Abstract
Purpose
To explore the amplitude of low frequency fluctuation (ALFF) and functional connectivity (FC) disorders in non-neuropsychiatric systemic lupus erythematosus (non-NPSLE) patients by resting-state functional magnetic resonance imaging (rs-fMRI) and to study whether there are some clinical biomarkers that can be used to monitor the brain dysfunction.
Methods
Based on the rs-fMRI data of 36 non-NPSLE patients and 30 normal controls, we first obtained the regions with abnormal ALFF signals in non-NPSLE patients. Then, by taking these areas as seed regions of interest (ROIs), we calculated the FC between ROIs and the whole brain to assess the network-level alterations. Finally, we correlated the altered values of ALFF and FC in non-NPSLE patients to some clinical data.
Results
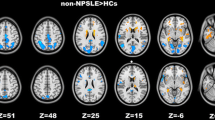
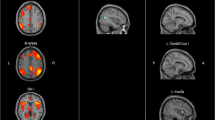
Compared with the controls, non-NPSLE patients showed decreased ALFF in bilateral precuneus and increased ALFF in right cuneus and right calcarine fissure surrounding cortex (CAL). At network level, non-NPSLE patients exhibited higher FC between left precuneus and left middle occipital gyrus (MOG)/left superior occipital gyrus (SOG)/right middle frontal gyrus (MFG)/right dorsolateral superior frontal gyrus (SFGdor), and higher FC between right cuneus and bilateral precuneus/left posterior cingulate gyrus (PCG). The abnormal ALFF in right CAL and abnormal FC in right cuneus–left precuneus, right cuneus–right precuneus, and right cuneus–left PCG were correlated with the patients’ certain clinical data (p < 0.05).
Conclusion
Rs-fMRI is a promising tool for detecting the brain function disorders in non-NPSLE patients and to help understand the neurophysiological mechanisms. C4 and Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Disease Activity Index may be biomarkers of brain dysfunction in non-NPSLE patients.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jafri K, Patterson SL, Lanata C (2017) Central nervous system manifestations of systemic lupus erythematosus. Rheum Dis Clin N Am 43:531–545
Zhang XD, Jiang XL, Cheng Z, Zhou Y, Xu Q, Zhang ZQ, Qi R, Luo S, Yun YS, Chen HJ, Kong X, Lu GM, Zhang LJ (2017) Decreased coupling between functional connectivity density and amplitude of low frequency fluctuation in non-neuropsychiatric systemic lupus erythematosus: a resting-stage functional MRI study. Mol Neurobiol 54:5225–5235
Fujita Y, Fukui S, Ishida M, Endo Y, Tsuji S, Takatani A, Igawa T, Shimizu T, Umeda M, Sumiyoshi R, Nishino A, Koga T, Kawashiri SY, Iwamoto N, Ichinose K, Tamai M, Nakamura H, Origuchi T, Kawakami A (2018) Reversible cognitive dysfunction in elderly-onset systemic lupus erythematosus, successfully treated with aggressive immunosuppressive therapy. In: Intern Med, vol 57, pp 3025–3028
Ceccarelli F, Perricone C, Pirone C, Massaro L, Alessandri C, Mina C et al (2018) Cognitive dysfunction improves in systemic lupus erythematosus: results of a 10 years prospective study. PLoS One 13:e196103
Barraclough M, Elliott R, McKie S, Parker B, Bruce IN (2015) Cognitive dysfunction and functional magnetic resonance imaging in systemic lupus erythematosus. Lupus 24:1239–1247
Lin Y, Zou QH, Wang J, Wang Y, Zhou DQ, Zhang RH, Zhang YW, Lii HT, Fang YF (2011) Localization of cerebral functional deficits in patients with non-neuropsychiatric systemic lupus erythematosus. Hum Brain Mapp 32:1847–1855
Greicius MD, Krasnow B, Reiss AL, Menon V (2003) Functional connectivity in the resting brain: a network analysis of the default mode hypothesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 100:253–258
Niu C, Tan X, Liu X, Han K, Niu M, Xu J, et al (2018) Cortical thickness reductions associate with abnormal resting-state functional connectivity in non-neuropsychiatric systemic lupus erythematosus. Brain Imaging Behav 12(3):674–684
Hou J, Lin Y, Zhang W, Song L, Wu W, Wang J, Zhou D, Zou Q, Fang Y, He M, Li H (2013) Abnormalities of frontal-parietal resting-state functional connectivity are related to disease activity in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. PLoS One 8:e74530
Li F, He N, Li Y, Chen L, Huang X, Lui S, Guo L, Kemp GJ, Gong Q (2014) Intrinsic brain abnormalities in attention deficit hyperactivity disorder: a resting-state functional MR imaging study. Radiology 272:514–523
Yuan C, Zhu H, Ren Z, Yuan M, Gao M, Zhang Y, Li Y, Meng Y, Gong Q, Lui S, Qiu C, Zhang W (2018) Precuneus-related regional and network functional deficits in social anxiety disorder: a resting-state functional MRI study. Compr Psychiatry 82:22–29
Zhang JJ, Ding J, Li JY, Wang M, Yuan YS, Zhang L, Jiang SM, Wang XX, Zhu L, Zhang KZ (2017) Abnormal resting-state neural activity and connectivity of fatigue in Parkinson's disease. CNS Neurosci Ther 23:241–247
Gladman DD, Urowitz MB, Kagal A, Hallett D (2000) Accurately describing changes in disease activity in systemic lupus erythematosus. J Rheumatol 27:377–379
Macedo AC, Isaac L (2016) Systemic lupus erythematosus and deficiencies of early components of the complement classical pathway. Front Immunol 7:55
Hochberg MC (1997) Updating the American College of Rheumatology revised criteria for the classification of systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum 40:1725
(1999) The American College of Rheumatology nomenclature and case definitions for neuropsychiatric lupus syndromes. Arthritis Rheum 42:599–608
Nasreddine ZS, Phillips NA, Bedirian V, Charbonneau S, Whitehead V, Collin I et al (2005) The Montreal Cognitive Assessment, MoCA: a brief screening tool for mild cognitive impairment. J Am Geriatr Soc 53:695–699
Cockrell JR, Folstein MF (1988) Mini-mental state examination (MMSE). Psychopharmacol Bull 24:689–692
Bajaj JS, Wade JB, Sanyal AJ (2009) Spectrum of neurocognitive impairment in cirrhosis: implications for the assessment of hepatic encephalopathy. Hepatology 50:2014–2021
Biswal B, Yetkin FZ, Haughton VM, Hyde JS (1995) Functional connectivity in the motor cortex of resting human brain using echo-planar MRI. Magn Reson Med 34:537–541
Cordes D, Haughton VM, Arfanakis K, Carew JD, Turski PA, Moritz CH, Quigley MA, Meyerand ME (2001) Frequencies contributing to functional connectivity in the cerebral cortex in “resting-state” data. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 22:1326–1333
Zang YF, He Y, Zhu CZ, Cao QJ, Sui MQ, Liang M, Tian LX, Jiang TZ, Wang YF (2007) Altered baseline brain activity in children with ADHD revealed by resting-state functional MRI. Brain and Development 29:83–91
Tzourio-Mazoyer N, Landeau B, Papathanassiou D, Crivello F, Etard O, Delcroix N, Mazoyer B, Joliot M (2002) Automated anatomical labeling of activations in SPM using a macroscopic anatomical parcellation of the MNI MRI single-subject brain. Neuroimage 15:273–289
Chen X, Lu B, Yan CG (2018) Reproducibility of R-fMRI metrics on the impact of different strategies for multiple comparison correction and sample sizes. Hum Brain Mapp 39:300–318
Wang C, Pan Y, Liu Y, Xu K, Hao L, Huang F, Ke J, Sheng LQ, Ma HR, Guo WF (2018) Aberrant default mode network in amnestic mild cognitive impairment: a meta-analysis of independent component analysis studies. Neurol Sci 39:919–931
Zuo N, Yang Z, Liu Y, Li J, Jiang T (2018) Core networks and their reconfiguration patterns across cognitive loads. Hum Brain Mapp. https://doi.org/10.1002/hbm.24193
Asano T, Ito H, Kariya Y, Hoshi K, Yoshihara A, Ugawa Y et al (2017) Evaluation of blood-brain barrier function by quotient alpha2 macroglobulin and its relationship with interleukin-6 and complement component 3 levels in neuropsychiatric systemic lupus erythematosus. PLoS One 12:e186414
Rayes HA, Tani C, Kwan A, Marzouk S, Colosimo K, Medina-Rosas J, Mustafa A, Su J, Lambiris P, Mosca M, Touma Z (2018) What is the prevalence of cognitive impairment in lupus and which instruments are used to measure it? A systematic review and meta-analysis. Semin Arthritis Rheum 48:240–255
Shapira-Lichter I, Vakil E, Litinsky I, Oren N, Glikmann-Johnston Y, Caspi D, Hendler T, Paran D (2013) Learning and memory-related brain activity dynamics are altered in systemic lupus erythematosus: a functional magnetic resonance imaging study. Lupus 22:562–573
Fortin A, Ptito A, Faubert J, Ptito M (2002) Cortical areas mediating stereopsis in the human brain: a PET study. Neuroreport 13:895–898
Udden J, Snijders TM, Fisher SE, Hagoort P (2017) A common variant of the CNTNAP2 gene is associated with structural variation in the left superior occipital gyrus. Brain Lang 172:16–21
Tu S, Qiu J, Martens U, Zhang Q (2013) Category-selective attention modulates unconscious processes in the middle occipital gyrus. Conscious Cogn 22:479–485
Renier LA, Anurova I, De Volder AG, Carlson S, VanMeter J, Rauschecker JP (2010) Preserved functional specialization for spatial processing in the middle occipital gyrus of the early blind. Neuron 68:138–148
DiFrancesco MW, Holland SK, Ris MD, Adler CM, Nelson S, DelBello MP et al (2007) Functional magnetic resonance imaging assessment of cognitive function in childhood-onset systemic lupus erythematosus: a pilot study. Arthritis Rheum 56:4151–4163
Petrides M (2000) The role of the mid-dorsolateral prefrontal cortex in working memory. Exp Brain Res 133:44–54
Mak A, Ren T, Fu EH, Cheak AA, Ho RC (2012) A prospective functional MRI study for executive function in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus without neuropsychiatric symptoms. Semin Arthritis Rheum 41:849–858
Lai CH, Wu YT (2013) Decreased regional homogeneity in lingual gyrus, increased regional homogeneity in cuneus and correlations with panic symptom severity of first-episode, medication-naive and late-onset panic disorder patients. Psychiatry Res 211:127–131
Li J, Luo C, Peng Y, Xie Q, Gong J, Dong L, Lai Y, Li H, Yao D (2014) Probabilistic diffusion tractography reveals improvement of structural network in musicians. PLoS One 9:e105508
Zhu CM, Ma Y, Xie L, Huang JZ, Sun ZB, Duan SX, Lin ZR, Yin JJ, le HB, Sun DM, Xu WC, Ma SH (2017) Spatial working memory impairment in patients with non-neuropsychiatric systemic lupus erythematosus: a blood-oxygen-level dependent functional magnetic resonance imaging study. J Rheumatol 44:201–208
Acknowledgments
We thank Tian-wu Chen, MD, for editing guidance. We are indebted to Dr. Li Chen for technical guidance on MRI scanning.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Funding
No funding was received for this study.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in the studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yu, H., Qiu, X., Zhang, Yq. et al. Abnormal amplitude of low frequency fluctuation and functional connectivity in non-neuropsychiatric systemic lupus erythematosus: a resting-state fMRI study. Neuroradiology 61, 331–340 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-018-2138-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-018-2138-6