Abstract
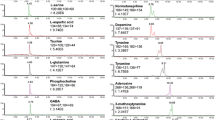
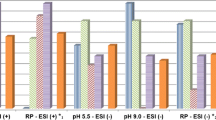
The simultaneous profiling of 43 functional metabolites in the brain of the small model vertebrate organism, marine medaka (Oryzais melastigma), has been accomplished via dansyl chloride derivatization and LC–MS/MS quantification. This technique was applied to examine effects of 2,2′,4,4′-tetrabromodiphenyl ether (BDE-47), one of the most abundant polybrominated diphenyl ether flame retardants in the natural environment, on the central nervous system (CNS) of vertebrates. The model teleosts were fed with bioencapsulated Artemia nauplii for up to 21 days. Multivariate statistical analysis has demonstrated that levels of numerous classical neurotransmitters and their metabolites in the CNS of the fish were perturbed even at the early phase of dietary exposure. Subsequent metabolic pathway analysis further implied potential impairment of the arginine and proline metabolism; glycine, serine and threonine metabolism; d-glutamine and d-glutamate metabolism; alanine, aspartate, and glutamate metabolism; valine, leucine, and isoleucine biosynthesis, and the cysteine and methionine metabolism in the brain of the test organism. Our results demonstrate that targeted profiling of functional metabolites in the CNS may shed light on how the various neurological pathways of vertebrates, including humans, are affected by toxicant/stress exposure.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alaee M, Arias P, Sjodin A, Bergman A (2003) An overview of commercially used brominated flame retardants, their applications, their use patterns in different countries/regions and possible modes of release. Environ Int 29:683–689
Anderson TD, MacRae JD (2006) Polybrominated diphenyl ethers in fish and wastewater samples from an area of the Penobscot River in central Maine. Chemosphere 62:1153–1160
Bisesi JH, Bridges W, Klaine SJ (2014) Effects of the antidepressant venlafaxine on fish brain serotonin and predation behavior. Aquat Toxicol 148:130–138
Bradner JM, Suragh TA, Wilson W, Lazo CR, Stout KA, Kim HM et al (2013) Exposure to the polybrominated diphenyl ether mixture DE-71 damages the nigrostriatal dopamine system: role of dopamine handling in neurotoxicity. Exp Neurol 241:138–147
Cai HL, Zhu RH, Li HD (2010) Determination of dansylated monoamine and amino acid neurotransmitters and their metabolites in human plasma by liquid chromatography-electrospray ionization tandem mass spectrometry. Anal Biochem 396:103–111
Dingemans MML, de Groot A, van Kleef RGDM, Bergman A, van den Berg M, Vijverberg HPM et al (2008) Hydroxylation increases the neurotoxic potential of BDE-47 to affect exocytosis and calcium homeostasis in PC12 cells. Environ Health Perspect 116:637–643
Eriksson P, Viberg H, Jakobsson E, Örn U, Fredriksson A (2002) A brominated flame retardant, 2,2′,4,4′,5-pentabromodiphenyl ether: uptake, retention, and induction of neurobehavioral alternations in mice during a critical phase of neonatal brain development. Toxicol Sci 67:98–103
Eskenazi B, Chevrier J, Rauch SA, Koqut K, Harley KG, Johnson C et al (2013) In utero and childhood polybrominated diphenyl ether (PBDE) exposures and neurodevelopment in the CHAMACOS study. Environ Health Perspect 121:257–262
Fitsanakis VA, Aschner M (2004) The importance of glutamate, glycine and gamma-aminobutyric acid transport and regulation in manganese, mercury and lead neurotoxicity. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 204:343–354
Guglielmotti V, Cristino L (2006) The interplay between the pineal complex and the habenular nuclei in lower vertebrates in the context of the evolution of cerebral asymmetry. Brain Res Bull 69:475–488
Guo K, Li L (2009) Differential 12C-/13C-isotope dansylation labeling and fast liquid chromatography/mass spectrometry for absolute and relative quantification of the metabolome. Anal Chem 81:3919–3932
Harry JG, Billingsley M, Bruinink A, Campbell IL, Classen W, Dorman DC et al (1998) In vitro techniques for the assessment of neurotoxicity. Environ Health Perspect 106:131–158
Herbstman JB, Sjödin A, Kurzon M, Ledeman SA, Jones RS, Rauh V et al (2010) Prenatal exposure to PBDEs and neurodevelopmental. Environ Health Perspect 118:712–719
Kasahara M, Naruse K, Sasaki S, Nakatani Y, Qu W, Ahsan B et al (2007) The medaka draft genome and insights into vertebrate genome evolution. Nature 447:714–719
Kodavanti PRS, Cobum CG, Moser VC, MacPhail RC, Fenton SE, Stoker TE et al (2010) Developmental exposure to a commercial PBDE mixture, DE-71: neurobehavioral, hormonal, and reproductive effects. Toxicol Sci 116:297–312
Li S, Pozhitkov A, Ryan RA, Manning CS, Brown-Pterson N, Brouwer M (2010) Constructing a fish metabolic network model. Genome Biol 11:R115
Marsh G, Stenutz R, Bergman A (2003) Synthesis of hydroxylated and methoxylated polybrominated diphenyl ethers—natural products and potential polybrominated diphenyl ether metabolites. Eur J Org Chem 14:2566–2576
National Research Council (1992) Environmental neurotoxicology. The National Academies Press, Washington
Reiter L (1978) An introduction to neurobehavioural toxicology. Environ Health Perspect 26:5–7
Rico EP, Rosemberg DB, Seibt KJ, Capiotti KM, Da Silva RS, Bonan CD (2011) Zebrafish neurotransmitter system as potential pharmacological and toxicological targets. Neurotoxicol Teratol 33:608–617
Sanders JM, Chen LJ, Lebetkin EH, Burka LT (2006) Metabolism and disposition of 2,2′,4,4′-tetrabromodiphenyl ether following administration of single or multiple doses to rats and mice. Xenobiotica 36:103–117
Signore IA, Guerrero N, Loosli F, Colombo A, Villalón A, Wittbrodt J et al (2009) Zebrafish and medaka: model organisms for a comparative developmental approach of brain asymmetry. Phil Trans R Soc B 364:991–1003
Stapleton HM, Letcher RJ, Li J, Baker JE (2004) Dietary accumulation and metabolism of polybrominated diphenyl ethers by juvenile carp (Cyprinus carpio). Environ Toxicol Chem 23:1939–1946
Stapleton HM, Brazil B, Holbrook RD, Mitchelmore CL, Benedict R, Konstantinov A (2006) In vivo and in vitro debromination of decabromodiphenyl ether (BDE 209) by juvenile rainbow trout and common carp. Environ Sci Technol 40:4653–4658
Tomy GT, Palace VP, Halldorson T, Braekevelt E, Danell R, Wautier K et al (2004) Bioaccumulation, biotransformation, and biochemical effects of brominated diphenyl ethers in juvenile lake trout (Salvelinus namaycush). Environ Sci Technol 38:1496–1504
U. S. EPA (U. S. Environmental Protection Agency). (2009) Polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs) Action Plan Summary. http://www.epa.gov/oppt/existingchemicals/pubs/actionplans/pbdes_ap_2009_1230_final.pdf. Accessed 8 Oct 2013
van de Merwe JP, Chan AKY, Lei ENY, Yau MS, Lam MHW, Wu RSS (2011) Bioaccumulation and maternal transfer of PBDE 47 in the marine medaka (Oryzias melastigma). Aquat Toxicol 103:199–204
van Thriel C, Westerink R, Beste C, Bale AS, Lein PJ, Leist M (2012) Translating neurobehavioural endpoints of developmental neurotoxicity tests into in vitro assays and readouts. Neurotoxicology 33:911–924
Xia J, Psychogios N, Young N, Wishart DS (2009) MetaboAnalyst: a web server for metabolomics data analysis and interpretation. Nucl Acid Res 37:W652–W660
Xia J, Sinelnikov IV, Han B, Wishart DS (2015) MetaboAnalyst 30-making metabolomics more meaningful. Nucl Acid Res. doi:10.1093/nar/gkv380
Yan T, Xiang L, Xuejun J, Chengzhi C, Youbin Q, Xuelan Y et al (2012) Spatial learning and memory deficit of low level polybrominated diphenyl ethers-47 in male adult rat is modulated by intracellular glutamate receptors. J Toxicol Sci 37:223–233
Ye RR, Lei ENY, Lam MHW, Chan AKY, Bo J, van de Merwe JP, Fong ACC, Yang MS, Lee JS, Segner HE, Wong CKC, Wu RSS, Au DWT (2012) Gender-specific modulation of immune system complement gene expression in marine medaka Oryzias melastigma following dietary exposure of BDE-47. Environ Sci Poll Rep 19:2477–2487
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the State Key Laboratory for Marine Pollution, City University of Hong Kong, and the State Key Laboratory of Environmental and Biological Analysis, Hong Kong Baptist University, Hong Kong Special Administrative Region, China.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Elva Ngai-Yu Lei and Man-Shan Yau are co-first authors of this manuscript.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lei, E.NY., Yau, MS., Yeung, CC. et al. Profiling of Selected Functional Metabolites in the Central Nervous System of Marine Medaka (Oryzias melastigma) for Environmental Neurotoxicological Assessments. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 72, 269–280 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00244-016-0342-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00244-016-0342-0