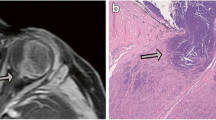
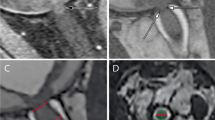
Abstract
Purpose
Preoperative MRI detection of post-laminar optic nerve invasion (PLONI) offers guidance in assessing the probability of total tumor resection, an estimation of the extent of surgery, and screening of candidates for eye-preserving therapies or neoadjuvant chemotherapies in the patients with retinoblastoma (RB). The purpose of this systematic review and meta-analysis was to evaluate the diagnostic performance of MRI for detecting PLONI in patients with RB and to demonstrate the factors that may influence the diagnostic performance.
Methods
Ovid-MEDLINE and EMBASE databases were searched up to January 11, 2020, for studies identifying the diagnostic performance of MRI for detecting PLONI in patients with RB. The pooled sensitivity and specificity of all studies were calculated followed by meta-regression analysis.
Results
Twelve (1240 patients, 1255 enucleated globes) studies were included. The pooled sensitivity was 61%, and the pooled specificity was 88%. Higgins I2 statistic demonstrated moderate heterogeneity in the sensitivity (I2 = 72.23%) and specificity (I2 = 78.11%). Spearman correlation coefficient indicated the presence of a threshold effect. In the meta-regression, higher magnetic field strength (3 T than 1.5 T), performing fat suppression, and thinner slice thickness (< 3 mm) were factors causing heterogeneity and enhancing diagnostic power across the included studies.
Conclusions
MR imaging was demonstrated to have acceptable diagnostic performance in detecting PLONI in patients with RB. The variation in the magnetic field strength and protocols was the main factor behind the heterogeneity across the included studies. Therefore, there is room for developing and optimizing the MR protocols for patients with RB.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jonas JB, Berenshtein E, Holbach L (2003) Anatomic relationship between lamina cribrosa, intraocular space, and cerebrospinal fluid space. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 44:5189–5195
Brisse HJ, Guesmi M, Aerts I, Sastre-Garau X, Savignoni A, Lumbroso-le Rouic L, Desjardins L, Doz F, Asselain B, Bours D, Neuenschwander S (2007) Relevance of CT and MRI in retinoblastoma for the diagnosis of postlaminar invasion with normal-size optic nerve: a retrospective study of 150 patients with histological comparison. Pediatr Radiol 37:649–656
Shields CL, Shields JA, Baez K, Cater JR, De Potter P (1994) Optic nerve invasion of retinoblastoma. Metastatic potential and clinical risk factors. Cancer 73:692–698
Kopelman JE, McLean IW, Rosenberg SH (1987) Multivariate analysis of risk factors for metastasis in retinoblastoma treated by enucleation. Ophthalmology 94:371–377
Magramm I, Abramson DH, Ellsworth RM (1989) Optic nerve involvement in retinoblastoma. Ophthalmology 96:217–222
Messmer EP, Heinrich T, Hopping W, de Sutter E, Havers W, Sauerwein W (1991) Risk factors for metastases in patients with retinoblastoma. Ophthalmology 98:136–141
Chantada GL, Casco F, Fandino AC et al (2007) Outcome of patients with retinoblastoma and postlaminar optic nerve invasion. Ophthalmology 114:2083–2089
Sastre X, Chantada GL, Doz F, Wilson MW, de Davila MT, Rodríguez-Galindo C, Chintagumpala M, Chévez-Barrios P, International Retinoblastoma Staging Working Group (2009) Proceedings of the consensus meetings from the international retinoblastoma staging working group on the pathology guidelines for the examination of enucleated eyes and evaluation of prognostic risk factors in retinoblastoma. Arch Pathol Lab Med 133:1199–1202
Khelfaoui F, Validire P, Auperin A, Quintana E, Michon J, Pacquement H, Desjardins L, Asselain B, Schlienger P, Vielh P, Dufier JL, Zucker JM, Doz F (1996) Histopathologic risk factors in retinoblastoma: a retrospective study of 172 patients treated in a single institution. Cancer 77:1206–1213
Aerts I, Sastre-Garau X, Savignoni A, Lumbroso-le Rouic L, Thebaud-Leculée E, Frappaz D, Coze C, Thomas C, Gauthier-Villars M, Lévy-Gabriel C, Brisse HJ, Desjardins L, Doz F (2013) Results of a multicenter prospective study on the postoperative treatment of unilateral retinoblastoma after primary enucleation. J Clin Oncol 31:1458–1463
Armenian SH, Panigrahy A, Murphree AL, Jubran RF (2008) Management of retinoblastoma with proximal optic nerve enhancement on MRI at diagnosis. Pediatr Blood Cancer 51:479–484
Lumbroso-Le Rouic L, Aerts I, Levy-Gabriel C et al (2008) Conservative treatments of intraocular retinoblastoma. Ophthalmology 115(8):1405–1410 1410.e1401–1402
Chantada G, Doz F, Antoneli CB et al (2006) A proposal for an international retinoblastoma staging system. Pediatr Blood Cancer 47:801–805
Zelter M, Damel A, Gonzalez G, Schwartz L (1991) A prospective study on the treatment of retinoblastoma in 72 patients. Cancer 68:1685–1690
Sirin S, Schlamann M, Metz KA, Bornfeld N, Schweiger B, Holdt M, Temming P, Schuendeln MM, Goericke SL (2015) High-resolution MRI using orbit surface coils for the evaluation of metastatic risk factors in 143 children with retinoblastoma: part 1: MRI vs. histopathology. Neuroradiology 57:805–814
Hiasat JG, Saleh A, Al-Hussaini M et al (2019) The predictive value of magnetic resonance imaging of retinoblastoma for the likelihood of high-risk pathologic features. Eur J Ophthalmol 29:262–268
Chawla B, Chaurasia S, Sharma S, Pattebahadur R, Hasan F, Seth R, Kashyap S, Sen S (2018) Magnetic resonance imaging for tumor restaging after chemotherapy in retinoblastoma with optic nerve invasion. Ophthalmic Genet 39:584–588
Cui Y, Luo R, Wang R, Liu H, Zhang C, Zhang Z, Wang D (2018) Correlation between conventional MR imaging combined with diffusion-weighted imaging and histopathologic findings in eyes primarily enucleated for advanced retinoblastoma: a retrospective study. Eur Radiol 28:620–629
De Jong MC, van der Meer FJ, Goricke SL et al (2016) Diagnostic accuracy of intraocular tumor size measured with MR imaging in the prediction of postlaminar optic nerve invasion and massive choroidal invasion of retinoblastoma. Radiology 279:817–826
Chawla B, Sharma S, Sen S, Azad R, Bajaj MS, Kashyap S, Pushker N, Ghose S (2012) Correlation between clinical features, magnetic resonance imaging, and histopathologic findings in retinoblastoma: a prospective study. Ophthalmology 119:850–856
Khurana A, Eisenhut CA, Wan W, Ebrahimi KB, Patel C, O’Brien JM, Yeom K, Daldrup-Link HE (2013) Comparison of the diagnostic value of MR imaging and ophthalmoscopy for the staging of retinoblastoma. Eur Radiol 23:1271–1280
Lee BJ, Kim JH, Kim DH, Park SH, Yu YS (2012) The validity of routine brain MRI in detecting post-laminar optic nerve involvement in retinoblastoma. Br J Ophthalmol 96:1237–1241
Song KD, Eo H, Kim JH, Yoo SY, Jeon TY (2012) Can preoperative MR imaging predict optic nerve invasion of retinoblastoma? Eur J Radiol 81:4041–4045
Liberati A, Altman DG, Tetzlaff J, Mulrow C, Gøtzsche PC, Ioannidis JP, Clarke M, Devereaux PJ, Kleijnen J, Moher D (2009) The PRISMA statement for reporting systematic reviews and meta-analyses of studies that evaluate health care interventions: explanation and elaboration. Ann Intern Med 151:W65–W94
Whiting PF, Rutjes AW, Westwood ME, Mallett S, Deeks JJ, Reitsma JB, Leeflang MM, Sterne JA, Bossuyt PM, QUADAS-2 Group (2011) QUADAS-2: a revised tool for the quality assessment of diagnostic accuracy studies. Ann Intern Med 155:529–536
Suh CH, Park SH (2016) Successful publication of systematic review and meta-analysis of studies evaluating diagnostic test accuracy. Korean J Radiol 17:5–6
Kim KW, Lee J, Choi SH, Huh J, Park SH (2015) Systematic review and meta-analysis of studies evaluating diagnostic test accuracy: a practical review for clinical researchers-part I. general guidance and tips. Korean J Radiol 16:1175–1187
Lee J, Kim KW, Choi SH, Huh J, Park SH (2015) Systematic review and meta-analysis of studies evaluating diagnostic test accuracy: a practical review for clinical researchers-part II. Statistical methods of meta-analysis. Korean J Radiol 16:1188–1196
Reitsma JB, Glas AS, Rutjes AW, Scholten RJ, Bossuyt PM, Zwinderman AH (2005) Bivariate analysis of sensitivity and specificity produces informative summary measures in diagnostic reviews. J Clin Epidemiol 58:982–990
Rutter CM, Gatsonis CA (2001) A hierarchical regression approach to meta-analysis of diagnostic test accuracy evaluations. Stat Med 20:2865–2884
Deeks JJ, Macaskill P, Irwig L (2005) The performance of tests of publication bias and other sample size effects in systematic reviews of diagnostic test accuracy was assessed. J Clin Epidemiol 58:882–893
Deville WL, Buntinx F, Bouter LM et al (2002) Conducting systematic reviews of diagnostic studies: didactic guidelines. BMC Med Res Methodol 2:9
Brisse HJ, de Graaf P, Galluzzi P et al (2015) Assessment of early-stage optic nerve invasion in retinoblastoma using high-resolution 1.5 Tesla MRI with surface coils: a multicentre, prospective accuracy study with histopathological correlation. Eur Radiol 25:1443–1452
Li Z, Guo J, Xu X, Wang Y, Mukherji SK, Xian J (2020) Diagnosis of postlaminar optic nerve invasion in retinoblastoma with MRI features. J Magn Reson Imaging 51(4):1045–1052
Ainbinder DJ, Haik BG, Frei DF, Gupta KL, Mafee MF (1996) Gadolinium enhancement: improved MRI detection of retinoblastoma extension into the optic nerve. Neuroradiology 38:778–781
Berry JL, Zolfaghari E, Chen A, Murphree AL, Jubran R, Kim JW (2017) Optic nerve obscuration in retinoblastoma: a risk factor for optic nerve invasion? Ocular Oncol Pathol 3:283–291
Galluzzi P, Cerase A, Hadjistilianou T, de Francesco S, Toti P, Vallone IM, Filosomi G, Monti L, Bracco S, Gennari P, Ginanneschi C, Venturi C (2003) Retinoblastoma: abnormal gadolinium enhancement of anterior segment of eyes at MR imaging with clinical and histopathologic correlation. Radiology 228:683–690
Kim U, Rathi G, Chowdhary G, Srinavasan KG, Shanthi R, Krishna RSP (2019) Accuracy of preoperative imaging in predicting optic nerve invasion in retinoblastoma: a retrospective study. Indian J Ophthalmol 67:2019–2022
Sow AS, Ndiaye JMM, Ka AM, Sacramento DGT, Kane H, Nguer M, Diagne JP, Wane AM, Ba EA, Ndoye Roth PA, Ndiaye PA (2019) Role of CT in diagnosis and monitoring of retinoblastoma in Senegal. J Fr Ophtalmol 42:1085–1089
Wilson MW, Rodriguez-Galindo C, Billups C, Haik BG, Laningham F, Patay Z (2009) Lack of correlation between the histologic and magnetic resonance imaging results of optic nerve involvement in eyes primarily enucleated for retinoblastoma. Ophthalmology 116:1558–1563
Lemke AJ, Kazi I, Mergner U, Foerster PI, Heimann H, Bechrakis N, Schüler A, von Pilsach MIS, Foerster M, Felix R, Hosten N (2007) Retinoblastoma - MR appearance using a surface coil in comparison with histopathological results. Eur Radiol 17:49–60
de Graaf P, Barkhof F, Moll AC, Imhof SM, Knol DL, van der Valk P, Castelijns JA (2005) Retinoblastoma: MR imaging parameters in detection of tumor extent. Radiology 235:197–207
de Graaf P, van der Valk P, Moll AC, Imhof SM, Schouten-van Meeteren AYN, Knol DL, Castelijns JA (2010) Contrast-enhancement of the anterior eye segment in patients with retinoblastoma: correlation between clinical, MR imaging, and histopathologic findings. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 31:237–245
de Jong MC, de Graaf P, Brisse HJ, Galluzzi P, Göricke SL, Moll AC, Munier FL, Beck Popovic M, Moulin AP, Binaghi S, Castelijns JA, Maeder P, Castelijns JA, de Graaf P, de Jong MC, Brisse HJ, Galluzzi P, Göricke SL, Maeder P (2015) The potential of 3T high-resolution magnetic resonance imaging for diagnosis, staging, and follow-up of retinoblastoma. Surv Ophthalmol 60:346–355
Sirin S, Schlamann M, Metz KA, Bornfeld N, Schweiger B, Holdt M, Schuendeln MM, Lohbeck S, Krasny A, Goericke SL (2013) Diagnostic image quality of gadolinium-enhanced T1-weighted MRI with and without fat saturation in children with retinoblastoma. Pediatr Radiol 43:716–724
Galluzzi P, Hadjistilianou T, Cerase A, Toti P, Leonini S, Bracco S, de Francesco S, Galimberti D, Balducci D, Piu P, Monti L, Bellini M, Caini M, Rossi A (2015) MRI helps depict clinically undetectable risk factors in advanced stage retinoblastomas. Neuroradiol J 28(1):53–61
Choucair ML, Brisse H, Freneaux P, Lumbroso L, Chevrier M, Doz FP, Aerts I (2017) Management of uni- or bilateral retinoblastoma with radiologic optic nerve invasion at diagnosis. J Clin Oncol 35:10551
Choucair ML, Brisse HJ, Freneaux P et al (2020) Management of advanced uni- or bilateral retinoblastoma with macroscopic optic nerve invasion. Pediatr Blood Cancer 67:e27998
Ciller C, De Zanet S, Kamnitsas K et al (2017) Multi-channel MRI segmentation of eye structures and tumors using patient-specific features. PLoS One 12
Kim JW, Madi I, Lee R, Zolfaghari E, Jubran R, Lee TC, Murphree AL, Berry JL (2017) Clinical significance of optic nerve enhancement on magnetic resonance imaging in enucleated retinoblastoma patients. Ophthalmol Retina 1:369–374
Brisse H, Gerber S, Sastre X et al (2010) Retinoblastoma: correlation between high resolution MRI and histology for optic nerve assessment prior to enucleation. Pediatr Radiol 40:1077
Eo H, Kim JH, Yoo SY, Jeon TY (2011) Can preoperative MR imaging predict optic nerve invasion of retinoblastoma? Pediatr Radiol 41:S301
de Jong MC, de Graaf P, Noij DP, Göricke S, Maeder P, Galluzzi P, Brisse HJ, Moll AC, Castelijns JA (2014) Diagnostic performance of magnetic resonance imaging and computed tomography for advanced retinoblastoma: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Ophthalmology 121:1109–1118
De Graaf P, Göricke S, Rodjan F et al (2012) Guidelines for imaging retinoblastoma: imaging principles and MRI standardization. Pediatr Radiol 42:2–14
de Jong MC, de Graaf P, Pouwels PJW, Beenakker JW, Jansen RW, Geurts JJG, Moll AC, Castelijns JA, van der Valk P, van der Weerd L (2018) 9.4T and 17.6T MRI of retinoblastoma: ex vivo evaluation of microstructural anatomy and disease extent compared with histopathology. J Magn Reson Imaging 47(6):1487–1497
Funding
No funding was received for this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
Waived due to systematic review and meta-analysis.
Informed consent
Waived due to systematic review and meta-analysis.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cho, S.J., Kim, J.H., Baik, S.H. et al. Diagnostic performance of MRI of post-laminar optic nerve invasion detection in retinoblastoma: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Neuroradiology 63, 499–509 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-020-02538-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-020-02538-1