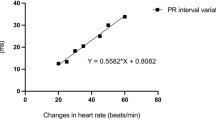
Abstract
This study aimed to investigate the feasibility and effectiveness of left bundle branch area pacing (LBBaP) in young children. From September 2020 to May 2021, a total of 31 children (≤ 7 years) with complete atrioventricular block were included. All patients were scheduled to undergo LBBaP. Pacing parameters, and cardiac function and synchrony were evaluated during follow-up. LBBaP succeeded in 21 children (3.3 ± 2.1 years old), with a success rate of 70.9%. LBBaP failed in nine children, who eventually received right ventricular septal pacing (RVSP). The average postoperative QRS duration in patients of LBBaP group was narrower than that of RVSP group: 100.9 ± 9.1 versus 114.2 ± 11.9 ms (P = 0.002). The median follow-up duration was 12 [interquartile range (IQR) 6–15] months. At last time of follow-up, the capture threshold of ventricular electrode in patients of LBBaP group were significantly lower than that of RVSP group (0.70 ± 0.25 versus 1.39 ± 0.94 V, P = 0.011). The echo-left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) in patients in the LBBaP group was better than that in the RVSP group (66.1 ± 3.3 versus 63.1 ± 2.2%, P = 0.025). LBBaP can be safely and effectively administered in young children. Satisfactory pacing parameters, and narrow QRS durations were obtained.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
All data and materials, as well as software applications or custom codes, support our published claims and comply with field standards.
References
Siu C, Wang M, Zhang X et al (2008) Analysis of ventricular performance as a function of pacing site and mode. Prog Cardiovasc Dis 51:171–182. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pcad.2008.01.001
Gebauer RA, Tomek V, Salameh A et al (2009) Predictors of left ventricular remodelling and failure in right ventricular pacing in the young. Eur Heart J 30:1097–1104. https://doi.org/10.1093/eurheartj/ehp060
Safak E, Ince H, Gkouvatsou L et al (2019) Pacing-induced cardiomyopathy in chronic right ventricular apical pacing: a midterm follow-up study. Eur J Med Res 24:23–28. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40001-019-0386-5
Li X, Qiu C, Xie R et al (2020) Left bundle branch area pacing delivery of cardiac resynchronization therapy and comparison with biventricular pacing. ESC Heart Fail 7:1711–1722. https://doi.org/10.1002/ehf2.12731
Vijayaraman P, Subzposh FA, Naperkowski A et al (2019) Prospective evaluation of feasibility and electrophysiologic and echocardiographic characteristics of left bundle branch area pacing. Heart Rhythm 16:1774–1782. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hrthm.2019.05.011
Shah MJ, Silka MJ, Avari SJ et al (2021) 2021 PACES expert consensus statement on the indications and management of cardiovascular implantable electronic devices in pediatric patients. Indian Pacing Electrophysiol J 21:367–393. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hrthm.2021.07.038
Michele B, Angelo A, Gonzalo BE et al (2013) 2013 ESC Guidelines on cardiac pacing and cardiac resynchronization therapy. Eur Heart J 34:2281–2329. https://doi.org/10.1093/eurheartj/eht150
Zhang J, Wang Z, Cheng L et al (2019) Immediate clinical outcomes of left bundle branch area pacing vs conventional right ventricular pacing. Clin Cardiol 42:768–773. https://doi.org/10.1002/clc.23215
Huang W, Su L, Wu S et al (2017) A novel pacing strategy with low and stable output: pacing the left bundle branch immediately beyond the conduction block. Can J Cardiol 33:e1–e3. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cjca.2017.09.013
Ponnusamy SS, Arora V, Namboodiri N et al (2020) Left bundle branch pacing: a comprehensive review. J Cardiovasc Electr 31:2462–2473. https://doi.org/10.1111/jce.14681
Zhang S, Zhou X, Gold MR (2019) Left bundle branch pacing: JACC review topic of the week. J Am Coll Cardiol 74:3039–3049. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jacc.2019.10.039
Jimenez E, Zaban N, Sharma N et al (2020) His bundle and left bundle pacing in pediatrics and congenital heart disease: a single center experience. Pediatr Cardiol 41:1425–1431. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00246-020-02398-9
Dai C, Dai W, Guo B (2020) Clinical observation on six children of left bundle branch area pacing. Chin J Pediatr 58:107–112. https://doi.org/10.3760/cma.j.issn.0578-1310.2020.02.008
Jiang H, Hou X, Qian Z et al (2020) A novel 9-partition method using fluoroscopic images for guiding left bundle branch pacing. Heart Rhythm 17:1759–1767. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hrthm.2020.05.018
Abdelrahman M, Subzposh FA, Beer D et al (2018) Clinical outcomes of his bundle pacing compared to right ventricular pacing. J Am Coll Cardiol 71:2319–2330. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jacc.2018.02.048
Guo J, Li L, Meng F et al (2020) Short-term and intermediate-term performance and safety of left bundle branch pacing. J Cardiovasc Electr 31:1472–1481. https://doi.org/10.1111/jce.14463
Acknowledgements
None
Funding
This study was funded by Dr. Wu Shunde Foundation for Research in Medical Science, Grant No. 20240000811.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
JL performed manuscript writing and clinical data analysis. XL and HJ performed manuscript revision and supervision. HJ, YZ, and JC participated in the methodology. ML and HZ participated in clinical data collection.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval
This is an observational study. All procedures involving human participants were performed in accordance with the ethical standards of the institution and the Helsinki Declaration of 1964. This study was approved by the Ethics Committee of our hospital (Ethics Document Batch Number:202003).
Informed Consent
Every patient provided an informed consent form and an anaesthesia consent form. Consent forms were signed by the patient’s guardian prior to pacemaker implantation.
Consent for Publication
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Li, J., Jiang, H., Zhang, Y. et al. A Study to Analyse the Feasibility and Effectiveness of Left Bundle Branch Area Pacing Used in Young Children. Pediatr Cardiol 45, 681–689 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00246-023-03119-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00246-023-03119-8