Abstract
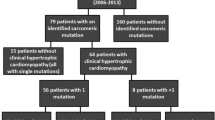
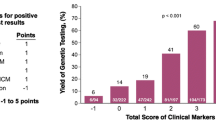
Genetic testing is recommended in patients with dilated cardiomyopathy (DCM); however, limited studies demonstrate high yields of genetic testing in non-hypertrophic (HCM) patients. Furthermore, there is sparse genotype–phenotype data in pediatric DCM patients. We performed a retrospective review of 70 consecutive probands with cardiomyopathy (non-HCM) who underwent genetic evaluation. Mean age at presentation was 5.48 years. Echocardiography revealed mean ejection fraction of 32.4%. The LVEDd z score ranged from − 5.7 to + 15.9. Cardiomyopathy was classified as dilated in 56, 10 with non-compaction, 2 with restrictive, and 2 with ARVC. TTN gene mutations were the most common gene involved. Genetic testing was negative in 16/70 (23%) giving a yield of 77% including VUS. 33% (23/70) of probands had a positive family history among whom the diagnostic yield was 57% (13/23) for pathogenic mutations. Yield for positive genetic testing in the DCM with positive family history group was 9/18 (50%). There were 6 deaths (9%) and 26/70 (37%) underwent transplantation. More frequent cardiac transplantations (48 vs. 34%) and deaths (17 vs. 2%) were seen in mutation-positive vs. mutation-negative subgroups. This study demonstrates an increasing yield of genetic testing in DCM although with a high rate of VUS detection. Use of genetic information for better management and prognostication will require big data analysis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Grenier MA, Osganian SK, Cox GF, Towbin JA, Colan SD, Lurie PR et al (2000) Design and implementation of the North American pediatric cardiomyopathy registry. Am Heart J 139(2 Pt 3):S86–S95
Kindel SJ, Miller EM, Gupta R, Cripe LH, Hinton RB, Spicer RL et al (2012) Pediatric cardiomyopathy: importance of genetic and metabolic evaluation. J Card Fail 18(5):396–403
Colan SD, Lipshultz SE, Lowe AM, Sleeper LA, Messere J, Cox GF et al (2007) Epidemiology and cause-specific outcome of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy in children: findings from the pediatric cardiomyopathy registry. Circulation 115(6):773–781
Hershberger RE, Lindenfeld J, Mestroni L, Seidman CE, Taylor MR, Towbin JA (2009) Genetic evaluation of cardiomyopathy: a Heart Failure Society of America practice guideline. J Card Fail 15(2):83–97
Ware SM (2011) Genetic diagnosis in pediatric cardiomyopathy: clinical application and research perspectives. Progress Pediatr Cardiol 31(2):99–102
Lai WW, Geva T, Shirali GS, Frommelt PC, Humes RA, Brook MM et al (2006) Guidelines and standards for performance of a pediatric echocardiogram: a report from the Task Force of the Pediatric Council of the American Society of Echocardiography. J Am Soc Echocardiogr 19(12):1413–1430
Towbin JA, Lowe AM, Colan SD, Sleeper LA, Orav EJ, Clunie S et al (2006) Incidence, causes, and outcomes of dilated cardiomyopathy in children. JAMA 296(15):1867–1876
Tariq M, Ware SM (2014) Importance of genetic evaluation and testing in pediatric cardiomyopathy. World J Cardiol 6(11):1156–1165
Ho CY (2011) New Paradigms in Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy: Insights from Genetics. Progress Pediatr Cardiol 31(2):93–98
Hershberger RE, Morales A, Siegfried JD (2010) Clinical and genetic issues in dilated cardiomyopathy: a review for genetics professionals. Genet Med 12(11):655–667
Mestroni L, Brun F, Spezzacatene A, Sinagra G, Taylor M (2014) Genetic causes of dilated cardiomyopathy. Prog Pediatr Cardiol 37(1–2):13–18
Herman DS, Lam L, Taylor MR, Wang L, Teekakirikul P, Christodoulou D et al (2012) Truncations of titin causing dilated cardiomyopathy. New Engl J Med 366(7):619–628
Akinrinade O, Ollila L, Vattulainen S, Tallila J, Gentile M, Salmenpera P et al (2015) Genetics and genotype-phenotype correlations in Finnish patients with dilated cardiomyopathy. Eur Heart J 36(34):2327–2337
Ashley EA, Hershberger RE, Caleshu C, Ellinor PT, Garcia JG, Herrington DM et al (2012) Genetics and cardiovascular disease: a policy statement from the American Heart Association. Circulation 126(1):142–157
Funding
This study did not receive any funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors. Institutional review board approved this retrospective chart review study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ellepola, C.D., Knight, L.M., Fischbach, P. et al. Genetic Testing in Pediatric Cardiomyopathy. Pediatr Cardiol 39, 491–500 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00246-017-1779-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00246-017-1779-2