Abstract
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a systemic autoimmune disease. So far, it is unclear whether there exist common RA-related genes shared in different tissues/cells. In this study, we conducted an integrative analysis on multiple datasets to identify potential shared genes that are significant in multiple tissues/cells for RA. Seven microarray gene expression datasets representing various RA-related tissues/cells were downloaded from the Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO). Statistical analyses, testing both marginal and joint effects, were conducted to identify significant genes shared in various samples. Followed-up analyses were conducted on functional annotation clustering analysis, protein-protein interaction (PPI) analysis, gene-based association analysis, and ELISA validation analysis in in-house samples. We identified 18 shared significant genes, which were mainly involved in the immune response and chemokine signaling pathway. Among the 18 genes, eight genes (PPBP, PF4, HLA-F, S100A8, RNASEH2A, P2RY6, JAG2, and PCBP1) interact with known RA genes. Two genes (HLA-F and PCBP1) are significant in gene-based association analysis (P = 1.03E-31, P = 1.30E-2, respectively). Additionally, PCBP1 also showed differential protein expression levels in in-house case-control plasma samples (P = 2.60E-2). This study represented the first effort to identify shared RA markers from different functional cells or tissues. The results suggested that one of the shared genes, i.e., PCBP1, is a promising biomarker for RA.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abeles AM, Pillinger MH (2006) The role of the synovial fibroblast in rheumatoid arthritis: cartilage destruction and the regulation of matrix metalloproteinases. Bull NYU Hosp Jt Dis 64:20–24
Alexander DH, Lange K (2011) Stability selection for genome-wide association. Genet Epidemiol 35:722–728. doi:10.1002/gepi.20623
Amsen D et al (2007) Direct regulation of Gata3 expression determines the T helper differentiation potential of Notch. Immunity 27:89–99. doi:10.1016/j.immuni.2007.05.021
Andres Cerezo L, Mann H, Pecha O, Plestilova L, Pavelka K, Vencovsky J, Senolt L (2011) Decreases in serum levels of S100A8/9 (calprotectin) correlate with improvements in total swollen joint count in patients with recent-onset rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Res Ther 13:R122. doi:10.1186/ar3426
Barnes MG et al (2004) Gene expression in juvenile arthritis and spondyloarthropathy: pro-angiogenic ELR+ chemokine genes relate to course of arthritis. Rheumatology (Oxford) 43:973–979. doi:10.1093/rheumatology/keh224
Bhatnagar P et al (2012) Genetic variants in platelet factor 4 modulate inflammatory and platelet activation biomarkers. Circ Cardiovasc Genet 5:412–421. doi:10.1161/CIRCGENETICS.111.961813
Chen Q, Cai ZK, Chen YB, Gu M, Zheng DC, Zhou J, Wang Z (2015) Poly r(C) binding protein-1 is central to maintenance of cancer stem cells in prostate cancer cells cellular physiology and biochemistry. Int J Exp Cell Physiol, Biochem Pharmacol 35:1052–1061. doi:10.1159/000373931
Criswell LA (2010) Gene discovery in rheumatoid arthritis highlights the CD40/NF-kappaB signaling pathway in disease pathogenesis. Immunol Rev 233:55–61. doi:10.1111/j.0105-2896.2009.00862.x
Edgar R, Domrachev M, Lash AE (2002) Gene Expression Omnibus: NCBI gene expression and hybridization array data repository. Nucleic Acids Res 30:207–210
Erdem H, Pay S, Musabak U, Simsek I, Dinc A, Pekel A, Sengul A (2007) Synovial angiostatic non-ELR CXC chemokines in inflammatory arthritides: does CXCL4 designate chronicity of synovitis? Rheumatol Int 27:969–973. doi:10.1007/s00296-007-0317-6
Franceschini A et al (2013) STRING v9.1: protein-protein interaction networks, with increased coverage and integration. Nucleic Acids Res 41:D808–D815. doi:10.1093/nar/gks1094
Goodridge JP et al (2013) HLA-F and MHC-I open conformers cooperate in a MHC-I antigen cross-presentation pathway. J Immunol 191:1567–1577. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.1300080
Grayson BL, Wang L, Aune TM (2011) Peripheral blood gene expression profiles in metabolic syndrome, coronary artery disease and type 2 diabetes. Genes Immun 12:341–351. doi:10.1038/gene.2011.13
Gusnanto A, Calza S, Pawitan Y (2007) Identification of differentially expressed genes and false discovery rate in microarray studies. Curr Opin Lipidol 18:187–193. doi:10.1097/MOL.0b013e3280895d6f
Hammer HB et al (2007) Calprotectin (a major leucocyte protein) is strongly and independently correlated with joint inflammation and damage in rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis 66:1093–1097. doi:10.1136/ard.2006.064741
Han Z, Boyle DL, Manning AM, Firestein GS (1998) AP-1 and NF-kappaB regulation in rheumatoid arthritis and murine collagen-induced arthritis. Autoimmunity 28:197–208. doi:10.3109/08916939808995367
Haupl T, Stuhlmuller B, Grutzkau A, Radbruch A, Burmester GR (2010) Does gene expression analysis inform us in rheumatoid arthritis? Ann Rheum Dis 69(Suppl 1):i37–i42. doi:10.1136/ard.2009.119487
Hu X, Daly M (2012) What have we learned from six years of GWAS in autoimmune diseases, and what is next? Curr Opin Immunol 24:571–575. doi:10.1016/j.coi.2012.09.001
Huang da W, Sherman BT, Lempicki RA (2009) Systematic and integrative analysis of large gene lists using DAVID bioinformatics resources. Nat Protoc 4:44–57. doi:10.1038/nprot.2008.211
Huang J, Breheny P, Ma S (2012) A selective review of group selection in high-dimensional. Models Stat Sci 27:481–499. doi:10.1214/12-STS392
Huber R, Hummert C, Gausmann U, Pohlers D, Koczan D, Guthke R, Kinne RW (2008) Identification of intra-group, inter-individual, and gene-specific variances in mRNA expression profiles in the rheumatoid arthritis synovial membrane. Arthritis Res Ther 10:R98. doi:10.1186/ar2485
Huo LR et al (2010) Identification of differentially expressed transcripts and translatants targeted by knock-down of endogenous PCBP1. Biochim Biophys Acta 1804:1954–1964. doi:10.1016/j.bbapap.2010.07.002
Hwang SY, Kim JY, Kim KW, Park MK, Moon Y, Kim WU, Kim HY (2004) IL-17 induces production of IL-6 and IL-8 in rheumatoid arthritis synovial fibroblasts via NF-kappaB- and PI3-kinase/Akt-dependent pathways. Arthritis Res Ther 6:R120–R128. doi:10.1186/ar1038
Johne B, Fagerhol MK, Lyberg T, Prydz H, Brandtzaeg P, Naess-Andresen CF, Dale I (1997) Functional and clinical aspects of the myelomonocyte protein calprotectin. Mol Pathol 50:113–123
Kageyama R, Ohtsuka T, Shimojo H, Imayoshi I (2008) Dynamic Notch signaling in neural progenitor cells and a revised view of lateral inhibition. Nat Neurosci 11:1247–1251. doi:10.1038/nn.2208
Kang KY, Woo JW, Park SH (2014) S100A8/A9 as a biomarker for synovial inflammation and joint damage in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Korean J Intern Med 29:12–19. doi:10.3904/kjim.2014.29.1.12
Karatoprak C, Uyar S, Abanonu GB, Pehlevan SM, Okuroglu N, Demirtunc R (2013) The levels of beta-thromboglobulin in female rheumatoid arthritis patients as activation criteria. Rheumatol Int 33:1229–1232. doi:10.1007/s00296-012-2511-4
Karouzakis E, Neidhart M, Gay RE, Gay S (2006) Molecular and cellular basis of rheumatoid joint destruction. Immunol Lett 106:8–13. doi:10.1016/j.imlet.2006.04.011
Khine AA et al (2006) Human neutrophil peptides induce interleukin-8 production through the P2Y6 signaling pathway. Blood 107:2936–2942. doi:10.1182/blood-2005-06-2314
Kim TH, Choi SJ, Lee YH, Song GG, Ji JD (2014) Gene expression profile predicting the response to anti-TNF treatment in patients with rheumatoid arthritis; analysis of GEO datasets. Joint Bone Spine 81:325–330. doi:10.1016/j.jbspin.2014.01.013
Lee HM et al (2011) Abnormal networks of immune response-related molecules in bone marrow cells from patients with rheumatoid arthritis as revealed by DNA microarray analysis. Arthritis Res Ther 13:R89. doi:10.1186/ar3364
Lee N, Ishitani A, Geraghty DE (2010) HLA-F is a surface marker on activated lymphocytes. Eur J Immunol 40:2308–2318. doi:10.1002/eji.201040348
Li J, Feng Q, Wei X, Yu Y (2016) MicroRNA-490 regulates lung cancer metastasis by targeting poly r(C)-binding protein 1 tumour biology. J Int Soc Oncodevelopmental Biol Med. doi:10.1007/s13277-016-5347-9
Li MX, Gui HS, Kwan JS, Sham PC (2011) GATES: a rapid and powerful gene-based association test using extended Simes procedure. Am J Hum Genet 88:283–293. doi:10.1016/j.ajhg.2011.01.019
Mak W, Shao X, Dunstan CR, Seibel MJ, Zhou H (2009) Biphasic glucocorticoid-dependent regulation of Wnt expression and its inhibitors in mature osteoblastic cells. Calcif Tissue Int 85:538–545. doi:10.1007/s00223-009-9303-1
Okada Y et al (2014) Genetics of rheumatoid arthritis contributes to biology and drug discovery. Nature 506:376–381. doi:10.1038/nature12873
Paradowska-Gorycka A, Romanowska-Prochnicka K, Haladyj E, Manczak M, Maslinski S, Olesinska M (2014) Association of the Smad3 and NFATc2 gene polymorphisms and their serum levels with susceptibility to rheumatoid arthritis in Polish cohorts. Clin Exp Immunol. doi:10.1111/cei.12482
Pathak S, Bajpai D, Banerjee A, Bhatla N, Jain SK, Jayaram HN, Singh N (2014) Serum one-carbon metabolites and risk of cervical cancer. Nutr Cancer 66:818–824. doi:10.1080/01635581.2014.916318
Postlethwaite AE, Holness MA, Katai H, Raghow R (1992) Human fibroblasts synthesize elevated levels of extracellular matrix proteins in response to interleukin 4. J Clin Invest 90:1479–1485. doi:10.1172/JCI116015
Shi X, Shen S, Liu J, Huang J, Zhou Y, Ma S (2014) Similarity of markers identified from cancer gene expression studies: observations from GEO. Brief Bioinform 15:671–684. doi:10.1093/bib/bbt044
Simard JC, Cesaro A, Chapeton-Montes J, Tardif M, Antoine F, Girard D, Tessier PA (2013) S100A8 and S100A9 induce cytokine expression and regulate the NLRP3 inflammasome via ROS-dependent activation of NF-kappaB (1.). PLoS One 8:e72138. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0072138
Sirota M, Schaub MA, Batzoglou S, Robinson WH, Butte AJ (2009) Autoimmune disease classification by inverse association with SNP alleles. PLoS Genet 5:e1000792. doi:10.1371/journal.pgen.1000792
Teixeira VH et al (2009) Transcriptome analysis describing new immunity and defense genes in peripheral blood mononuclear cells of rheumatoid arthritis patients. PLoS One 4:e6803. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0006803
Terenzi R, Romano E, Manetti M, Peruzzi F, Nacci F, Matucci-Cerinic M, Guiducci S (2013) Neuropeptides activate TRPV1 in rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast-like synoviocytes and foster IL-6 and IL-8 production. Ann Rheum Dis 72:1107–1109. doi:10.1136/annrheumdis-2012-202846
Ungethuem U et al (2010) Molecular signatures and new candidates to target the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. Physiol Genomics 42A:267–282. doi:10.1152/physiolgenomics.00004.2010
Wagener R et al (2015) The PCBP1 gene encoding poly (rC) binding protein I is recurrently mutated in Burkitt lymphoma. Genes, Chromosome Cancer 54:555–564. doi:10.1002/gcc.22268
Xia S, Zhao Z, Xie F, He J, Li H (2016) Poly r (C) binding protein is post-transcriptionally repressed by MiR-490-3p to potentiate squamous cell carcinoma tumour biology. J Int Soc Oncodevelopmental Biol Med. doi:10.1007/s13277-016-5234-4
Yarilina A, Park-Min KH, Antoniv T, Hu X, Ivashkiv LB (2008) TNF activates an IRF1-dependent autocrine loop leading to sustained expression of chemokines and STAT1-dependent type I interferon-response genes. Nat Immunol 9:378–387. doi:10.1038/ni1576
Yui S, Nakatani Y, Mikami M (2003) Calprotectin (S100A8/S100A9), an inflammatory protein complex from neutrophils with a broad apoptosis-inducing activity. Biol Pharm Bull 26:753–760
Zhang M, Wang X, Tan J, Zhao M, Lian L, Zhang W (2016) Poly r (C) binding protein (PCBP) 1 is a negative regulator of thyroid carcinoma. Am J Transl Res 8:3567–3573
Zhou M, Tong X (2015) Downregulated poly-C binding protein-1 is a novel predictor associated with poor prognosis in acute myeloid leukemia. Diagn Pathol 10:147. doi:10.1186/s13000-015-0377-y
Acknowledgments
The study was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of China (81473046, 31401079, 81401343, 31271336, and 81373010), the Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province (BK20130300), the Startup Fund from Soochow University (Q413900112, Q413900712), the Project funded by China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (2014M551649), and a Project of the Priority Academic Program Development of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Wei Xia and Jian Wu contribute equally to the work.
Electronic supplementary material
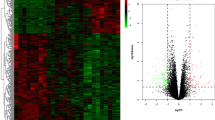
Note: The heatmaps show the correlation matrices between the GVPs of seven datasets, positive correlations are shown in red, and negative correlations in green. A, B, C show the results of Pearson, Kendall, and Spearman correlation, respectively
Table S1
Marginal analysis, approach1: overlaps of top100 ranked genes across the seven datasets. (PDF 19 kb)
Table S2
Marginal analysis, approach 2-t test: overlaps of genes selected using FDR = 0.1 and 0.01 across the seven datasets. (PDF 20 kb)
Table S3
Analysis of joint effects: Lasso and stability selection with cutoff 0.1 (PDF 19 kb)
Table S4
The functional annotation clustering analysis (PDF 96 kb)
Table S5
Characteristics of the eight novel RA-associated genes in PPI analysis (PDF 97 kb)
Figure S1
Analysis of marginal effects: approach 3 with three correlations (PDF 174 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xia, W., Wu, J., Deng, FY. et al. Integrative analysis for identification of shared markers from various functional cells/tissues for rheumatoid arthritis. Immunogenetics 69, 77–86 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00251-016-0956-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00251-016-0956-4