Abstract
Background
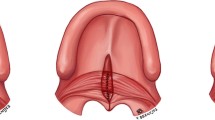
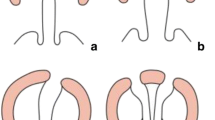
A cleft palate is a congenital condition in which the palate has an opening that can be on either one or both sides of the roof of the mouth and vary in size. Different surgical techniques are used to correct cleft palate. The choice of surgical approach for cleft palate repair relies on the nature and size of the aperture as well as the surgeon’s experience and preferences. The current systematic review and meta-analysis’s main goal was to evaluate and compare the efficacy of various cleft palate surgical procedures.
Methods
The databases of PubMed, ScienceDirect, and Google Scholar were searched for English papers having online complete texts. Preclinical studies, abstracts, theses, editorials, commentaries, meta-analyses, systematic reviews, and evidence synthesis were all disregarded. A prevalence meta-analysis and subgroup analysis were carried out with the use of Stata and the Meta XL statistical software.
Results
Medline, Google Scholar, and PubMed were among the databases searched. A first search revealed 3059 studies. Only 2562 studies remained after duplicates were eliminated. The abstracts and titles of the articles were skimmed. 266 papers were examined after being cut based on predetermined eligibility criteria. Finally, 36 articles were found to have successfully met the eligibility requirements.
Conclusions
Furlow palatoplasty was superior to other procedures in terms of incidence of velopharyngeal insufficiency. The effectiveness of techniques for speech based on fistula formation was Bardach, Furlow, Wardill-Kilner then von Langenbeck. The one stage palatoplasty was superior to the two-stage approach in terms of fistula formation and velopharyngeal insufficiency.
Level of evidence: Not ratable














Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agrawal K (2009) Cleft palate repair and variations. Indian J Plast Surg 42:S102–S109. https://doi.org/10.1055/S-0039-1699382
Canfield MA, Honein MA, Yuskiv N et al (2006) National estimates and race/ethnic-specific variation of selected birth defects in the United States, 1999–2001. Birth Defects Res A Clin Mol Teratol 76:747–756. https://doi.org/10.1002/BDRA.20294
Campbell A, Costello BJ, Ruiz RL (2010) Cleft lip and palate surgery: an update of clinical outcomes for primary repair. Oral Maxillofac Surg Clin North Am 22:43–58. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.COMS.2009.11.003
LaRossa D (2000) The state of the art in cleft palate surgery. Cleft Palate Craniofac J 37(3):225–228. https://doi.org/10.1597/1545-1569_2000_037_0225_tsotai_2.3.co_2
Eliason MJ, Hadford S, Green L, Reeves T (2020) Incidence of fistula formation and velopharyngeal insufficiency in early versus standard cleft palate repair. J Craniofac Surg 31:980–982. https://doi.org/10.1097/SCS.0000000000006307
Gustafsson C, Vuola P, Leikola J, Heliövaara A (2020) Pierre robin sequence: incidence of speech-correcting surgeries and fistula formation. Cleft Palate Craniofac J 57:344–351. https://doi.org/10.1177/1055665619874991
Pitkanen VV, Geneid A, Saarikko AM et al (2023) Diagnosing and managing velopharyngeal insufficiency in patients with cleft palate after primary palatoplasty. J Craniofac Surg. https://doi.org/10.1097/SCS.0000000000009822
Kummer AW (2011) Perceptual assessment of resonance and velopharyngeal function. Semin Speech Lang 32:159–167. https://doi.org/10.1055/S-0031-1277718/ID/32/BIB
Kara M, Calis M, Kara I et al (2021) Comparison of speech outcomes using type 2b intravelar veloplasty or furlow double-opposing Z plasty for soft palate repair of patients with unilateral cleft lip and palate. J Cranio-Maxillofacial Surg 49:215–222. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JCMS.2021.01.003
Spauwen PHM, Goorhuis-Brouwer SM, Schutte HK (1992) Cleft palate repair: Furlow versus von Langenbeck. J Cranio-Maxillofacial Surg 20:18–20. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1010-5182(05)80190-8
Correction of secondary velopharyngeal insufficiency in clef... : plastic and reconstructive surgery. https://journals.lww.com/plasreconsurg/Abstract/1994/12000/Correction_of_Secondary_Velopharyngeal.5.aspx. Accessed 7 Jul 2023
Deren O, Ayhan M, Tuncel A et al (2005) The correction of velopharyngeal insufficiency by Furlow palatoplasty in patients older than 3 years undergoing Veau-Wardill-Kilner palatoplasty: a prospective clinical study. Plast Reconstr Surg 116:85–93. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.PRS.0000169714.38796.AD
Kirschner RE, Wang P, Jawad AF et al (1999) Cleft-palate repair by modified Furlow double-opposing Z-plasty: the Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia experience. Plast Reconstr Surg 104:1998–2010. https://doi.org/10.1097/00006534-199912000-00009
Chan EKW, Lee KH, Tsui BSY et al (2014) From von Langenbeck to Furlow palatoplasty: a 16-year review of cleft palate repair. Surg Pract 18:67–71. https://doi.org/10.1111/1744-1633.12054
Randag AC, Dreise MM, Ruettermann M (2014) Surgical impact and speech outcome at 2.5 years after one- or two-stage cleft palate closure. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol 78:1903–1907. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.IJPORL.2014.08.021
Koh KS, Kim SC, Oh TS (2013) Management of velopharyngeal insufficiency using double opposing z-plasty in patients undergoing primary two-flap palatoplasty. Arch Plast Surg 40:97–103. https://doi.org/10.5999/APS.2013.40.2.97
Seagle MB, Patti CS, Williams WN, Wood VD (1999) Submucous cleft palate: a 10-year series. Ann Plast Surg 42:142–148. https://doi.org/10.1097/00000637-199902000-00006
Farzaneh F, Lindman R, Becker M et al (2009) von Langenbeck procedures at 8 months or Wardill at 18 months for primary repair of cleft palate in adult Swedish patients with unilateral complete cleft lip and palate: a study of facial growth. 42:67–76. https://doi.org/10.1080/02844310701850512
Dong Y, Dong F, Zhang X et al (2012) An effect comparison between Furlow double opposing Z-plasty and two-flap palatoplasty on velopharyngeal closure. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg 41:604–611. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijom.2012.01.010
Wójcicki P, Wójcicka G (2008) The management of velopharyngeal insufficiency with Furlow double-opposing Z-plasty procedure. Eur J Plast Surg 31:115–121. https://doi.org/10.1007/S00238-008-0254-Y/METRICS
Williams WN, Seagle MB, Pegoraro-Krook MI et al (2011) Prospective clinical trial comparing outcome measures between furlow and von langenbeck palatoplasties for UCLP. Ann Plast Surg 66:154–163. https://doi.org/10.1097/SAP.0B013E3181D60763
De Mey A, Franck D, Cuylits N et al (2009) Early one-stage repair of complete unilateral cleft lip and palate. J Craniofac Surg 20:1723–1728. https://doi.org/10.1097/SCS.0B013E3181B3EF71
Becker M, Svensson H, McWilliam J et al (2009) Adult skeletal profile in isolated cleft palate: a comparison of the von langenbeck and wardill procedures for primary repair of the palate. 35:387–397. https://doi.org/10.1080/028443101317149354
Sullivan SR, Vasudavan S, Marrinan EM, Mulliken JB (2011) Submucous cleft palate and velopharyngeal insufficiency: comparison of speech outcomes using three operative techniques by one surgeon. 48:561–570. https://doi.org/10.1597/09-127
Holtmann B, Wray RC, Weeks PM (1984) A comparison of three techniques of palatorrhaphy: early speech results. Ann Plast Surg 12:514–518. https://doi.org/10.1097/00000637-198406000-00004
Brothers DB, Dalston RW, Peterson HD, Lawrence WT (1995) Comparison of the Furlow double-opposing Z-palatoplasty with the Wardill-Kilner procedure for isolated clefts of the soft palate. Plast Reconstr Surg 95:969–977. https://doi.org/10.1097/00006534-199505000-00003
Liao YF, Noordhoff MS, Huang CS et al (2004) Comparison of obstructive sleep apnea syndrome in children with cleft palate following Furlow palatoplasty or pharyngeal flap for velopharyngeal insufficiency. Cleft Palate Craniofac J 41:152–156. https://doi.org/10.1597/02-162
Dec W, Shetye PR, Grayson BH et al (2013) Incidence of oronasal fistula formation after nasoalveolar molding and primary cleft repair. J Craniofac Surg 24:57–61. https://doi.org/10.1097/SCS.0B013E31826D09B5
Holland S, Gabbay JS, Heller JB et al (2007) Delayed closure of the hard palate leads to speech problems and deleterious maxillary growth. Plast Reconstr Surg 119:1302–1310. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.PRS.0000258518.81309.70
Ravishanker R (2006) Furlow’s palatoplasty for cleft palate repair. Med J Armed Forces India 62:239. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0377-1237(06)80010-9
Losken HW, Van Aalst JA, Teotia SS et al (2011) Achieving Low cleft palate fistula rates: surgical results and techniques. 48:312–320. https://doi.org/10.1597/08-288
Yun SP, De Chalain T (2008) Incidence of oronasal fistulae and velopharyngeal insufficiency after cleft palate repair: an audit of 211 children born between 1990 and 2004. 45:172–178. https://doi.org/10.1597/06-205.1
Pradel W, Senf D, Mai R et al (2009) One-stage palate repair improves speech outcome and early maxillary growth in patients with cleft lip and palate. J Physiol Pharmacol 60(Suppl 8):37–41
Yamanishi T, Nishio J, Sako M et al (2011) Early two-stage double opposing z-plasty or one-stage push-back palatoplasty?: comparisons in maxillary development and speech outcome at 4 years of age. Ann Plast Surg 66:148–153. https://doi.org/10.1097/SAP.0B013E3181D6E426
Kahraman A, Yuce S, Kocak OF et al (2014) Comparison of the fistula risk associated with rotation palatoplasty and conventional palatoplasty for cleft palate repair. J Craniofac Surg 25:1728–1733. https://doi.org/10.1097/SCS.0000000000000967
Woo AS, Skolnick GB, Sachanandani NS, Grames LM (2014) Evaluation of two palate repair techniques for the surgical management of velopharyngeal insufficiency. Plast Reconstr Surg 134:588e–596e. https://doi.org/10.1097/PRS.0000000000000506
Gunther E, Wisser JR, Cohen MA, Brown AS (1998) Palatoplasty: Furlow’s double reversing Z-plasty versus intravelar veloplasty. 35:546–549. https://doi.org/10.1597/1545-1569_1998_035_0546_PFSDRZ_2.3.CO_2
Yuan N, Dorafshar AH, Follmar KE et al (2016) Effects of cleft width and veau type on incidence of palatal fistula and velopharyngeal insufficiency after cleft palate repair. Ann Plast Surg 76:406–410. https://doi.org/10.1097/SAP.0000000000000407
Deshpande GS, Campbell A, Jagtap R et al (2014) Early complications after cleft palate repair: a multivariate statistical analysis of 709 patients. J Craniofac Surg 25:1614–1618. https://doi.org/10.1097/SCS.0000000000001113
Karsten DA, Larson DM, Larson DO (2003) Dental occlusion after Veau-Wardill-Kilner versus minimal incision technique repair of isolated clefts of the hard and soft palate. 40:504–510. https://doi.org/10.1597/1545-1569_2003_040_0504_DOAVVM_2.0.CO_2
Basta MN, Silvestre J, Stransky C et al (2014) A 35-year experience with syndromic cleft palate repair: operative outcomes and long-term speech function. Ann Plast Surg 73:S130–S135. https://doi.org/10.1097/SAP.0000000000000286
Rohrich RJ, Rowsell AR, Johns DF et al (1996) Timing of hard palatal closure: a critical long-term analysis. Plast Reconstr Surg 98:236–246. https://doi.org/10.1097/00006534-199608000-00005
Grobbelaar AO, Hudso DA, Fernandes DB, Lentin R (1995) Speech results after repair of the cleft soft palate. Plast Reconstr Surg 95:1150–1154. https://doi.org/10.1097/00006534-199506000-00002
Vedung S (1995) Pharyngeal flaps after one- and two-stage repair of the cleft palate: a 25-year review of 520 patients. Cleft Palate Craniofac J 32:206–216. https://doi.org/10.1597/1545-1569_1995_032_0206_PFAOAT_2.3.CO_2
Funding
The authors declare that no funds, grants, or other support were received during the preparation of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
The authors made substantial contributions to the design and analysis of the systematic review while working with other professionals. Additionally, they actively took part in the selection, screening, and examination of studies, the collection of data and information, the evaluation of the randomized controlled trials’ quality, and the data synthesis process. The entire process of examining and approving the finished manuscript was handled by the authors.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
Due to the nature of the study, ethical approval was waived.
Consent to participate
For this type of study, informed consent is not required.
Consent to publish
For this type of study, consent to publish is not required.
Competing interests
Muhannad Q. Alqirnas, Abdulaziz S. Almosa, Salman Sufian Qasim, Hanan Alhusainan have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Alqirnas, M.Q., Almosa, A.S., Qasim, S.S. et al. Systematic review and meta-analysis of speech outcome among different surgical techniques post cleft palate repair: Furlow against other palatoplasty techniques. Eur J Plast Surg 47, 50 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00238-024-02198-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00238-024-02198-x