Abstract
Purpose
The aim of this study was to evaluate the diagnostic performance of Inhance 3D Velocity (I3DV) in intracranial venous thrombosis and investigate the possible impact of venous sinus hypoplasia/aplasia on false thrombosis diagnosis made with I3DV.
Methods
This study included 540 patients. Contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance venography combined with conventional sequences was considered the gold standard test (GST), while I3DV was considered as diagnostic test. We accessed the diagnostic success of I3DV for intracranial venous thrombosis detection, thrombosed vessel identification, and total/partial thrombus distinction. The possible relationship between false-positive thrombus diagnosed by I3DV and venous sinus hypoplasia or aplasia diagnosed by GST was investigated.
Results
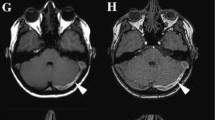
The sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value, negative predictive value, and accuracy of I3DV in the detection of intracranial venous thrombosis were 95.7%, 92.1%, 64.1%, 99.3%, and 92.6%, respectively. A significant association was observed between I3DV and GST in terms of thrombosis detection and total/partial thrombus distinction (p < 0.001). A significant relationship was observed between false-positive thrombosis diagnosis in I3DV and hypoplasia in the left transverse sinus (p < 0.001).
Conclusion
Intracranial venous thrombosis may be diagnosed faster and more accurately than traditional phase contrast magnetic resonance angiography in I3DV. This technique can be used in situations where contrast medium application is contraindicated. As in other non-contrast magnetic resonance venography techniques, left transverse sinus hypoplasia can be diagnosed as a thrombosed vessel in I3DV.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Leach JL, Fortuna RB, Jones BV, Gaskill-Shipley MF (2006) Imaging of cerebral venous thrombosis: current techniques, spectrum of findings, and diagnostic pitfalls. Radiographics. 26(Suppl 1):S19–S43
Morris PP, Black DF, Port J, Campeau N (2017) Transverse sinus stenosis is the most sensitive mr imaging correlate of idiopathic intracranial hypertension. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 38:471–477
Mas JL, Meder JF, Meary E, Bousser MG (1990) Magnetic resonance imaging in lateral sinus hypoplasia and thrombosis. Stroke. 21:1350–1356
Ghoneim A, Straiton J, Pollard C, Macdonald K, Jampana R (2020) Imaging of cerebral venous thrombosis. Clin Radiol 75:254–264
Dmytriw AA, Song JSA, Yu E, Poon CS (2018) Cerebral venous thrombosis: state of the art diagnosis and management. Neuroradiology. 60:669–685
Shigenaga Y, Sasaki M, Ishimoto T, Ama K (2018) Simultaneous visualization of vessels and brain tumor with contrast-enhanced three-dimensional phase-contrast MR imaging. Magn Reson Med Sci 17:184–188
Lummel N, Boeckh-Behrens T, Lutz J, Burke M, Linn J (2012) Evaluation of the supraaortic arteries using non-contrast-enhanced velocity MR angiography “Inhance”. Neuroradiology. 54:1215–1219
Provenzale JM, Kranz PG (2011) Dural sinus thrombosis: sources of error in image interpretation. AJR Am J Roentgenol 196:23–31
Higgins JN, Gillard JH, Owler BK, Harkness K, Pickard JD (2004) MR venography in idiopathic intracranial hypertension: unappreciated and misunderstood. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 75:621–625
Bousser MG, Ferro JM (2007) Cerebral venous thrombosis: an update. Lancet Neurol 6:162–170
Ozturk K, Soylu E, Parlak M (2018) Dural venous sinus thrombosis: the combination of noncontrast CT, MRI and PC-MR venography to enhance accuracy. Neuroradiol J 31:473–481
Sari S, Verim S, Hamcan S, Battal B, Akgun V, Akgun H, Celikkanat S, Tasar M (2015) MRI diagnosis of dural sinus - cortical venous thrombosis: tmmediate post-contrast 3D GRE T1-weighted imaging versus unenhanced MR venography and conventional MR sequences. Clin Neurol Neurosurg 134:44–54
Jalli R, Zarei F, Farahangiz S, Khaleghi F, Petramfar P, Borhani-Haghighi A, Yadollahikhales G (2016) The sensitivity, specificity, and accuracy of contrast-enhanced T1-weighted image, T2*-weighted image, and magnetic resonance venography in diagnosis of cerebral venous sinus thrombosis. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis 25:2083–2086
Saposnik G, Barinagarrementeria F, Brown RD Jr, Bushnell CD, Cucchiara B, Cushman M, deVeber G, Ferro JM, Tsai FY (2011) Diagnosis and management of cerebral venous thrombosis: a statement for healthcare professionals from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke. 42:1158–1192
Liang L, Korogi Y, Sugahara T, Onomichi M, Shigematsu Y, Yang D, Kitajima M, Hiai Y, Takahashi M (2001) Evaluation of the intracranial dural sinuses with a 3D contrast-enhanced MP-RAGE sequence: prospective comparison with 2D-TOF MR venography and digital subtraction angiography. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 22:481–492
Klingebiel R, Bauknecht HC, Bohner G, Kirsch R, Berger J, Masuhr F (2007) Comparative evaluation of 2D time-of-flight and 3D elliptic centric contrast-enhanced MR venography in patients with presumptive cerebral venous and sinus thrombosis. Eur J Neurol 14:139–143
Fu JH, Lai PH, Hsiao CC, Li SC, Weng MJ, Wang PC, Chen CKH (2010) Comparison of real-time three-dimensional gadolinium-enhanced elliptic centric-ordered MR venography and two-dimensional time-of-flight MR venography of the intracranial venous system. J Chin Med Assoc 73:131–138
van Dam LF, van Walderveen MAA, Kroft LJM, Kruyt ND, Wermer MJH, van Osch M, Huisman MV, Klok FA (2020) Current imaging modalities for diagnosing cerebral vein thrombosis - a critical review. Thromb Res 189:132–139
Canedo-Antelo M, Baleato-González S, Mosqueira AJ, Casas-Martínez J, Oleaga L, Vilanova JC, Luna-Alcalá A, García-Figueiras R (2019) Radiologic clues to cerebral venous thrombosis. Radiographics. 39:1611–1628
Ferro JM, Canhão P, Bousser MG, Stam J, Barinagarrementeria F, Stolz E, ISCVT Investigators (2010) Cerebral venous thrombosis with nonhemorrhagic lesions: clinical correlates and prognosis. Cerebrovasc Dis 29:440–445
Ferro JM, Canhão P, Stam J, Bousser MG, Barinagarrementeria F, ISCVT Investigators (2004) Prognosis of cerebral vein and dural sinus thrombosis: results of the International Study on Cerebral Vein and Dural Sinus Thrombosis (ISCVT). Stroke. 35:664–670
Tantawy HF, Morsy MM, Basha MA, Nageeb RS (2020) Different normal anatomical variations of the transverse dural sinus in magnetic resonance venography (MRV): do age and sex matter? Eur J Anat 24:49–56
Goyal G, Singh R, Bansal N, Paliwal VK (2016) Anatomical variations of cerebral MR venography: is gender matter? Neurointervention. 11:92–98
Ayanzen RH, Bird CR, Keller PJ, McCully F, Theobald MR, Heiserman JE (2000) Cerebral MR venography: normal anatomy and potential diagnostic pitfalls. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 21:74–78
Han K, Chao AC, Chang FC et al (2016) Diagnosis of transverse sinus hypoplasia in magnetic resonance venography: new insights based on magnetic resonance imaging in combined dataset of venous outflow impairment case-control studies: post hoc case-control study. Medicine (Baltimore) 95:e2862
Chang YM, Kuhn AL, Porbandarwala N, Rojas R, Ivanovic V, Bhadelia RA (2020) Unilateral nonvisualization of a transverse dural sinus on phase-contrast MRV: frequency and differentiation from sinus thrombosis on noncontrast MRI. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 41:115–121
Wang G, Yang X, Duan J, Zhang N, Maya MM, Xie Y, Bi X, Ji X, Li D, Yang Q, Fan Z (2019) Cerebral venous thrombosis: MR black-blood thrombus imaging with enhanced blood signal suppression. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 40:1725–1730
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Ozpar R – Data curation, conceptualization
Tonkaz M – Investigation, methodology
Erkal D – Resources, investigation
Ongen G – Resources, data curation
Hakyemez B – Supervision, validation
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest
Ethics approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards. The study was approved by the Ethics Committee of Bursa Uludag University Faculty of Medicine.
Consent to participate (include appropriate statements)
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ozpar, R., Tonkaz, M., Erkal, D. et al. Non-contrast magnetic resonance venography with Inhance 3D Velocity: diagnostic performance for intracranial venous thrombosis. Neuroradiology 63, 1853–1861 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-021-02710-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-021-02710-1