Abstract
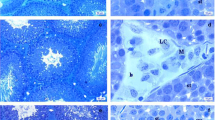
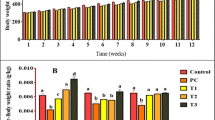
Few or no studies have measured the toxic effects of subchronic exposure to leachate using key markers linked with spermatogenesis and cellular adenosine triphosphate (ATP) in an experimental rat model. This study was undertaken to evaluate the toxic effects of leachate obtained from the Elewi Odo municipal battery-recycling site (EOMABRL) on male reproductive function using testicular hormones and biomarker of cellular ATP. EOMABRL was administered at 0, 20, 40, 60, 80, and 100 % concentrations to adult male rats for 60 days. After exposure, serum was collected for hormonal biochemistry assays, and testes were collected to determine the activity of xanthine oxidase (XO) and lactate dehydrogenase (LDH). Exposure of animals to EOMABRL resulted in a 519.7, 285.7, 569.1, 606.1, and 1,793.2 % increase in XO activity with a sequential decrease in LDH activity (marker of cellular ATP) by 44.1, 55.9, 61.4, 69.3, and 89.7 %, respectively, compared with the control. Furthermore, EOMABRL caused a significant inhibitory effect on serum luteinizing hormone, follicle-stimulating hormone, and testosterone levels. We conclude that some possible mechanisms by which EOMABRL elicits toxicity in male rat testes could be through inhibition of LDH activity and depletion of serum hormone levels.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aitken RJ, Ryan AL, Curry BJ, Baker MA (2004) Multiple forms of redox activity in populations of human spermatozoa. Mol Hum Reprod 9:645–661
Akintunde JK, Oboh G (2012) In vitro oxidative damage induced in livers, hearts and kidneys of rats treated with leachate from battery recycling site: Evidence for environmental contamination and tissue damage. J Clin Exp Pathol 2:129
Akintunde JK, Oboh G (2013a) Municipal auto-battery recycling-site leachate activates key enzymes linked to non-insulin dependent diabetes mellitus (NIDDM) and hypertension. J Diabetes Metab 4:235
Akintunde JK, Oboh G (2013b) Exposure to leachate from municipal battery recycling site: Implication as key inhibitor of steroidogenic enzymes and risk factor of prostate damage in rats. 28(2–3):107–115
Akintunde JK, Oboh G, Akindahunsi AA (2013) Testicular membrane lipid damage by complex mixture of leachate from municipal battery recycling site as indication of idiophatic male infertility in rat. J Interdiscip Toxicol 6(4):192–197
Aleksandra D, Urszula B (2008) The impact of nickel on human health. J Elem 13(4):685–696
Alexander BH, Chckoway H, Van Netten C, Muller CH, Ewers TG, Kaufman JD et al (1996) Semen quality of men employed at a lead smelter. Occup Environ Med 55:364–374
Apostoli P, Telišman S, Sager PR (2007) Reproductive and developmental toxicity of metals. In: Nordberg GF, Fowler BA, Nordberg M, Friberg LT (eds) Handbook on the toxicology of metals. Academic Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 213–249
Apostoll P, Kiss P, Porru S, Bonde JP, Vanhoorne M (1998) Male reproductive toxicity of lead in animals and humans. Occup Environ Med 55:364–374
Assenato G, Paci C, Baser ME, Molinini R, Candela RG, Altamura BM et al (1987) Sperm count suppression without endocrine dysfunction in lead-exposed men. Arch J Environ Health 42:124–127
Association of Official Analytical Chemists (2005) Official methods of analysis (15th ed). Longman, Washington
Biswas NM, Sengupta R, Chatopadyay GR, Choudhury A, Sarkar M (2001) Effects of ethanol on cadmium-induced testicular toxicity in male rats. Reprod Toxicol 15:699–704
Bonde JP, Joffe M, Apostoll P, Dale A, Kiis P, Spano M et al (2002) Sperm count and chromatin structure in men exposed to inorganic lead: Lowest adverse effect levels. Occup Environ Med 59:234–242
Bray TM, Levy MA, Noseworthy MD (1997) The role of zinc Zn in free radical mediated diseases. In: Fischer PWF, Abb´e MR, Cockell KA, Gibson RS (eds) Trace elements in man and animals—9: Proceedings of the Ninth International Symposium on Trace Elements in Man and Animals. NRC Research Press, Ottawa, Canada, pp 333–6
Bryant SD (2004) Lead-contaminated drinking waters in the public schools of Philadelphia. J Clin Toxicol 42:287–294
Brys M, Nawrocka AD, Miekos E (1997) Zinc and cadmium analysis in human prostate neoplasms. Biol Trace Elem Resour 59:145–152
California Environmental Protection Agency (CEPA) (2012) Chemicals known to the state to cause cancer or reproductive toxicity list as of June 22, 2012. Proposition 65: The Safe Drinking Water and Toxic Enforcement Act of 1986. Sacramento, CA. http://www.oehha.ca.gov. Accessed 19 May 2014
Centres for Disease Control and Prevention (CDCP) (2009). Fourth report on human exposure to environmental chemicals. CDCP, Atlanta, GA. http://www.cdc.gov/exposurereport/pdf/fourthreport.pdf. Accessed 17 Sept 2012
Chandra AK, Chatterjee A, Ghosh R, Sarkar M, Chaube SK (2007) Chromium induced testicular impairment in relation to adrenocortical activities in adult albino rats. Reprod Toxicol 24:388–396
Chia SE, Ong CN, Lee ST, Tsakok FH (1992) Blood concentrations of lead, cadmium, mercury, zinc and copper and human semen parameters. Arch Androl 29:177–183
Chowdhury AR (2009) Recent advances in heavy metals induced effect on male reproductive function. J Med Sci 2:37–42
Creasy DM (1999) Hormononal mechanism in male reproductive tract toxicity. In: Harvey PW, Rush KC, Cockburn A (eds) Endocrine and hormonal toxicology. Wiley, Chichester, pp 355–405
Creasy DM (2001) Pathogenesis of male reproductive toxicity. Toxicol Pathol 29:64–76
Cross CE (1987) Oxygen radicals and human disease. Annu Int Med 107:526
Dawson EB, Ritter S, Harris WA, Evans DR, Powell LC (1998) Comparison of sperm viability with seminal plasma metal levels. Biol Trace Elem Resour 64:215–219
De Krester DM (1987) A hormonal control of reproduction (2nd ed). Oxford University, Oxford, pp 76–90
De Lamirande E, Gagnon C (1992) Reactive oxygen species and human spermatozoa: Effects on the motility of intact spermatozoa and on sperm axoneme. J Androl 13:368–378
European Chemicals Bureau (2010) European Chemical Substances Information System [database on the Internet]. http://ecb.jrc.ec.europa.eu/esis. Accessed 22 Mar 2012
Farombi EO, Akintunde JK, Nsute N, Adedara IA, Arojojoye O (2011) Municipal landfill leachate induces hepatotoxicity and oxidative stress in rats. J Toxicol Indust Health 28(6):532–541
Ferrari B, Radetski CM, Veber AM, Ferard JF (1999) Ecotoxicological assessment of solid wastes: a combined liquid- and solid-phase testing approach using a battery of bioassays and biomarkers. Environ Toxicol Chem 18:1195–1202
Flora SJ, Mehta A, Rao PV, Kannan GM, Bhaokar A, Dube SN (2004) Therapeutic potential of mono-isoamyl and mono-methyl esters of meso 2,3-dimercaptosuccimic acid in gallium arsenide intoxicated rats. Toxicology 195:127–146
Freedman LP (1992) Anatomy of the steroid receptor zinc finger region. Endocrinol Rev 13:129–145
Friedmann AS (2002) Atrazine inhibition of testosterone production in rat males following peripubertal exposure. Reprod Toxicol 16:275–279
Gale EF, Cundliffe E, Reynolds PE (1981) The molecular basis of antibiotic action, 2nd edn. Wiley, New York
Gresser MJ (1981) ADP-arsenate formation by submitochondrial particles under phosphorylating conditions. J Biol Chem 256(12):5981–5983
Griffiths LM, Loeffler SH, Socha MT (2007) Effects of supplementing complexed zinc, manganese, copper and cobalt on lactation and reproductive performance of intensively grazed lactating dairy cattle on the South Island of New Zealand. Anim Feed Sci Technol 137:69–83
Houk VS (1992) The genotoxicity of industrial wastes and effluents. Mutat Resour 277:91–138
Huang K, Li J, Xu Z (2010) Characterization and recovery of cadmium from waste nickel–cadmium batteries. Waste Manag 30:2292–2298
International Agency for Research on Cancer (2012) Monographs on the evaluation of carcinogenic risks to humans. Some drinking-water disinfectants and contaminants, including arsenic 84:39. http://www.inchem.org/documents/iarc. Accessed 13 Feb 2013
Johnson L, Welsh Jr TH, Wilker CE (1997) Anatomy and physiology of male reproductive system and potential targets of toxicants. Comprehensive toxicology. Volume 10. Reproductive and endocrine toxicology. Elsevier Science International, New York, NY, pp 5–6
Klaassen C, Watkins J (2003) Casarett and Doull’s essentials of toxicology. McGraw-Hill, New York, p 512
Kumar S, Sathwara NG, Gautam AK, Agarwal K, Shah B, Kulkarni PK et al (2005) Semen quality of industrial workers occupationally exposed to chromium. J Occup Health 47:424–430
Li H, Chen Q, Li S, Yao W, Li L, Shi X et al (2001) Effect of Cr(VI) exposure on sperm quality: human and animal studies. Annu Occup Hygiene 45:505–511
Longe EO, Balogun MR (2010) Groundwater quality assessment near a municipal landfill, Lagos, Nigeria. Res J Appl Sci Eng Technol 2(1):39–44
Longe EO, Enekwechi LO (2007) Investigation on potential groundwater impacts and influence of local hydrogeology on natural attenuation of leachate at a municipal landfill. Int J Environ Sci Technol 4(1):133–140
Marouani N, Tebourbi O, Mahjoub S, Yacoubi MT, Sakly M, Benkhalifa M, Rhouma KB (2012) Effects of hexavalent chromium on reproductive functions of male adult rats. J Reprod Biol 12(2):119–133
Meeker JD, Rossano MG, Protas B, Diamond MP, Puscheck E, Daly D et al (2009) Multiple metals predict prolactin and thyrotropin (TSH) levels in men. Environ Resour 109:869–873
Naha N, Chowdhury AR (2006) Inorganic lead exposure in battery and paint factory: effect on human sperm structure and functional activity. J UOEH 28:157–171
Nduka JKC, Orisakwe OE, Nwangunna CK (2007) Heavy metals other than lead in flaked paints from buildings in Eastern Nigeria. Toxicol Ind Health 23:525–528
Parlakpinar H, Tasdemir S, Polat A, Bay-Karabulut A, Vardi N, Ucar M, Yanilmaz M, Kavakli A, Acet A (2006) Protective effect of chelerythrine on gentamicin-induced nephrotoxicity. Cell Biochem Funct 24:41–48
Robaire B, Hales BF (2003) Advances in male mediated developmental toxicity. Kluwer/Plenum, New York
Rosner M, Dolznig H, Schipany K, Mikula M, Brandau O (2010) Human amniotic fluid stem cells as a model for functional studies of genes involved in human genetic diseases or oncogenesis. Oncotarget 2:705–712
RoyChowdhurry A, Chinoy NJ, Gautam AK, Rao RV, Parikh DJ, Shah GM et al (1986) Effects of lead on human sperm. Adv Contracept Deliv Syst 11:208–210
Saaranen M, Kantola M, Saarikoski S (1989) Human seminal plasma cadmium: comparison with fertility and smoking habits. Andrologia 21:140–145
Shahida N, Ihsnullah Z, Shah MT, Iqbal Z (2009) Effect of time intervals on levels of selected heavy metals in surface and ground water in Peshawar basin. J Chem Soc Pak 31(5):757–771
Siddique HR, Gupta SC, Dhawan A, Murthy RC, Saxena DK, Chowdhuri DK (2005) Genotoxicity of industrial solid waste leachates in Drossophila melanogaster. Environ Mol Mutagen 46:189–197
Southorn PA, Powis G (1988) Free radicals in medicine. II Involvement in human disease. Mayo Clin Proc 63:390–408
Stryer L (2002) Biochemistry, 5th edn. Freeman, New York, p 6
Telišman S, Cvitković P, Jurasović J, Pizent A, Gavella M, Ročić B (2000) Semen quality and reproductive endocrine function in relation to biomarkers of lead, cadmium, zinc, and copper in men. Environ Health Perspect 108:45–53
Underwood EJ, Somers M (1969) Studies of zinc nutrition in sheep. 1. The relation of zinc to growth, testicular development, and spermatogenesis in young rams. Aust J Agric Res 20:889–897
Van Matthies J, Donat H, Schwarz I (1989) Einfluss Von Schwarmetallionen auf die mannliche fertilitat. Zentralbl Gynakol 111:155–166
Waalkes MP, Rehms S (1994) Cadmium and prostate cancer. J Toxicol Environ Health 43:251–269
Walker PDY, Barri SV (1999) Oxidant mechanisms in gentamicin nephrotoxicity. J Ren Fail 21:433
Watanabe G, Taya K, Sasamoto S (1985) Radioimmunoassay for progesterone, testosterone and estradiol-17β using125I-iodohistamine radioligands. Jpn J Anim Reprod 31:186–197
Weisshaar HD (1975) Normal ranges of alpha-HBDH, LDH, AP, and LAP as measured with substrate-optimated test charges. Med Welt 26:387–392
Williams RJP (1989) An introduction to the biochemistry of zinc. In: Mills CF (ed) Zinc in human biology. Springer-Verlag, London, pp 15–31
Winder C (1989) Reproductive and chromosomal effects of occupational exposure to lead in the male. Reprod Toxicol 3:221–233
Wirth JJ, Mijal RS (2010) Adverse effects of low level heavy metal exposure on male reproductive function. Syst Biol Reprod Med 56:147–167
Wong WY, Flik G, Groenen PMW (2001) The impact of calcium, magnesium, zinc, and copper in blood and seminal plasma on semen parameters in men. Reprod Toxicol 15:131–136
World Health Organisation (1993) Guidelines for drinking water quality: Recommendations (2nd ed). Volume 1. WHO, Geneva, Switzerland
World Health Organisation (1996) Health criteria and other supporting information. In: Guidelines for drinking-water quality (2nd ed). WHO, Geneva, Switzerland, pp 940–949
World Health Organisation (2008) International year of fresh water. General Assembly Resolution A/RES/55/196. www.wateryear2003.org. Accessed 13 Mar 2011
World Health Organization (1992) Laboratory manual for the examination of human semen and sperm-cervical mucus interaction. Cambridge University Press, London
Xu B, Chia SE, Tsakok M, Ong CN (1993) Trace elements in blood and seminal plasma and their relationship to sperm quality. Reprod Toxicol 7:613–618
Zar JH (1984) Biostatistical analysis. Prentice-Hall, Inc., Upper Saddle River, NJ, p 620
Zeng X, Jin T, Jiang X, Kong Q, Ye T, Nordberg GF (2004) Effects on the prostate of environmental cadmium exposure—A cross-sectional population study in China. Biometals 17:559–565
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Akintunde, J.K., Oboh, G. & Akindahunsi, A.A. Inhibition of Key Markers Linked With Spermatogenesis and Cellular ATP by Subchronic Exposure to Leachate in a Rat Model. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 68, 159–168 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00244-014-0068-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00244-014-0068-9