Abstract
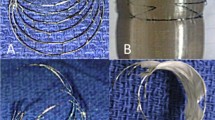
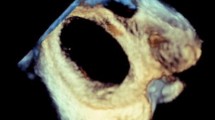
Diabolo stent configuration aids in stent positioning, stability, and creating a controlled defect with a predetermined size. A number of techniques to create the diabolo configuration have been previously described. The indications for creating a controlled “defect” are rapidly growing and include the Fontan circulation, patients with severe end-stage pulmonary hypertension, restrictive atrial communication in the setting of hypoplastic right or left heart syndrome, and diastolic left heart failure. We describe an alternative technique using a prefabricated readily available tool (gooseneck snare) to create a diabolo stent configuration. The chosen balloon expandable stent is mounted on a 5-mm gooseneck snare centered on an angioplasty catheter larger than 5 mm diameter. When deployed, the snare restricts the central waist to 5 mm and both ends expand to a larger diameter creating a dumbbell/diabolo configuration. A total of six diablo stent configurations were successfully implanted in four patients with failing Fontan physiology; five to create a transcatheter fenestration and one to relieve atrial septal restriction. Data expressed as median and IQR. Their weight was 24.8 kg (19.6–46.95), and age years was 9.2 (6.28–13.23). There were no complications and a consistent diabolo configuration with a 5-mm central waist was created in all patients. The snare serves as a sterile, preconfigured, radiopaque, readily available tool of adequate length and strength, to create consistent diabolo stent configuration without any modifications. This technique is a simple, reproducible, and easy to learn.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson B, Bhole V, Desai T, Mehta C, Stumper O (2010) Novel technique to reduce the size of a Fontan Diabolo stent fenestration. Catheter Cardiovasc Interv 76:860–864
Casadonte JR, Wax DF, Gossett JG (2015) Extracardiac Fontan fenestration using the SafeSept transseptal guidewire and snare-controlled diabolo-shaped covered-stent placement. Catheter Cardiovasc Interv. doi:10.1002/ccd.26081
Cheatham JP (2001) Intervention in the critically ill neonate and infant with hypoplastic left heart syndrome and intact atrial septum. J Interv Cardiol 14:357–366
Chiu JS, Zuckerman WA, Turner ME, Richmond ME, Kerstein D, Krishnan U, Torres A, Vincent JA, Rosenzweig EB (2015) Balloon atrial septostomy in pulmonary arterial hypertension: effect on survival and associated outcomes. J Heart Lung Transplant 34:376–380
Gewillig M, Boshoff D, Delhaas T (2006) Late fenestration of the extracardiac conduit in a Fontan circuit by sequential stent flaring. Catheter Cardiovasc Interv 67:298–301
Kreutzer J, Lock JE, Jonas RA, Keane JF (1997) Transcatheter fenestration dilation and/or creation in postoperative Fontan patients. Am J Cardiol 79:228–232
Kreutzer J, Graziano JN, Stapleton G, Rome JJ (2011) Late catheter interventions in hypoplastic left heart syndrome. Cardiol Young 21(Suppl 2):65–76
Mehta C, Jones T, De Giovanni JV (2008) Percutaneous transcatheter communication between the pulmonary artery and atrium following an extra-cardiac Fontan: an alternative approach to fenestration avoiding conduit perforation. Cathet Cardiovasc Interv 71:936–939
Pedra CA, Pihkala J, Benson LN, Freedom RM, Nykanen D (1999) Stent implantation to create interatrial communications in patients with complex congenital heart disease. Cathet Cardiovasc Interv 47:310–313 (discussion 314)
Prieto LR, Latson LA, Jennings C (2006) Atrial septostomy using a butterfly stent in a patient with severe pulmonary arterial hypertension. Catheter Cardiovasc Interv 68:642–647
Rupp S, Michel-Behnke I, Valeske K, Akinturk H, Schranz D (2007) Implantation of stents to ensure an adequate interatrial communication in patients with hypoplastic left heart syndrome. Cardiol Young 17:535–540
Rupp S, Schieke C, Kerst G, Mazhari N, Moysich A, Latus H, Michel-Behnke I, Akintuerk H, Schranz D (2015) Creation of a transcatheter fenestration in children with failure of fontan circulation: focus on extracardiac conduit connection. Catheter Cardiovasc Interv 86(7):1189–1194. doi:10.1002/ccd.26042
Seib PM, Faulkner SC, Erickson CC, Van Devanter SH, Harrell JE, Fasules JW, Frazier EA, Morrow WR (1999) Blade and balloon atrial septostomy for left heart decompression in patients with severe ventricular dysfunction on extracorporeal membrane oxygenation. Catheter Cardiovasc Interv 46:179–186
Sivaprakasam M, Kiesewetter C, Veldtman GR, Salmon AP, Vettukattil J (2006) New technique for fenestration of the interatrial septum. J Interv Cardiol 19:334–336
Stumper O, Gewillig M, Vettukattil J, Budts W, Chessa M, Chaudhari M, Wright JG (2003) Modified technique of stent fenestration of the atrial septum. Heart 89:1227–1230
Vlahos AP, Lock JE, McElhinney DB, van der Velde ME (2004) Hypoplastic left heart syndrome with intact or highly restrictive atrial septum: outcome after neonatal transcatheter atrial septostomy. Circulation 109:2326–2330
Vyas H, Driscoll DJ, Cabalka AK, Cetta F, Hagler DJ (2007) Results of transcatheter Fontan fenestration to treat protein losing enteropathy. Catheter Cardiovasc Interv 69:584–589
Author Contribution
Osamah Aldoss: Data collection, study design and data analysis/interpretation, drafting and revising the manuscript, and approval of article. Abhay Divekar: Study design and data analysis/interpretation, drafting and revising the manuscript, and approval of article.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest with respect to authorship and/or publication of the article.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Aldoss, O., Divekar, A. Modified Technique to Create Diabolo Stent Configuration. Pediatr Cardiol 37, 728–733 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00246-015-1339-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00246-015-1339-6