigens based on multiple feature fusion. Immunogenetics 74, 447–454 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00251-022-01258-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00251-022-01258-5