Abstract
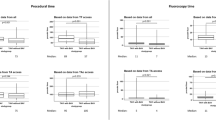
In neonates requiring balloon aortic valvuloplasty, both anterograde and retrograde approaches are feasible. A recent comparison of these two approaches is lacking. A retrospective cohort study of neonates at a single center undergoing BAV from 9/00 to 7/14 was performed. Records were reviewed including pre- and post-intervention echocardiograms and catheterization data. Comparisons of acute efficacy and procedural safety were made based on type of approach utilized. Forty-two neonates underwent BAV. Eleven cases utilized exclusively an anterograde approach, while 31 included a retrograde approach (including 4 with both approaches used). There were no significant differences between groups in baseline demographic and clinical characteristics. Additionally, by both pre-intervention echocardiogram and catheterization, there were no differences based on approach in aortic valve gradient, degree of aortic insufficiency (AI), or degree of mitral regurgitation (MR). Both approaches were equally efficacious in gradient reduction (45 ± 17 vs. 44 ± 21 mmHg, p = 0.97), and there was no difference in post-intervention AI as assessed by both catheterization and echocardiogram (52% vs. 64% none or trivial, p = 0.74). Additionally, there was no difference in the proportion of patients with an increased severity of MR after BAV (15% vs. 22%, p = 0.52). The retrograde approach required a larger arterial catheter and was associated with a higher rate of arterial thrombosis (61% vs. 18%, p = 0.014). Both anterograde and retrograde approaches to neonatal BAV appear to be equally efficacious in the short term. The anterograde approach avoids the need for a larger arterial catheter and may reduce the risk of arterial thrombosis.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lababidi Z, Wu JR, Walls JT (1984) Percutaneous balloon aortic valvuloplasty: results in 23 patients. Am J Cardiol 53:194–197
Zeevi B, Keane JF, Castaneda AR, Perry SB, Lock JE (1989) Neonatal critical valvar aortic stenosis: a comparison of surgical and balloon dilation therapy. Circulation 80:831–839
Gatzoulis MA, Rigby ML, Shinebourne EA, Redington AN (1995) Contemporary results of balloon valvuloplasty and surgical valvotomy for congenital aortic stenosis. Arch Dis Child 73:66–69
Zain Z, Zadinello M, Menahem S, Brizard C (2006) Neonatal isolated critical aortic valve stenosis: balloon valvuloplasty or surgical valvotomy. Heart Lung Circ 15:18–23
Magee AG, Nykanen D, McCrindle BW, Wax D, Freedom RM, Benson LN (1997) Balloon dilation of severe aortic stenosis in the neonate: comparison of anterograde and retrograde catheter approaches. J Am Coll Cardiol 30:1061–1066
Glatz AC, Shah SS, McCarthy AL, Geisser D, Daniels K, Xie D, Hanna BD, Grundmeier RW, Gillespie MJ, Rome JJ (2013) Prevalence of and risk factors for acute occlusive arterial injury following pediatric cardiac catheterization: a large single-center cohort study. Catheterization and Cardiovascular Interventions 82:454–462
Egito ES, Moore P, O’Sullivan J, Colan S, Perry SB, Lock JE, Keane JF (1997) Transvascular balloon dilation for neonatal critical aortic stenosis: early and midterm results. J Am Coll Cardiol 29:442–447
Burrows PE, Benson LN, Williams WG, Trusler JC, Smallhorn JF, Freedom RM (1990) Iliofemoral arterial complications of balloon angioplasty for systemic obstructions in infants and children. Circulation 82:1697–1704
McElhinney DB, Lock JE, Keane JF, Moran AM, Colan SD (2005) Left heart growth, function, and reintervention after balloon aortic valvuloplasty for neonatal aortic stenosis. Circulation 111:451–458
Hausdorf G, Schneider M, Schirmer KR, Schulze-Neick I, Lange PE (1993) Anterograde balloon valvuloplasty of aortic stenosis in children. Am J Cardiol 71:460–462
Justino H, Petit CJ (2016) Percutaneous common carotid artery access for pediatric interventional cardiac catheterization. Circ Cardiovasc Interv. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCINTERVENTIONS.115.003003
Choudhry S, Balzer D, Murphy J, Nicholas R, Shahanavaz S (2016) Percutaneous carotid artery access in infants < 3 months of age. Catheter Cardiovasc Interv 87:757–761
Robinson BV, Brzezinska-Rajszys G, Weber HS, Ksiazyk J, Fricker FJ, Fischer DR, Ettedgui JA (2000) Balloon aortic valvotomy through a carotid cutdown in infants with severe aortic stenosis: results of the multi-centric registry. Cardiol Young 10(3):225–232
Patel S, Saini AP, Nair A, Weber HS (2015) Transcarotid balloon valvuloplasty in neonates and small infants with critical aortic valve stenosis utilizing continuous transesophageal echocardiographic guidance: a 22 year single center experience from the cath lab to the bedside. Catheter Cardiovasc Interv 86(5):821–827
Brierley JJ, Reddy TD, Rigby ML, Thanopoulous V, Redington AN (1998) Traumatic damage to the mitral valve during percutaneous balloon valvuloplasty for critical aortic stenosis. Heart 79:200–202
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no potential conflicts of interest. This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Human and Animal Rights
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mozumdar, N., Burke, E., Schweizer, M. et al. A Comparison of Anterograde Versus Retrograde Approaches for Neonatal Balloon Aortic Valvuloplasty. Pediatr Cardiol 39, 450–458 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00246-017-1772-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00246-017-1772-9