Abstract
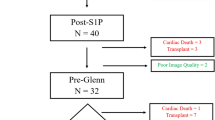
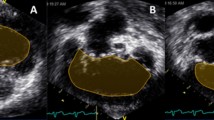
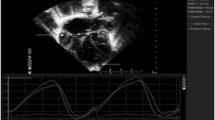
Multiple studies have shown that quantitative evaluation of right ventricular (RV) systolic function in children with hypoplastic left heart syndrome (HLHS) is associated with outcomes. However, the most widely used method is qualitative, or subjective echocardiographic evaluation. Tricuspid annular displacement (TMAD) is a quantitative method and has been shown to be associated with transplant/death in a cohort of pediatric patients with HLHS. In this study, the same echocardiograms used in the quantitative TMAD study were qualitatively evaluated to see if the assessment correlated with midterm outcomes. We hypothesized that TMAD measures would outperform qualitative measurements. A previously published retrospective study of patients with systemic right ventricle demonstrated that TMAD measurements of function prior to the Glenn procedure were associated with midterm mortality/transplant (mean TMAD 12.4% for survivors and 10.0% for non-survivors/transplant, p = 0.03). Echocardiographic images used in that study were re-evaluated using qualitative assessment of function. A score between severely depressed (0) and supra-normal (7) was assigned independently by three cardiologists. A chart review included short-term clinical outcome measures in addition to midterm mortality/transplant. Spearman correlations and logistic regression were used to estimate the associations between function scores and clinical outcomes. Function scores were measured with acceptable inter- and intra-rater reliabilities in 47 patients who had echocardiograms used in the prior analysis before their bidirectional Glenn. The mean functional score was 5.3 ± 1.32 in survivors and 5.0 ± 1.02 in non-survivors/transplant. Subjective echocardiographic scores of function were not predictive of mortality (p = 0.23). Scores were correlated with length of cardiac intensive care unit stay (Spearman’s rho = − 0.31, p = 0.04), but not post-Glenn total length of hospital stay (p = 0.4). A sub-analysis was performed for each individual operator. Only one of three operators produced scores with a significant association with mortality/transplant (p = 0.01, p = 0.25, p = 0.22, respectively). Averaged subjective measurement of function by three pediatric cardiologists in children with single right ventricle prior to the Glenn procedure was not associated with midterm outcomes. Previous work based on the same echocardiograms showed that quantitative analysis was associated with midterm outcomes. This suggests quantitative analysis may be more useful in prognostication. Future studies could confirm these results and identify which quantitative methods are most helpful.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altmann K, Printz BF, Solowiejczky DE, Gersony WM, Quaegebeur J, Apfel HD (2000) Two-dimensional echocardiographic assessment of right ventricular function as a predictor of outcome in hypoplastic left heart syndrome. Am J Cardiol 86(9):964–968
Kim AS, Witzenburg CM, Conaway M, Vergales JE, Holmes JW, L’Ecuyer TJ, Dean PN (2019) Trajectory of right ventricular indices is an early predictor of outcomes in hypoplastic left heart syndrome. Congenit Heart Dis 14(6):1185–1192. https://doi.org/10.1111/chd.12834 (Epub 2019 Aug 8)
Hormaza VM, Conaway M, Schneider DS, Vergales JE (2019) The effect of right ventricular function on survival and morbidity following stage 2 palliation: An analysis of the single ventricle reconstruction trial public data set. Congenit Heart Dis 14(2):274–279. https://doi.org/10.1111/chd.12722 (Epub 2018 Dec 2)
Raucci FJ Jr, Seckeler MD, Saunders C, Gangemi JJ, Peeler BB, Jayakumar KA (2013) Right-ventricular global longitudinal strain may predict neo-aortic arch obstruction after Norwood/Sano procedure in children with hypoplastic left heart syndrome. Pediatr Cardiol 34(8):1767–1771
Kalogeropoulos AP, Deka A, Border W et al (2012) Right ventricular function with standard and speckletracking echocardiography and clinical events in adults with D-transposition of the great arteries post atrial switch. J Am Soc Echocardiogr 25(3):304–312
Nadorlik H, Fleishman C, Brown DW, Miller-Tate H, Lenahan P, Nicholson L, Wheller J, Cua CL (2015) Survey of how pediatric cardiologists noninvasively evaluate patients with hypoplastic left heart syndrome. Congenit Heart Dis 10(2):E73–E82. https://doi.org/10.1111/chd.12224
Zaidi SJ, Lefaiver CA, Muangmingsuk S, Cui W, Roberson DA, Penk J (2018) Right ventricular longitudinal shortening before and after stage I surgical palliation correlates with outcomes. Pediatr Cardiol 39(3):526–532. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00246-017-1783-6 (Epub 2017 Nov 28)
Penk JS, Zaidi SJH, Lefaiver CA, Muangmingsuk S, Cui VW, Roberson DA (2018) Tissue Motion Annular Displacement Predicts Mortality/Transplant After the Bidirectional Glenn. World J Pediatr Congenit Hear Surg 9(2):171–176. https://doi.org/10.1177/2150135117742650
Asada D, Okumura K, Ikeda K, Itoi T (2018) Tissue Motion Annular Displacement of the Mitral Valve Can Be a Useful Index for the Evaluation of Left Ventricular Systolic Function by Echocardiography in Normal Children. Pediatr Cardiol 39(5):976–982. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00246-018-1847-2 (Epub 2018 Mar 8 PMID: 29520464)
Black DE, Bryant J, Peebles C, Godfrey KM, Hanson M, Vettukattil JJ (2014) Tissue motion annular displacement of the mitral valve using two-dimensional speckle tracking echocardiography predicts the left ventricular ejection fraction in normal children. Cardiol Young 24(4):640–648. https://doi.org/10.1017/S1047951113000863 (Epub 2013 Jun 27 PMID: 23803408)
Bellsham-Revell HR, Simpson JM, Miller OI, Bell AJ (2013) Subjective evaluation of right ventricular systolic function in hypoplastic left heart syndrome: how accurate is it? J Am Soc Echocardiogr 26(1):52–56
Puchalski MD, Williams RV, Askovich B, Minich LL, Mart C, Tani LY (2007) Congenit Heart Dis. 2(1):27–31. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1747-0803.2007.00068.x
Margossian R, Schwartz ML, Prakash A, Wruck L, Colan SD, Atz AM (2009) Comparison of echocardiographic and cardiac magnetic resonance imaging measurements of functional single ventricular volumes, mass, and ejection fraction (from the Pediatric Heart Network Fontan Cross-Sectional Study). Am J Cardiol. 104:419–428
Vitarelli A, Conde Y, Cimino E, D’Angeli I, D’Orazio S, Ventriglia F, Bosco G, Colloridi V (2005) Quantitative assessment of systolic and diastolic ventricular function with tissue Doppler imaging after Fontan type of operation. Int J Cardiol 102(1):61–69
Funding
This study received no funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Ethical Approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed Consent
Informed consent was not obtained from all individual participants as this was a retrospective study. This study was approved by the institutional IRB. Diligent measures were taken to maintain patient confidentiality.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zaidi, S.J., Ross, E., Gandhi, R. et al. Comparison of Quantitative Versus Qualitative Assessment of Single Right Ventricular Function for the Prediction of Midterm Outcomes. Pediatr Cardiol 42, 768–773 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00246-021-02539-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00246-021-02539-8